
记录组会将被提问题。
Figure 1 的具体实现步骤
- 设计用的Adobe Illustrator,然后用Tanner L-Edit软件进行了进一步处理。
- 做了一个双层图案化。首先是微通道,由于作者在Figure 6研究通道高度的影响,因此设计了2种高度的微通道:4.7 µm和3.2 µm。其中,4.7 µm是用的SU-8 2005光刻(5000 rpm/60 s),3.2 µm是反应离子刻蚀(负性胶nLOF 2020)。然后再图案化180 µm的分隔壁,用的SU-8 2075,软烘烤(50 °C/6 h),曝光后烘烤(50 °C/6 h),最后硬烘烤(90 °C/15 h)。
- 直接3D打印PDMS。
- 剥离PDMS,然后放在玻片上。播种细胞。
- 健康的神经元在设备上生成,并通过微通道阵列相互连接。
Figure 6里对面的神经细胞是什么,为什么没产生轴突
来自前脑的F‐hNSCs,大部分分化为星形胶质细胞;而来自于中脑腹侧的M‐hNSCs,大部分分化为多巴胺能神经元。
黑质纹状体途径是一种多巴胺能途径,连接了中脑的黑质致密部(SNpc)与前脑中的背侧纹状体。这种多巴胺能连接是单向的,其中多巴胺能神经元从SNpc投射并将多巴胺传递到背侧纹状体。该装置是对黑质纹状体途径的原理验证。上方为F‐hNSCs分化而来的星形胶质细胞,下方为M‐hNSCs分化而来的多巴胺能神经元。
神经细胞染色方案和原理
免疫细胞化学
是利用抗原与抗体特异性结合的原理,通过化学反应使标记抗体的显色剂 (荧光素、酶、金属离子、同位素) 显色来确定细胞内抗原的成分(主要是多肽和蛋白质),对其进行定位、定性及定量的研究。
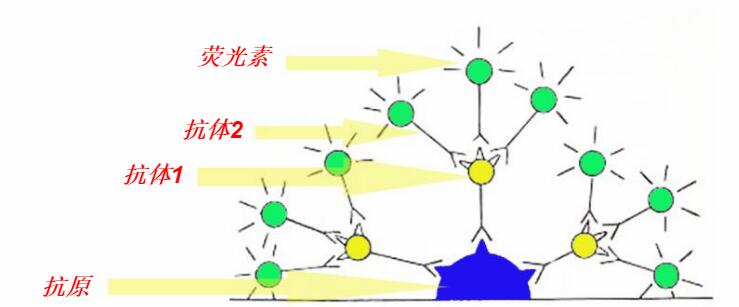
单克隆抗体:是一个B淋巴细胞克隆分泌的抗体,是应用细胞融合杂交瘤技术免疫动物制备的。特点是特异性强、抗体产量高。多克隆抗体:是将纯化后的抗原直接免疫动物后,从动物血中所获得的免疫血清,是多个B淋巴细胞克隆所产生的抗体混合物。特点是特异性低,会产生抗体的交叉反应。
DAPI/Hoechst染色
DAPI 可以穿透细胞膜与细胞核中的双链DNA结合而发挥标记的作用,显微镜下可以看到显蓝色荧光的细胞,荧光显微镜观察细胞标记的效率高(几乎为100 %) ,常用于细胞凋亡检测,染色后用荧光显微镜观察或流式细胞仪检测。
Hoechst 33342是一种可以穿透细胞膜的蓝色荧光染料,常用于细胞凋亡检测,染色后用荧光显微镜观察或流式细胞仪检测。也用于普通的细胞核染色,或常规的DNA染色。
死活细胞染色
死活细胞染色原理是Calcein AM进入细胞,和活细胞中的酶反应形成Calcein荧光分子,并保留在细胞内部,所以通过Calcein荧光分子来检测活细胞;而EthD-1不能透过活细胞膜,只能进入死细胞和细胞内的基因片段结合后出现荧光,故此检测死细胞。Calcein AM和EthD-1没和细胞接触前不发荧光 。也有用PI染死细胞的。
尼氏染色
神经元胞体里有大量嗜碱性的尼氏小体,可以与碱性染料(焦油紫、亚甲蓝、甲苯胺蓝和硫堇等)结合着色,可以清晰辨别尼氏体、核仁、树突、轴突等,但仅用于尼氏体较为丰富的组织染色。
3D打印的实现过程和原理
这里用的是RegenHU的生物打印机。生物打印机大概分为以下几种原理。
喷墨式:其基本原理是用加热或压电的方法以一定频率将“墨盒”中的“生物墨水”形成墨滴,通过针头喷洒在平台上,构成组织。喷墨式打印要求“墨水”具有较低的粘度,约 3.5 ~ 12 mPa s,即在“墨盒”中处于液态,滴到平台上后迅速固化(交联)。
挤出式:是最常用的一类生物3D打印方式,可以打印粘度更高的生物材料,如水凝胶等。基本原理有两种,一是是采用加热模块将高分子材料熔融变软(200°左右),然后用机械结构将高分子材料拉丝挤出,高温的丝状材料遇到较冷的平台后凝固成型。由于此过程中材料会经历高温过程,因此不适用于含细胞的打印。二是用气压式、螺纹挤出式讲材料挤出打印。
激光式:它可分为激光辅助式和光固化。激光辅助式打印采用激光代替喷墨打印中的加热或压电,聚焦在覆盖在含细胞的生物材料表面的“吸收层”上的一点,形成空泡,将该点的材料连同细胞一起挤出,滴在下面的平台上。光固化是采用激光作为固化的诱因,在激光聚焦的点诱使光致固化的材料固化,从而形成特定结构。
Sylgard 184的普通形式表现为牛顿流体,没有足够高的粘度,无法通过喷嘴可控地挤出并支撑印刷在其顶部的层的重量。
将墨水在双旋转混合器中以2700 rpm的速度混合30 s,然后装入5 cc注射器筒中。为了除去气泡,将注射器在1700 G下离心3分钟。然后用塑料锥形针(内径200 µm)盖住注射器,然后将其装入3D生物打印机。使用真空抽吸将包含母模的硅晶片固定在打印阶段。在BioCad软件(regenHU)中定义了基于母版制造的设计的打印路径。室温下通过气动挤出直接在硅片上进行印刷,其中垫片墨水在550 Pa的压力下挤出,隔室墨水在275 Pa的空气压力下挤出。两种墨水的喷嘴速度均设置为10 mm s-1。垫片墨水以150 µm的层高打印,而隔室墨水以190 µm的层高打印。对于具有PMMA或PLA扩展的装置,只打印了三层隔室墨水,以便存在用于附着纤维的平坦表面。
打印后,将包含打印装置的硅晶片放入60°C的烘箱中2天以完全固化硅弹性体。PLA扩展是使用透明的PLA丝在Felix Pro 3 3D打印机(Felix Robotics)上打印的。使用1.5毫米立铣刀在5 mm厚的PMMA薄板中微磨PMMA延伸部分。将延伸部分贴在一个薄层PDMS弹性体上并在60°C下将装置固化过夜。固化结束后,将单个器件从硅片上剥离下来,并在96%乙醇中灭菌。 通过暴露于空气等离子体将每个装置共价结合到玻璃盖玻片上。



