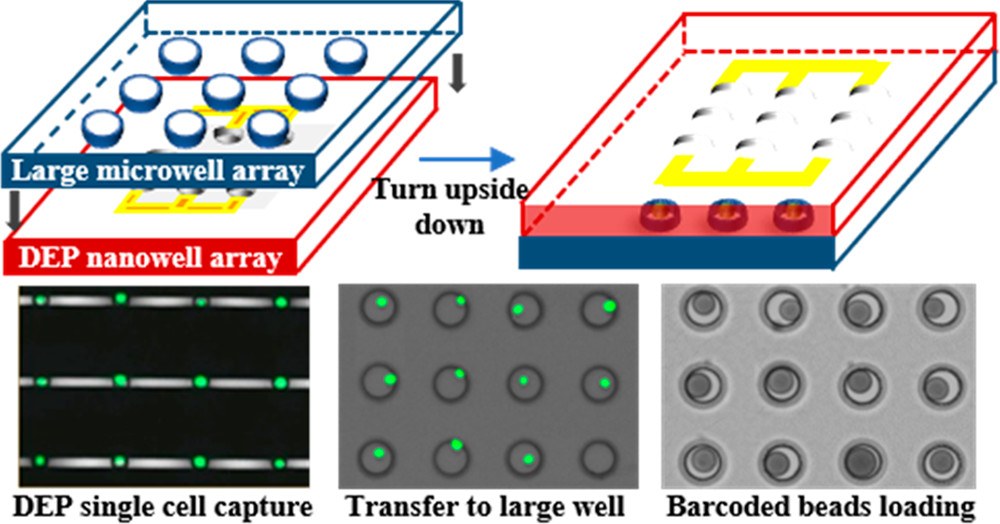
一种集成的介电泳-诱捕-纳米孔-转移方法,以亚泊松的方式进行细胞捕获和珠粒装载,以促进单细胞RNA测序。
Introduction
高通量的单细胞RNA测序(scRNA-seq)分析已经成为强大的工具用于大量研究领域包括免疫应答、肿瘤微环境和癌症异质性的鉴定和分类。微流控技术的改进,以及聚类算法和scRNA-seq的统计建模的成熟,改变了剖析单细胞水平的复杂生理系统的能力。在几乎所有的高通量scRNA-seq方法中,使用了独特条形码小珠的分子条码技术是可行且不可缺少的一步,允许我们能使用大批RNA-seq流程并保持单细胞分辨率。
尽管大量微流控平台已经改进了复现性、通量和敏感性,它们有一些根本性限制。对于基于液滴的方法,它会导致低细胞-小珠成对效率,妨碍了低输入样本的采用。此外不可避免的外设要求限制了它对偏远临床中心的便携性。替代的基于微米或者纳米孔的方法提供了一个简单的低开销、更便携且对高限制的病人潜在的兼容性。为了最小化2个或多个小珠进入相同的孔的比率,细胞用超泊松方式装载,只有少于10%的小珠占据的孔收到细胞。
介电泳(DEP)捕获是一种充分研究的主动捕获机制,可以作为解决这一挑战的潜在答案。然而将单细胞DEP捕获与纳米孔的scRNA-seq成功结合并不是一件容易的事,其主要障碍是大尺寸的DNA条码珠和小得多的感兴趣的细胞最佳捕获条件固有的不兼容性。
本文开发了一种高度集成的DEP-捕获-纳米孔-转移(dTNT)设备用于主动捕获单细胞在小的20 μm的纳米孔和转移到大的50 μm的装载条形码珠用于单细胞mRNA转录组捕获。
Figure 1. Design of dTNT-seq
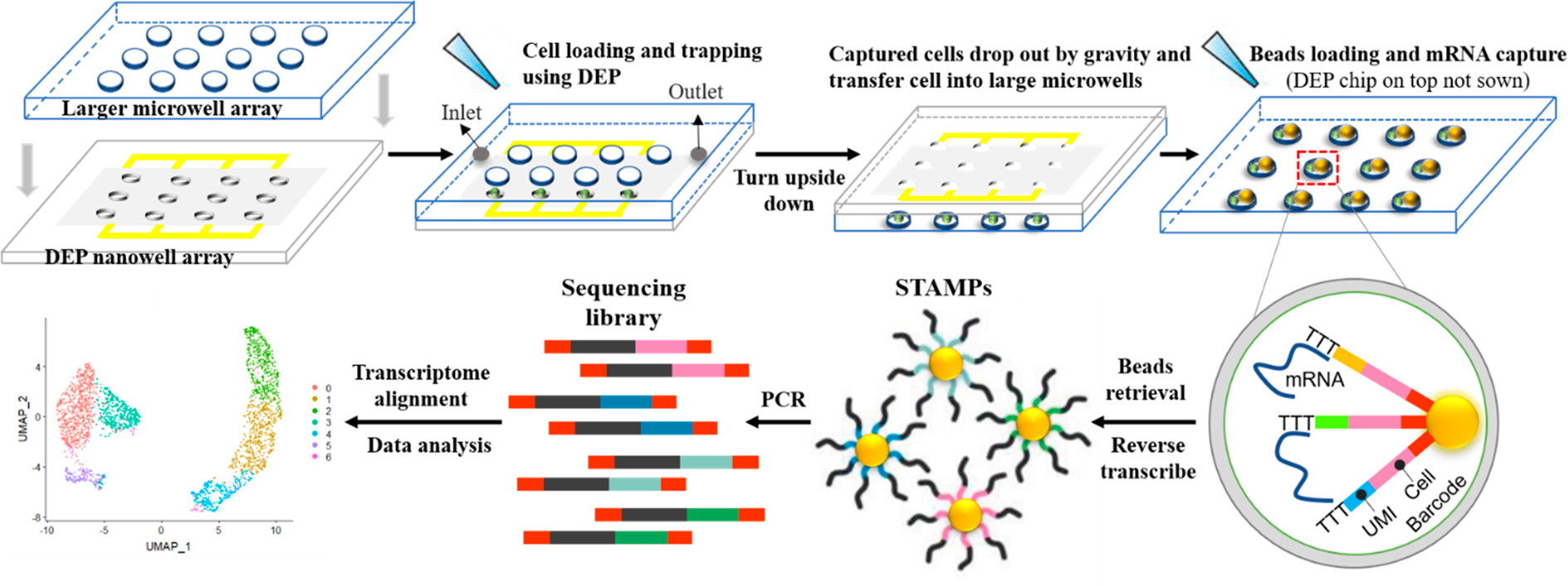
如图所示为一个基于DEP的单细胞mRNA测序平台和工作流程。
- 两个分离的层通过自制的操纵器预对齐并组合。
- 细胞装载后,单细胞在DEP作用下被主动捕获。
- 随后整个设备翻转,由于重力作用,细胞转移到大的微孔。
- 随后条码珠装载、细胞裂解以及mRNA被小珠表面的DNA寡聚物捕获,每个小珠都包含一个细胞条码以及一个单分子识别码(UMI)。
- 小珠被收集和集中,mRNAs被大批反转录,形成吸附在微粒上的单细胞转录组(STAMPs)。随后扩增和tagmentation,完成测序文库的准备。
- 用于转录组比对的测序数据生成基因表达矩阵以进行下游的数据分析。
tagmentation:即将全长的cDNA随机打断。
Figure 2. Design and configuration of the dTNT device

(a)用于单细胞捕获的DEP纳米孔阵列的俯视图。
(b)制成的电活性DEP阵列的显微镜图像。
(c)细胞捕获纳米孔的3D光学表明分析器,进行非接触测量,以确保尺寸符合原始设计。
(d)组装完的dTNT设备的横截面,包括一个上方的大的微孔层,底部的DEP阵列芯片和两者间的PDMS垫以形成流体通道装载细胞、小珠和所有试剂。
(e)使用自制对准器组装的预对准的两层dTNT装置的照片。右侧插图:光学图像,显示dTNT装置是代表性区域放大视野。
Figure 3. Evaluation of DEP-based single-cell trapping, occupancy rate, transfer efficiency, and bead loading
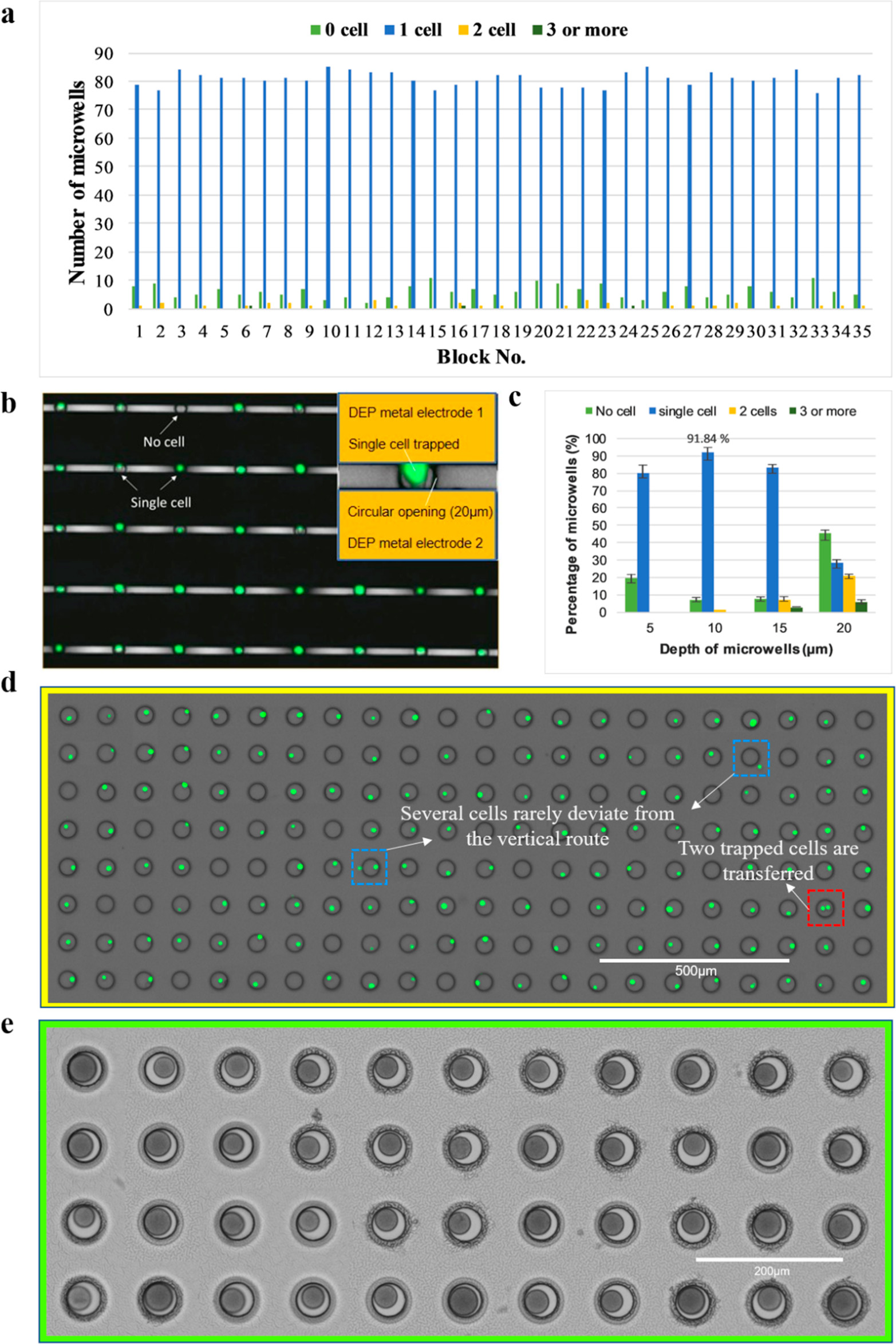
- (a)作者检查了35个代表性的区域,其中每个区域包含了88个纳米孔,共计3080个纳米孔以评估捕获效率,超过90%的纳米孔都只有一个细胞,双个细胞的概率小于2%。
- (b)10 μm深的纳米孔捕获单细胞的荧光图像。
- (c)捕获性能与纳米孔深度的关系。作者研究了5、10、15和20μm深度的影响。可以看到10 μm孔可产生最佳的单细胞捕获,双细胞率可忽略不计。
- (d)翻转dTNT设备后, 单细胞转移到大的微孔的荧光图像。平均82%的捕获细胞被转移。
- (e)由于微孔尺寸的排斥以及在流体通道里中来回移动小珠的能力,条形码小珠以接近100%的单珠占用率加载到微孔中。
Figure 4. Single-cell RNA sequencing of species-mixing samples using dTNT-seq
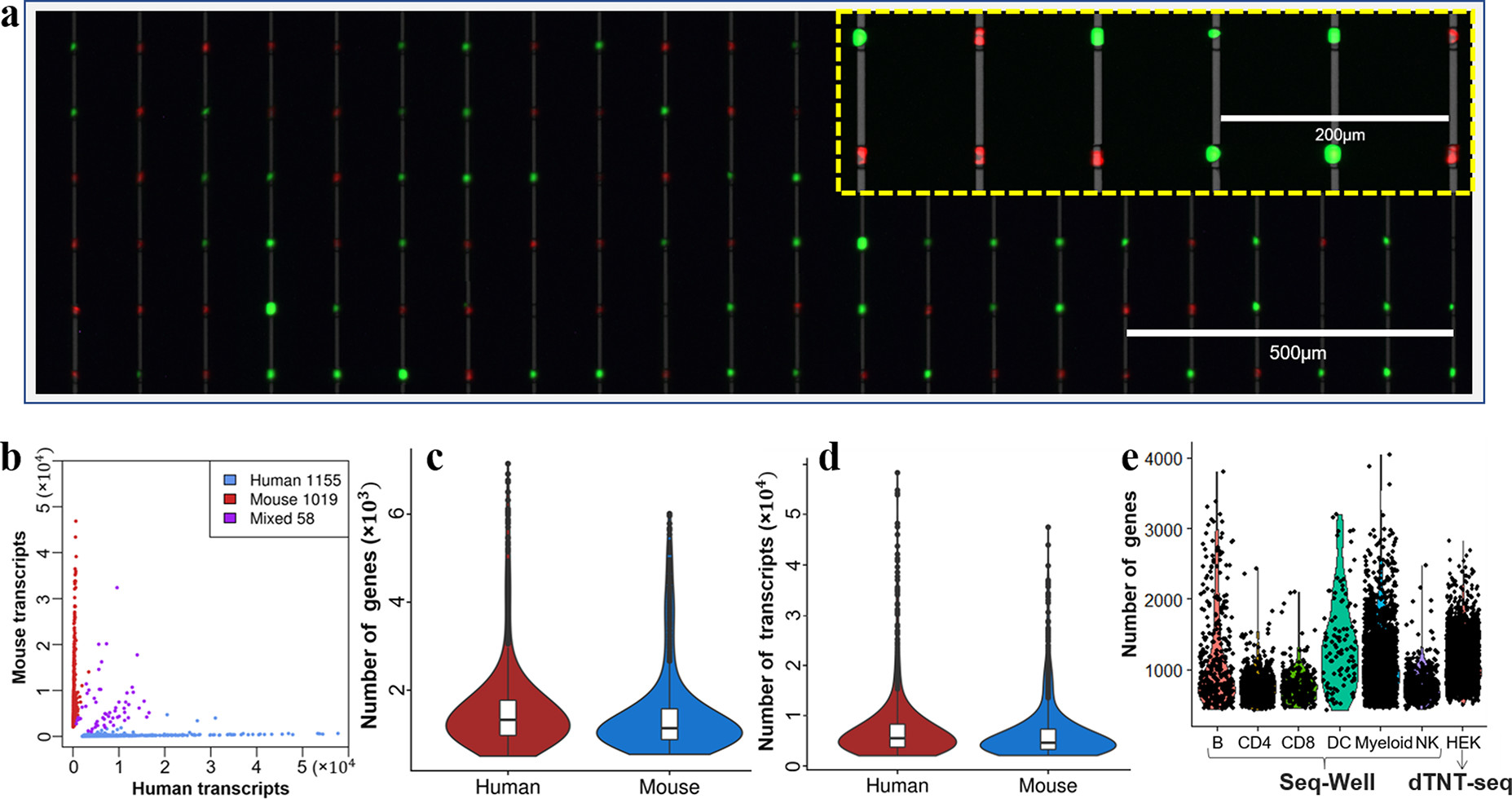
- (a)鼠胚胎成纤维细胞3T3(绿色)和人胚胎肾细胞HEK(红色)在DEP纳米孔阵列的荧光图像。
- (b)人和鼠基因组的测序读数映射图。
- (c)单细胞中检测到的基因数目的小提琴图。
- (d)单细胞中检测到的转录本的小提琴图。
- (e)保持相当的细胞和测序深度,将他们的结果和来自人外周血单核细胞的SeqWell数据比较,发现有相同的捕获效率。
关于测序深度:科普。
Figure 5. Graph-based unsupervised clustering analysis and the comparison with the nonelectrode method (scFTD-seq)

- (a)使用dTNT生成的鼠和人的UMAP可视化,每个组具有三个不同的单细胞簇。
- (b)每个簇前五的差异表达基因marker的热图。
- (c)使用scFTD-seq生成的单细胞转录组的UMAP可视化。与dTNT中的相同,确定了两个主要的物种特定组,每个组都有两个较大的亚群。
- (d)dTNT-seq和scFTD-seq中每个主要簇的细胞数目对比。
UMAP:统一流形逼近与投影,一种降维技术,见科普。
JackStraw plot & the Elbow plot:判断主成分数,见科普。
Figure 6. Comparison of biological processes underlying the identified clusters between dTNT-seq and scFTD-seq through GSEA analysis

为了确定介电泳的电场不会对转录组分析产生影响,做了基因集合富集分析。
- 通过图a(DEP_Human 0)、图b(Human 0)发现二者都是和蛋白质翻译和运输相关。RPS7是标记基因。
- 同理,图c(DEP_Mouse 1)、图d(Mouse 1)与有丝分裂有关(染色体着丝粒区域),标记基因Cenpa编码着丝粒蛋白A。
Table 1. Comparison of the Cell−Bead Pairing Efficiency across Different High-Throughput scRNA-Seq Platforms
| method | cell occupancy rate (droplets/wells containing single cells, %) | bead capture rate (droplets/wells containing single beads, %) | cell/bead pairing rate (droplets/wells co-occupied with single cells and beads, %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drop-Seq | ∼5–10 | ∼5–10 | <5 |
| InDrop | ∼10 | ∼80–100 | ∼10–50 |
| 10× chromium | ∼10 | ∼80–100 | ∼10 |
| SeqWell | 5–10 | ∼95 | ∼5–10 |
| dTNT-seq | ∼75 | ∼99 | ∼75 |
Conclusion
当前的scRNA-seq方法,如10× Genomics、DropSeq和SeqWell都是基于被动的包装或成对,受到泊松分布的根本限制,以妨碍细胞-小珠的成对效率。通过dTNT设备(一个电活性的DEP的3600纳米孔阵列和一个大尺寸的微孔阵列),作者证明了单细胞捕获率为91.84%且成对的细胞少于2%,转移效率为82%。此外,该方法减少了昂贵的DNA条码珠的开销。
Reference
Bai Z, Deng Y, Kim D, et al. An Integrated Dielectrophoresis-Trapping and Nanowell Transfer Approach to Enable Double-Sub-Poisson Single-Cell RNA Sequencing[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(6): 7412–7424.