
一种同时分离和分析黑色素瘤CTCs和癌症外泌体的微流控装置。
Introduction
黑色素瘤是最具侵袭性的一种癌症,其发病率持续上升。由于缺少有前景的标记物去预测疾病和转移的发生,在早期发现和评估治疗效果方面进展甚微。黑色素瘤的早期检测十分关键,因为早期局部黑素瘤患者生存率为98%,而转移性黑素瘤患者的5年生存率仅为5-19%。
CTC和癌症相关外泌体最近逐步变成很多癌症类型如肺癌、前列腺癌、乳腺癌中有前景的生物标记物,其中的癌症相关分子与癌症进程、总体生存率和治疗效率相关。然而当前的CTC分离装置:
- CellSearch及类似装置,主要使用上皮细胞黏附分子(EpCAM)的抗体,而该基因在黑色素瘤CTCs中下调。2011年后,开始使用黑素瘤细胞黏附分子(melanoma cell adhesion molecule, MCAM)、黑色素瘤关联硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖(melanoma-associated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan, MCSP)、硫酸软骨素蛋白聚糖4(chondroitin-surface proteoglycan 4, CSGP4)和人类高分子量黑素瘤相关抗原(human high molecular weight-melanoma-associated antigen, HMW-MAA)取代EpCAM,但仍有60%登记的病人检测不到CTCs。
- 使用含有2种特异性黑色素瘤抗体(抗MCSP和抗MCAM)的免疫磁性珠,被证明可有效分离IV期黑色素瘤患者血液样本中80%以上的CTCs,但其CTC计数的中位数每毫升血液中少于2 个CTCs(1.78 CTC mL-1)。
和CTCs一样,外泌体,主要由恶性细胞分泌的纳米尺度的细胞外囊泡(EVs)用于细胞间交流,已经被用于癌症研究和诊断。和CTCs相比,外泌体在体液中更稳定和丰富。
作者设计了一种微流控设备可以黑色素瘤特异性抗体MCAM和MCSP结合,实现了CTC和外泌体的同时分离。
Figure1. Dual‐isolation of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and cancer exosomes via dual‐utilization of OncoBean (DUO) microfluidic device
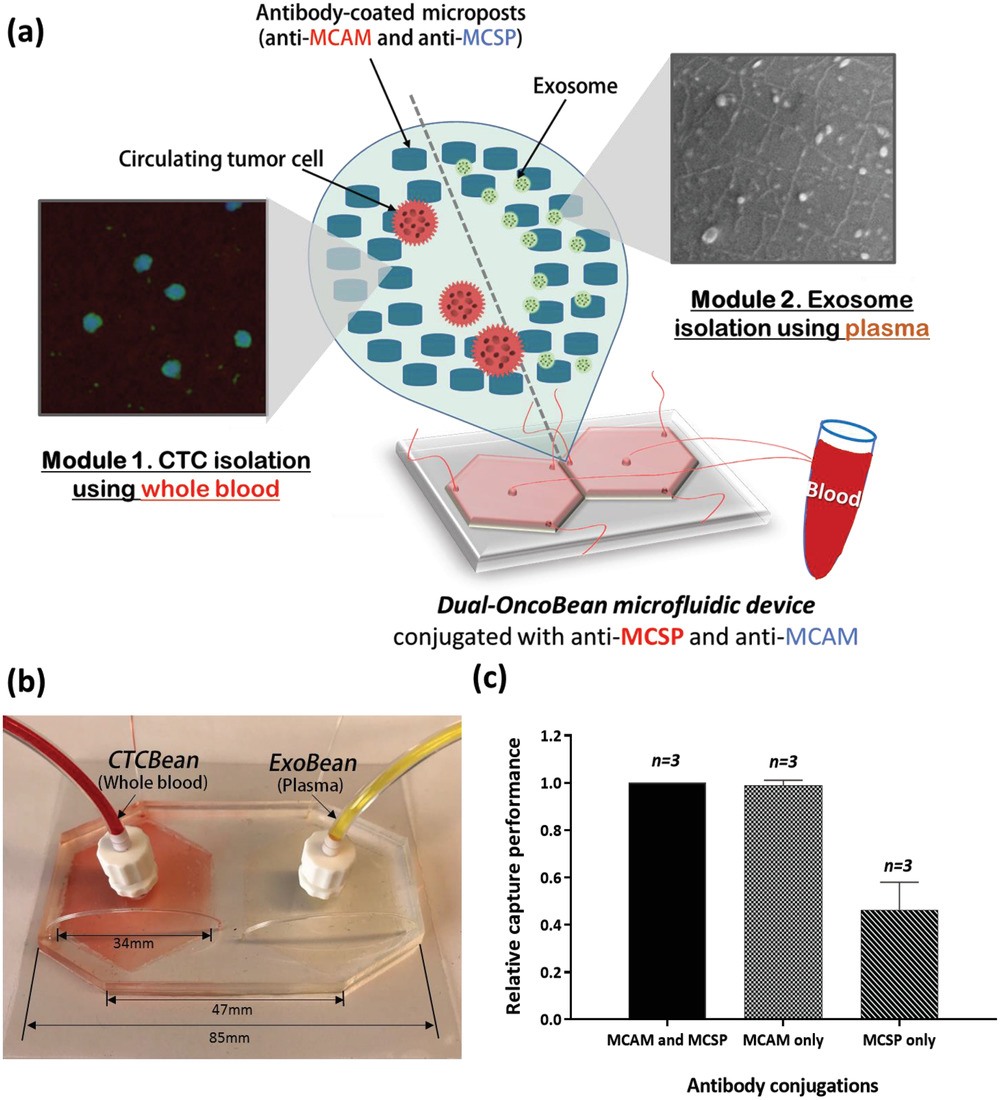
- (a)从黑色素瘤病人血样中双重分离CTCs和外泌体的示意图。
- (b)制作的DUO微流控装置的尺寸。
- (c)使用2种抗体及其联合的黑色素瘤细胞相关分离效率。但是为了分离多种黑色素瘤亚型包括MCSP过表达的黑色素瘤细胞,所以选择两种抗体联用。
Figure 2. Isolation of circulating melanoma markers using the MCAM/MCSP functionalized DUO device
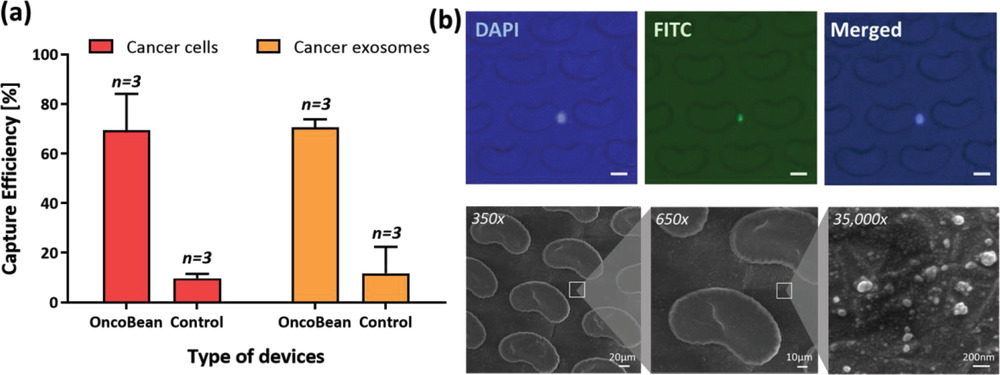
- (a)与没有抗体偶联的对照DUO装置相比,从黑色素瘤细胞系SK-MEL-103捕获黑色素瘤细胞和外泌体的效率。
- (b)分离出DAPI和CellTracker green染色的掺入的癌细胞(上)和设备上的癌细胞外囊泡(下)。
Figure 3. Evaluation of isolated melanoma circulating tumor cells and melanoma-associated exosomes by MCAM/MCSP functionalized OncoBean devices

- (a)循环黑色素瘤细胞由DAPI(细胞核)、CD45(白细胞)及Melan-A和S100混合染色(黑色素瘤)。
- (b)OncoBean装置上分离的外泌体样囊泡的扫描电镜图。
- (c)OncoBean装置分离的外泌体的WB分析。
Figure 4. Comparison between results from CTCs and exosomes in melanoma patients

- (a)比较每1 mL血样中的CTC数目和外泌体总蛋白量。
- (b)黑色素瘤患者和健康人的平均CTC数量和外泌体蛋白量。外泌体p值为0.2358,没有显著性差异。
- (c)CTC裂解液和外泌体裂解液的RNA量比较。
实验显示,MCTC与外泌体总蛋白量之间没有明显的相关性。因此,任何表明MCTC浓度或外泌体蛋白数量的检测结果都不能作为另一种检测的可靠指标。
Figure 5. Gene panel analysis of melanoma CTCs (MCTCs) and melanoma exosomes (MExos) isolated by DUO

- (a)黑色素瘤病人、健康人和黑色素瘤细胞系SK-MEL-103的MCTCs的基因表达热图分析。
- (b)MCTCs的基因表达的小提琴图分析。
- (c)黑色素瘤病人、健康人和黑色素瘤细胞系SK-MEL-103的MExos的基因表达热图分析。
- (d)MExos的基因表达的小提琴图分析。
- (e)同样品MCTCs和MExos的两两比较。
Conclusion
作者设计了一种同时分离和分析黑色素瘤CTCs和癌症外泌体的微流控装置。增加的MCAM/MCSP表达外泌体蛋白浓度的增加作为黑色素瘤存在的标志。
Reference
Kang Y-T, Hadlock T, Lo T-W, et al. Dual-Isolation and Profiling of Circulating Tumor Cells and Cancer Exosomes from Blood Samples with Melanoma Using Immunoaffinity-Based Microfluidic Interfaces[J]. Advanced Science, 2020, n/a(n/a): 2001581.



