
一种通过控制合成的细胞大小的隔间中酶/代谢物的分离/组合,同时保留重要的细胞成分来研究生物途径的策略。
Introduction
在活细胞中,存在着各种各样的顺序反应链。这些所谓的反应途径是由相互兼容和选择的酶催化的,这些酶具有重要的功能,例如分解毒素,将营养物质转化为能量或复制DNA 。然而,由于细胞的复杂性,最佳酶水平的测定依然不清楚,特别是因为特定的酶功能和它们的级联效应密切相关。一种巧妙的研究酶行为的方法是利用微米尺寸的球形结构室,可以提供想要的膜选择性和渗透性。
单一特定功能通过结合酶(催化化合物)和合成的超分子组装来展现,既有固有的半渗透如脂质覆盖的二氧化硅粒子、蛋白质笼、逐层胶囊和聚多巴胺胶囊,也有通过插入生物孔/膜蛋白(表现为分子通过的“门”)产生渗透性如基于脂质或聚合物的巨大单层囊泡(giant unilamellar vesicles, GUVs)。
目前,由两亲性嵌段共聚物形成的GUVs尤其具有吸引力,因为它们具有比脂类更强的结构膜性能,因为它们具有具有更高的化学通用性、可控制的渗透性、耐用性和稳定性的隔间。然而,通过自组装形成聚合物GUVs的常见方法,如电形成和膜复水,都依赖于封装生物分子的统计过程,在隔间内找到设计量的一种酶概率为12-57%。在至少存在两种酶的基本生化途径的背景下,这种情况甚至更不令人满意,在一个隔间内共封装两种酶的比例低至10-22%。且由于特定性质的酶(溶解性和稳定性)导致的不确定性,这种短板可能会更糟。到目前为止,由于自组装过程的严重稀释,这些酶的数量/质量非常不具有代表性(受样本量的限制),而且非常低,科学家们一直在努力研究最先进的酶的数量/质量平均值。
双乳化微流控在这些参数(封装内容和膜组成)的精细控制方面发挥着重要作用,同时还具有高通量和按需产生的能力。然而,尽管双乳化已被广泛用于形成GUV,以程序性释放封装的亲水性和/或疏水性物质,但它们在研究酶促途径方面的能力仍未得到开发,且被期望具有实质性优势。为此,双乳相可以作为模版生成理想的细胞大小隔间,精准控制属性如:i) 尺寸(根据设计)和极窄的尺寸分布;ii) 内部的生物分子内容和分布;iii) 膜组织,即合成膜的组成和肽/膜蛋白的插入;iv) 酶促反应和通路信号的特征。
在这里,作者介绍了一种新颖的策略,用于在定制的隔间内的研究多步酶促反应,系统地将其布置成各种组合配置。这些聚合物GUVs形式的隔间是通过高精度双乳化技术生产的,该技术可对封装酶的数量/数量/比例进行必要的控制。此外,该技术已经过优化,使GUVs的膜可渗透以便于酶促底物/产物在隔间向内或向外扩散,以支持原位酶促反应。使用疏水的PDMS和亲水的PMOXA制作两亲性嵌段共聚物。
由于他们的方法提供了恒定的酶摩尔比,因此,诸如酶和代谢物的接近性以及通过膜的分子扩散等作用已解耦,从而可以理解限制因素并优化级联反应。这种精细的空间控制为减少竞争性副反应,减少抑制性或反应性中间体的积累,并通过最大化级联生产率以最终提高反应速率提供了最佳条件。此外,这一策略允许在一个控制的空间和时间的方式分步研究和优化复杂的级联反应,而不涉及困难和时间消耗的改变酶浓度的劳动。因此,他们的组合研究代表了一个系统独立的工具,用于协调多步途径,其复杂性更接近细胞,以探索新的应用领域。
在这篇文献中,两种独立的方法用于在微流控装置中创造双乳化模板的GUVs,即玻璃毛细管和PDMS模具。
- 玻璃毛细管广泛用于制造不同类型的胶囊,包括有超薄壳的GUVs。但是装置生产和操作十分具有挑战性:如果毛细管没有对齐或没很好的打磨,会出现不稳定并且由于不可控的液体相遇双乳化可能不会生成。
- 如果使用掩模和模具制造微流控装置,其重复性制造更容易实现,这主要是在使用软光刻制造PDMS微芯片的情况。然而,尽管快速成型和易于复制,但仍难以修改PDMS表面的化学性质以调节其对不同流体的润湿性。
在这些条件下形成双乳化需要包裹内部液滴的油相变厚以避免其塌陷,这可能会阻止GUVs的组装。因此,为了获得具有有利于生物孔/膜蛋白插入的均匀的聚合物膜的GUVs,需要更高水平的精确度和重现性才能产生具有薄的有机壳的双乳化,从长远来看,玻璃毛细管和PDMS微装置都无法提供这种双重乳状液。因此,作者结合上述两种方法的最佳特性来生产基于高分辨率固态制造的新型微流控装置,旨在利用硅玻璃装置的高化学和机械兼容性。
Figure 1. Microfluidic process of simultaneous double emulsion generation and functionalization
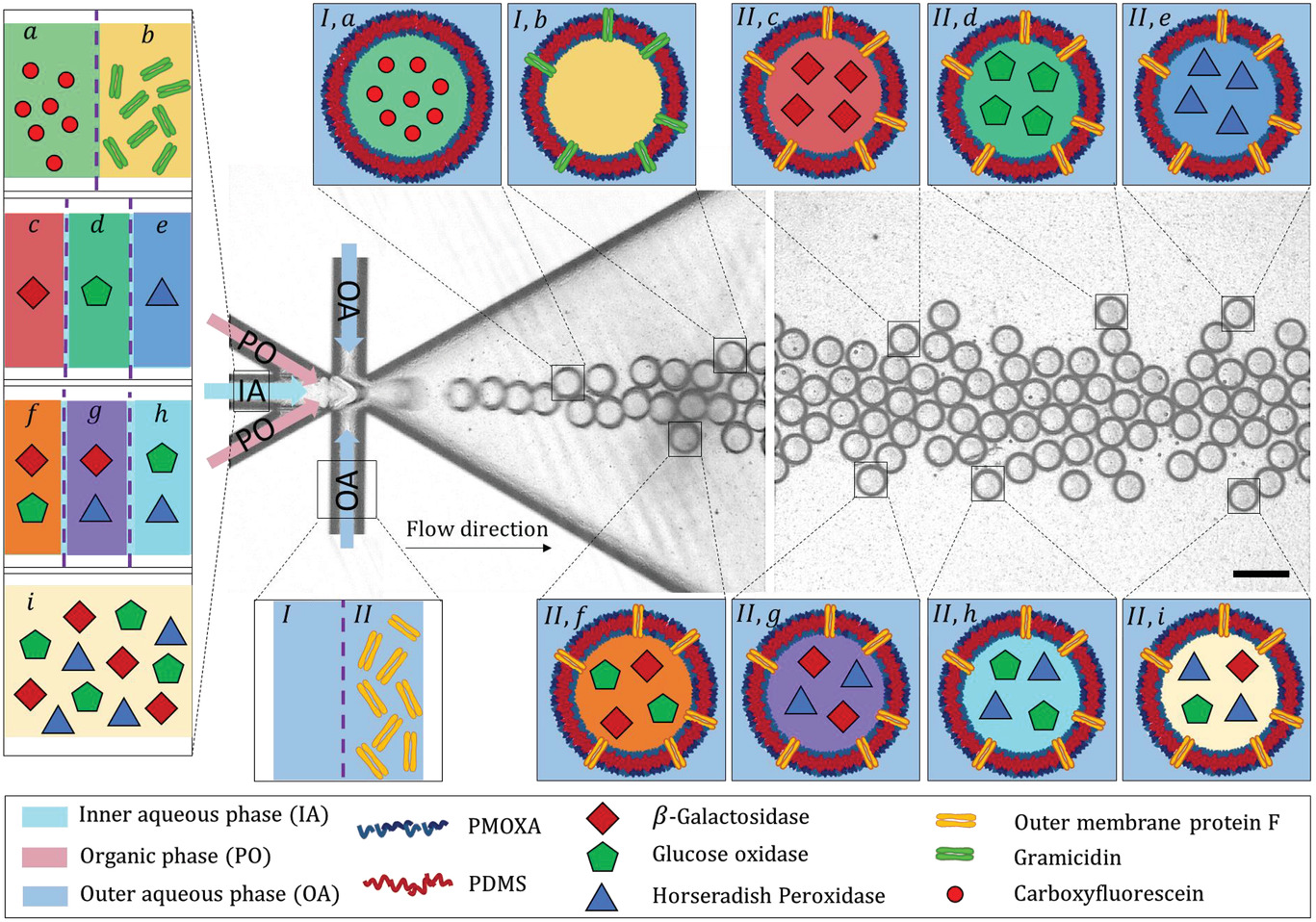
示意图展示了高通量的双乳化生成过程以创建包含了精确数量的生物分子的隔间(GUVs),在其内部的水腔和聚合物膜中有大量可能的组合。
- (a-i)代表IA中各种生物分子组成。
- (I-II)代表不同的OA相。
- (I, a)装载羧基荧光素(Carboxyfluorescein)水溶液的不能渗透的GUVs。
- (I, b)装载短杆菌肽(Gramicidin)的GUVs。
- (I, c)装载外膜蛋白(Outer membrane protein, OmpF)和β-半乳糖苷酶(β-galactosidase)水溶液的GUVs。
- (I, d)装载外膜蛋白和葡萄糖氧化酶(Glucose oxidase)水溶液的GUVs。
- (I, e)装载外膜蛋白和辣根过氧化物酶(Horseradish peroxidase)水溶液的GUVs。
- (I, f)装载外膜蛋白和β-半乳糖苷酶、葡萄糖氧化酶水溶液的GUVs。
- (I, g)装载外膜蛋白和β-半乳糖苷酶、辣根过氧化物酶水溶液的GUVs。
- (I, h)装载外膜蛋白和葡萄糖氧化酶、辣根过氧化物酶水溶液的GUVs。
- (I, i)装载外膜蛋白和三种酶的水溶液的GUVs。
Figure 2. Optimization of double emulsion sizes and characterization of sizes and permeability of GUVs

- (a)双乳化在微流控芯片主通道内流动的典型图像。用Matlab编写的图像处理软件测量双乳的外径(红色圆)和内径(蓝色圆)。
- (b)2361个液滴测量值的直方图。
- (c)在固定流量比QIA / QPO = 2时,内外径变化与外相流量QOA的关系。
- (d)恒定的外相流量QOA = 50 μL min−1的情况下。内外径变化与流量比QIA / QPO的关系。
- (e)所得的聚合物GUVs的典型激光共聚焦扫描显微镜(CSLM)图像。插图为放大的GUV,在其上表面包含一个口袋。
- (f)在80个测得的GUVs中直方图。
- (g)渗透性实验开始时,装有羧基荧光素的GUVs的CLSM图像。
- (h)沿三个代表性GUVs中心线测量的荧光信号强度。
- (i)荧光强度随时间变化。
Figure 3. GUVs equipped with biopores and membrane proteins

- (a)装有生物孔短杆菌肽(gA)且含有钠绿(SG)的GUVs,在Na +离子穿过gA形成的孔后,荧光增强。
- (b)
- 在左侧,含有β-半乳糖苷酶(β-gal)的GUVs,在缺少外膜蛋白F(OmpF)的情况下,不允许基质的试卤灵半乳糖吡喃糖苷酶(RGP)穿过聚合物膜;红色荧光信号是平的(插图)。
- 在右侧,装有OmpF且含有β-gal的GUVs,允许RGP穿过聚合物膜并反应,产生荧光产物试卤灵;红色荧光信号在GUV中高,在外面低(在产物外流之后)。
- (c)尺寸选择性。在左侧装有OmpF的GUVs限制了异硫氰酸荧光素葡聚糖(fluorescein isothiocyanate dextran, FITC-dextran, 10 kDa)的通过。 在右侧装有OmpF的GUVs允许羧基荧光素(carboxyfluorescein, CF, 376 Da)
Figure 4. Combinatorial study of a three-step cascade

- (a)Cy5标记的β-gal酶。
- (b)Oregon green 488标记的GOx酶。
- (c)Atto 550标记的HRP酶。
- (d)以43:139摩尔比混合的GOx和β-gal。
- (e)以43:139:1摩尔比混合的三种酶:β-gal、GOx和HRP。
- (f)β-gal或GOx或HRP分离。
- (g)三步级联反应的方案。◊代表β-gal; ⬠代表GOx; △代表HRP。
- (h-l)荧光素荧光强度随时间的变化。
- (h)荧光素(级联反应第一步的产物)的产生仅取决于底物FGP对β-gal的可用性,并且当这种酶被封装时,反应被直接减缓。
- (m-q)试卤灵荧光强度随时间的变化。
- (m)试卤灵(级联反应的最终产物)的产生受整个级联反应的影响,特别是底物H2O2的可利用性(间接依赖于半乳糖)和AR对HRP的影响。当这种酶被封装时,整个级联过程同样被减缓,这同样是由于HRP底物通过膜的扩散。
- (p)( β-gal+GOx)+(HRP)组(橙圈)比(β-gal)+(GOx+HRP)组(蓝绿)的试卤灵水平低,是因为过量H2O2的抑制,由于隔间的距离而不能快速消耗。
Reference
Santos E C dos, Belluati A, Necula D, et al. Combinatorial Strategy for Studying Biochemical Pathways in Double Emulsion Templated Cell-Sized Compartments[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, n/a(n/a): 2004804.



