
一种微流控平台,拥有开放孔设计,可以培养血管化的类器官。
Introduction
为了探索建模系统,寻求概括身体机能并创建尽可能与生理相关的系统,以解决药物开发和生物研究中现有范例的局限性,许多最近的研究都集中在类器官的使用上。类器官是一种自组织分化细胞的3D细胞培养。使它们成为如此出色的建模系统的原因是它们能够以较小的规模概括体内形态和细胞组织,同时还显示出与原始组织非常相似的遗传指纹。
类器官的主要优势是结构精密,尽管这种方法受到缺乏血管化和灌注的限制。通常在静态多孔板内培养类器官。即使血管系统在人体中盛行,许多类器官模型系统仍完全省略了血管网络。先前的研究同样证明了血管内灌流对血管稳定十分关键,缺乏灌流可能会导致血管退化。因此,整合血管和血管内灌流对生成功能性血管网络以支持上皮组织十分重要。尽管尝试了几种通过动物植入产生血管化类器官的策略,并产生了出色的结果,但这些方法缺乏体外应用所需的可扩展性和适应性。
作者开发了一个平台,通过在由内皮细胞自组装的可灌注血管床上生长类器官来使类器官血管化。
- 这个平台首次实现了血管化的类器官的血管内灌注。随后他们将平台扩展到一个定制的384孔平板(这里被称为IFlowPlate),在该板上可以方便地一次制造,培养,灌注和测试多达128种独立的血管化类器官培养物。
- 不同于很多闭合的基于微流控的系统,开放孔的设计使组织很容易被回收以用于下游分析,比如基因表达和组织病理分析,或者甚至体内移植。
- 最后,他们利用了该平台独特的灌注能力用于结肠炎建模,使其能观察炎症过程中不同的步骤包括循环单核细胞的募集和分化的巨噬细胞对结肠类器官的浸润以应对上皮组织损伤。
Figure 1. IFlowPlate operation and setup
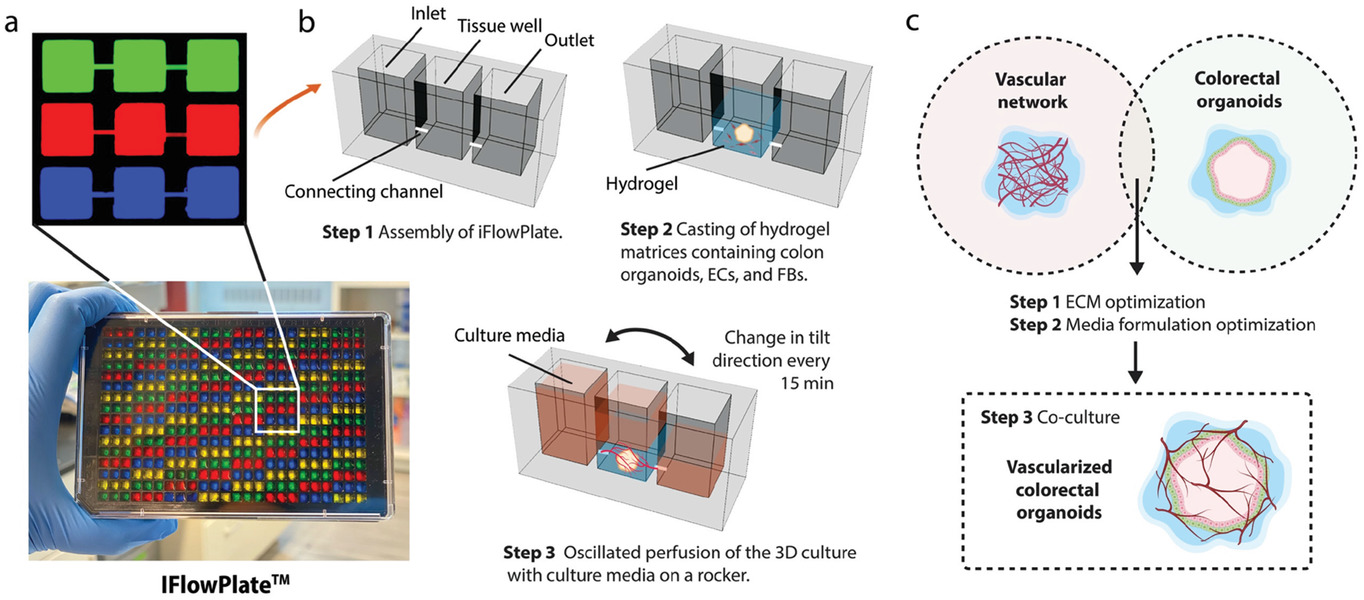
- (a)装填不同颜色染料的IFlowPlate图像,以描述128个独立的单元。通过在可定制的384孔平板上引入微通道以制作微流控装置。三个孔(入口,组织孔,出口)一起构成一个可灌注单元。这些可灌注微通道被染色以便于可视化。
- (b-c)描述用于在IFowPlate中培养结肠类器官的微流控装置和实验的安排。包含结肠类器官、内皮细胞和成纤维细胞的基质被浇铸在组织孔的底部。凝胶化后,通过将平板放在可编程的摇杆上,将介质灌注到血管网络中。我们还测试了不同的水凝胶基质和培养基配方,以找到生长这些血管化结肠类器官的最佳条件。
Figure 2. Culture of perfusable microvascular bed in IFlowPlate and optimization of hydrogel matrices
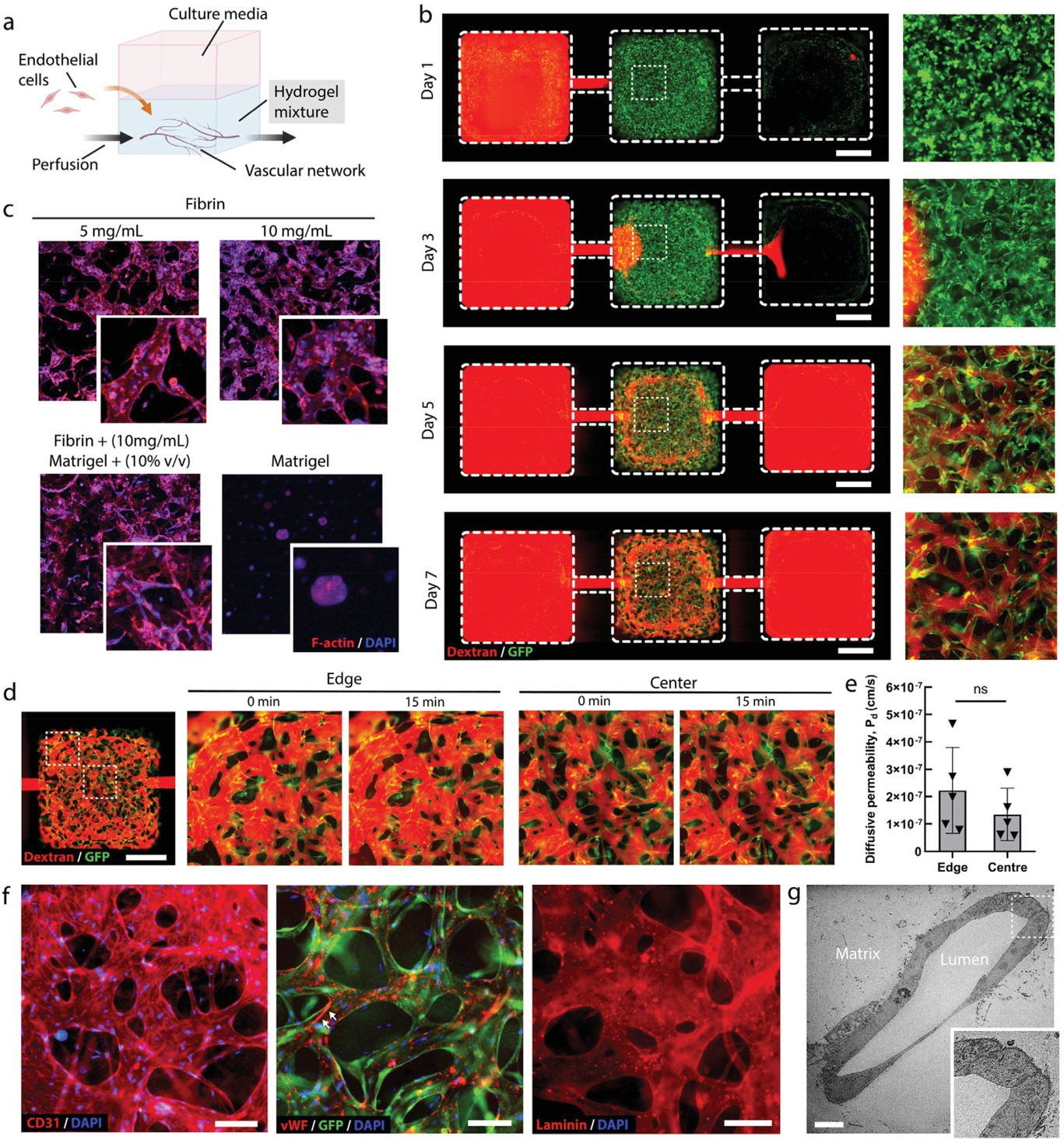
- (a)血管网络形成实验的示意图。
- (b)荧光图像下,GFP标记人脐静脉内皮细胞(GFP-HUVECs)(绿色)组装成微血管网络,并在成纤维细胞存在的情况下,随时间灌注荧光的70 kDa的葡聚糖(红色)。第3天就可以看到组装的血管网络。第5天可以看到灌注网络连接进、出通道。
- (c)IFlowPlate中不同配方的基质中自组装微血管网络共聚焦荧光图像。F-肌动蛋白:红色,DAPI:蓝色。显示了10 mg/mL的纤维蛋白和10% v/v的Matrigel有较好的促血管网络形成效果。
- (d-e)尽管由于较低的流动阻力,在小孔边缘附近的血管中似乎灌注更快,但是在所有区域中血管渗透性都相似,这表明血管没有泄漏,灌注液也没有在中央孔中泄漏或汇聚。
- (d)在第6天对血管灌注葡聚糖进行渗透率定量。
- (e)网络不同区域中血管扩散渗透率的量化,表明没有显著性。
- (f)血管形成细胞间连接,分泌对血栓形成有重要影响的血管性血友病因子(vWF),并沉积在富含层蛋白的基底膜。白色箭头指的是流体驱动形成的vWF纤维。
- (g)单个血管横截面的透射电子显微镜(TEM)图像。
Matrigel含有层粘连蛋白(laminin)和IV型胶原(collagen IV),是基膜的组成成分。
CD31:标记血管内皮。
F-actin:F-肌动蛋白,细胞骨架染色。
根据Fig. S1,低浓度的凝血酶有助于内皮细胞的组装,因为会允许更多细胞定居在小孔底部。
Figure 3. Optimization of hydrogel matrices for culturing human colon organoids

- (a)结直肠类器官形成实验的示意图。
- (b)随着时间推移,384孔平板上不同配方基质下生长的结肠类器官的明场图。
- (c)静态环境下,生长在含10% v/v Matrigel的纤维蛋白胶中的结肠类器官共聚焦荧光显微镜图像。F-肌动蛋白:红色,DAPI:蓝色。其中类器官腔表面的F-肌动蛋白的局部染色指示了极化的上皮细胞。
- (d)对不同配方的凝胶基质中的类器官面积进行量化。
上皮细胞呈现明显的极性(polarity),它们朝向身体表面或有腔器官腔面,称游离面;与其相对的朝向深部结缔组织的一面,称基底面。游离面和基底面在结构和功能上具有明显的差别。
Figure 4. Media formulation optimization of vascularized human colon organoids on IFlowPlate

- (a)共培养实验的示意图图。
- (b)使血管化类器官生长的不同培养基的优化列表。
- (c)不同配方培养基下血管化的结肠类器官的明场-GFP叠加图。放大的自组装微血管网络的荧光图像(绿色)和血管化结肠类器官(亮场GFP覆盖)显示在右边,以更好地可视化组装的组织。可见培养基1的血管网络直径和血管面积更大,更适合类器官的灌注。
- (d-g)对不同培养基配方中组装的血管网络的特征进行量化。
- (d)平均血管长度。
- (e)血管面积。
- (f)血管直径。
- (g)连接密度。
- (h)类器官面积。
ECGM2:内皮细胞生长培养基。
Figure 5. Culture of vascularized human colon organoids on IFlowPlate

- (a)13天时,培养基1中的血管化的结肠类器官的明场图叠加自组装的微血管网络(绿色GFP标记的内皮细胞)的荧光图。自组装的微血管网络(绿色)的荧光图在右边再一次被展示。白色虚线圆圈描绘了类器官轮廓。
- (b)在IFlowPlate中,用红色荧光粒子(RFP)灌注的血管化结肠类器官的GFP明场叠加图像。侧面显示了灌注血管网络的荧光图像,以便于更好的可视化。白色虚线圆圈标记了类器官。
- (c)血管化类器官的共聚焦荧光z堆栈图像,显示F-actin(红色),DAPI(蓝色)和GFP内皮细胞(绿色)染色。插图显示了结肠类器官的横截面,一圈F-actin显示了结肠上皮细胞的极性。该图表示结肠类器官被GFP-血管近距离包围。
- (d)定量11天内血管化类器官的动态组装过程。发现血管在第5天结构稳定而类器官持续生长,且当第5天开始灌注时,类器官的生长呈加速趋势。
- (e)使用镊子(显示在左下角)从孔中取出第11天的血管化结肠类器官(包括脉管系统在内的整个组织),然后切片以进行组织学检查。从上到下分别为正常人结肠组织,血管化结肠类器官和非血管化结肠类器官的组织学切片。这些组织上的苏木精和伊红(即H&E,细胞核染色为蓝色;ECM和细胞质染色为粉红色),E-钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin),CD31,绒毛蛋白(Villin)和Ki67(深棕色)。
- villin染色显示类器官的极性化,表达了微绒毛蛋白。
- Ki67显示增殖祖细胞的出现,推动了类器官的生长。
- (f)量化血管化结肠类器官(vOrganoids)和人类结肠组织(hColon)中血管与结肠上皮之间的距离,显示无显著性差异。
- (g)第9天,生长在IFlowPlate和静态384孔板的有和没有内皮细胞共培养在纤维蛋白/Matrigel联合凝胶的结肠类器官明场图像。可以看出有血管网络和灌注的情况下结肠类器官的形成更健壮。作者发现血管和类器官间存在交互作用(cross-talk),当没有血管网络时类器官生长会完全停止,强调了血管网络和灌流的重要性。
- (h)四种条件下结肠类器官形成百分比的定量。
绒毛蛋白(Villin)是一种分子量为95KD的细胞骨架蛋白,为肌动蛋白结合蛋白,存在于常微绒毛细胞骨架,对保持刷状缘组织结构具有关键作用。正常分布于肠上皮和肾近曲小管上皮,可用于肠上皮来源肿瘤与非肠上皮肿瘤的鉴别诊断,亦可作为胃肠道神经内分泌肿瘤诊断的参考指标。
E-钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)是一种在上皮细胞中表达的粘附蛋白。在腺上皮以及肺、胃肠道腺癌和卵巢中存在表达。
Ki67是一种增殖细胞的相关抗原,其功能与丝分裂密切相关,在细胞增殖中是不可缺少的。所以在临床上Ki67主要用于标记增殖周期中的细胞 。
Figure 6. Vascularized human colon organoid model of tissue inflammation with innate immunity

- (a)单核细胞响应促炎因子浸润结肠类器官的实验示意图(跨内皮迁移)。
- (b)第0天和第1天的有无TNF-α刺激(50 ng mL−1 , 12 h)的血管化的结肠类器官上单核细胞浸润的明场和荧光图。单核细胞被标记为红色。血管性质用绿色标记。TNF-α刺激的情况下,大多数灌注的单核细胞被微血管捕获,而在非刺激的血管中,大多数单核细胞直接通过网络。
- (c)有无TNF-α处理的血管(绿色)的荧光图像。ICAM-1:红色,DAPI:绿色。
- (d)ICAM-1染色的定量分析。
- (e)有无TNF-α刺激的单核细胞吸附的定量分析。
- (f)有无TNF-α刺激的单核细胞浸润结肠类器官的定量分析。1天的孵化后,作者发现经TNF-α刺激的单核细胞分化而来的巨噬细胞可以浸润接近80%的结肠类器官。
作者证明,单核细胞募集的程度与炎症和TNF-α释放的程度相关,方法是简单地通过血管系统灌注循环单核细胞,模拟体内发生的确切过程,而不需要用M-CSF人工激活单核细胞。
ICAM-1:细胞间黏附分子-1, 介导黏附反应 。
Discussion
鉴于血管系统在募集和激活循环单核细胞以及放大炎症反应中扮演的关键角色,这种生物过程不能被静态的单独培养的类器官复制。因此作者提出的这个平台可以成为一个实用工具以研究更多涉及血管和上皮细胞之间相互作用的生物过程。
现有的一些方法是通过分离类器官,然后将异质细胞群播种到基于膜的器官芯片中,从而将类器官与芯片器官系统结合起来。虽然可以建立这种形式的血管灌注,但这种膜在物理上限制了类器官培养提供的三维生物重建。因此有一种无需分离和破碎细胞而保留器官等级的结构的血管化和灌注类器官和重建类器官能力的需求。
作者开发了一个平台,通过在由内皮细胞自组装的可灌注血管床上生长类器官来使类器官血管化。后续可以进行下游分析,或者整合泵进行。
Impressions
装置制造
- 标准光刻技术制造带有出入口通道的标准384孔板的SU8母模。
- 1:30的PDMS倒在母模上。
- 将除气和固化的PDMS剥离,浸泡在5% w/v普郎尼克酸中30 min。用去离子水洗涤并盖在经过等离子处理的光学质量的聚苯乙烯板上。
- 70℃下融化的聚乙二醇二甲醚(PEGDM)注入进出口通道,并填满通道。
- PDMS模具冷却至室温,使PEGDM重新固化。
- 将PDMS模具从聚苯乙烯板上剥离,有进出口通道图案的PEGDM被转移在聚苯乙烯板上。
- 将含有PEGDM结构的聚苯乙烯板使用高粘度的PDMS胶以1:10的比例在无底384孔板上粘上一夜。
论证思路
提出设计,然后分别验证了某配方的凝胶基质下,血管网络和类器官生长的可行性。再优化了共培养的培养基。最后为了证明血管的重要性,使用了一个结肠炎模型来验证。
葡聚糖为什么不在凝胶中渗透
查不到葡聚糖和凝胶有什么必然联系。
葡聚糖通常用于标记血管,它会粘附于内皮细胞表面、部分可能会被内皮细胞吸收而滞留于血管腔中。
根据后面单核细胞也是在血管中流动并参考荧光图绿色在通道出现,应该是血管长到通道,连接了出入口。这样凝胶和血管存在阻力差,会优先从血管流动。
The network can connect to the inlet and outlet channels
根据这篇文章,可知70 kDa的葡聚糖不会穿过肠上皮细胞。
Reference
Rajasekar S, Lin D S Y, Abdul L, et al. IFlowPlate-A Customized 384-Well Plate for the Culture of Perfusable Vascularized Colon Organoids[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020: e2002974.



