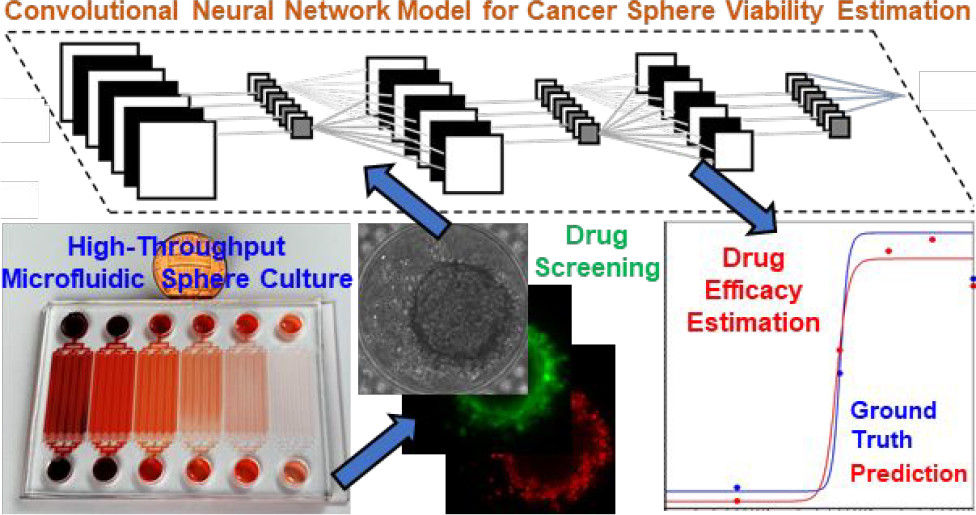
一种无标签的,使用神经网络估计3D肿瘤球的治疗有效性的方法。
Introduction
癌症是导致全球居民死亡的主要原因,也是提高预期寿命的最大障碍。 据统计,到2018年世界范围内预计有1810万新发病例和960万死亡病例。虽然当前在癌症治疗上取得了一些进步,但开发新的治疗试剂对癌症患者仍是意义非凡的。尽管动物模型拥有更好的生理相关性,但它具有高时间与金钱成本的缺点;二维细胞培养具有低成本与高通量的优点,但其缺乏细胞与细胞、细胞与细胞外基质的相互作用,使其不能充分模拟实体瘤微环境。三维细胞培养可以更好地模拟真实肿瘤中的药物暴露、营养和氧气供应情况,是一种在癌症药物筛选中更先进的模型。
微流控技术具有精准控制三维球以用于高通量药物测试的优点。但是在大规模药物筛选中,微流控的采用十分缓慢,一个主要的瓶颈是缺乏一个快速和低成本的读出方法。
为了测量药物有效性,开发了多种细胞活性试验。基于荧光的活死染色由两种成分组成。活细胞荧光试剂(如钙黄绿素)可以被细胞内酯酶激活以指示活细胞。死细胞荧光试剂(如溴乙啡锭二聚体1)能够扩散通过缺乏抵抗力的细胞膜使核酸着色,因此它可以指示死细胞的细胞膜完整性丧失。活死染色在流式细胞术中十分有用,然而它在三维模型中有一些缺点:
- 光的吸收、散射、穿透性差会使三维球/组织的成像质量变差。
- 荧光成像每张图像通常花费数百毫秒的曝光时间,明场显微镜只需要数毫秒,在大规模的药物筛选试验中会很不利。
- 活死细胞染色试剂在大规模的药物筛选中花费很大。
- 染色的细胞毒性使其仅适合作为终点检测。
还有其他更专门的细胞活性试验,测量半胱天冬酶(caspase)(如CellEvent)以指示凋亡细胞或ATP的发光读出(如CellTiter-Glo),依然存在高成本和潜在细胞毒性。比色法(如MTT和XTT)监控细胞的代谢功能,是一种快速和便宜的评估细胞活性的替代方法。健康细胞可以将基于四唑的染料还原成紫色的甲瓒,而死细胞失去了这个能力。这个方法成本低廉且易于读数,但是难以通过检查所有细胞区分杀死细胞的效果和降低细胞代谢活性的效果。在连续的监控中它的细胞读数也是让人关心的问题。最重要的是,MTT或XTT需要大量的细胞和试剂以积累显著的比色变化,在微流控平台不适用。
Figure 1. Tumor sphere chip and culture chamber

- (a)用于药物筛选的癌症球芯片的照片。芯片可以并行测试6个药物浓度用于估算IC50值。每个条件下有320个腔室培养细胞球。
- (b)8个含有流入和流出通道的肿瘤球培养腔室的显微图像,细胞通过流入通道进入球腔,由于细胞直径比微柱支撑的间隔大,细胞被细胞球培养腔捕获。带有细胞的培养基可以通过流出通道流出。
- (c)由Olympus OLS 4000 LEXT仪器测量的一个单元腔的激光共聚焦显微镜图像。
Figure 2. Cell loading in a sphere chamber and sphere aggregation
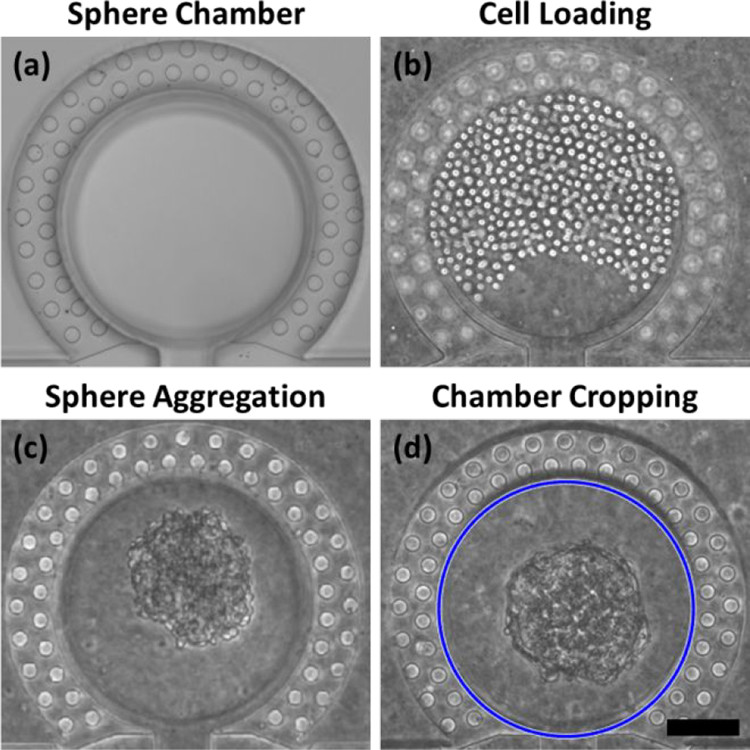
- (a)装载前空的癌症球腔。
- (b)SUM159乳腺癌细胞被装载进入癌症球腔。
- (c)2天后细胞聚集成癌症球。
- (d)一个自动的腔室裁剪程序将圆形腔室区域(蓝色圈)裁剪,以用于进一步的图像处理和机器学习。
Figure 3. Cancer spheres treated by doxorubicin

由6种不同浓度的阿霉素处理的SUM159癌症球的代表性图像。活死染色用于定量球生存力。FITC绿色荧光图像代表活细胞,TRITC红色荧光图像代表死细胞。当药物浓度增加时,绿色荧光强度减少,红色荧光强度增加。明场形态同样随药物处理而改变。
TRITC
TRITC [四甲基罗丹明-5(6)-异硫氰酸]。与 FITC 相反,TRITC 并非荧光素,而是罗丹明家族的衍生物。罗丹明也具有一个大的共轭芳香电子系统,正是该系统引发了它们的荧光行为。还有一点与FITC 相反,TRITC (479 g/mol) 由最大波长为 550nm的绿色光谱中的光所激发,它的最大发射波长为 573 nm。
Figure 4. Cancer sphere classification and drug inhibition score regression using the bright-field image and CNN model
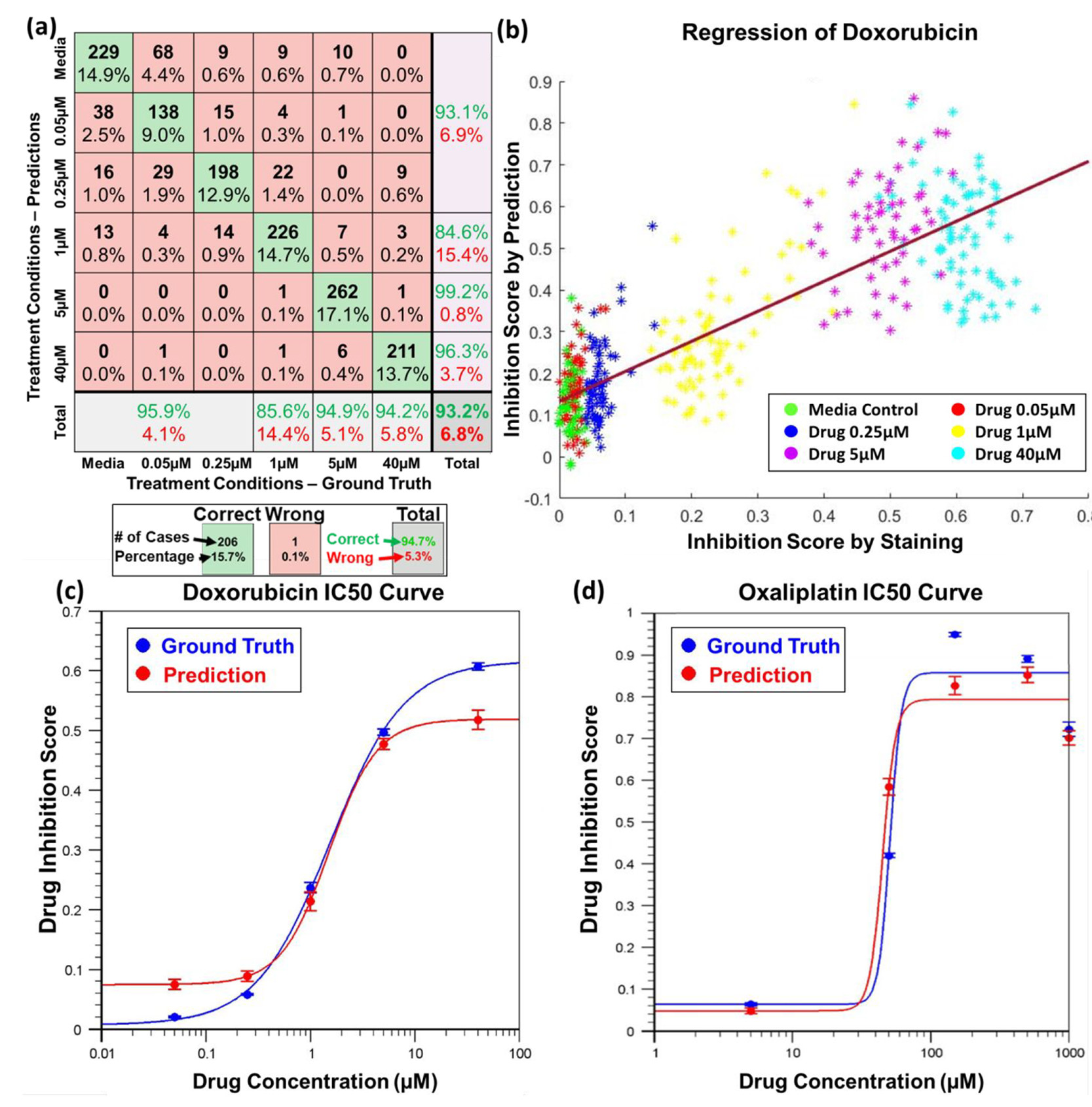
- (a)阿霉素处理分类器精确地(93.2%)预测了基于明场图像的药物处理浓度。绿色方框代表正确的预测,红色方框为错误预测,灰色方框为行/列的总和。预测数目和百分比都在方框中被描述。一列方框属于被相同浓度处理的球,一行方框属于被预测为相同浓度处理的球。由于其浓度远低于IC50的转换点难以被活死染色区分,前三类被合并。
- (b)X轴代表通过活死染色测量的抑制分数的真实数据,Y轴代表使用训练后的CNN模型预测的药物抑制分数。每个点代表一个球,不同的颜色代表不同的药物浓度。线性回归的R值( 也就是皮尔逊系数)为0.84,显示真值与预测的强相关性。
- (c-d)两种化疗药物的药效IC50曲线。X轴代表药物浓度,Y轴代表药物抑制分数。蓝色曲线基于活死染色的真值绘出,红色曲线基于明场图像的预测绘出。误差条指示平均标准偏差(standard error of the mean, SEM)。
- (c)阿霉素处理癌症球的药效IC50曲线。基于活死染色的预估IC50值为1.7 μM,基于明场图像的为1.6 μM。
- (d)奥沙利铂处理癌症球的药效IC50曲线。基于活死染色的预估IC50值为51 μM,基于明场图像的为47 μM。
Figure 5. Interdrug model validation and prediction model combining different drugs

- (a)通过阿霉素处理的肿瘤球训练的CNN模型,用于预测奥沙利铂处理的肿瘤球的药物抑制分数。X轴代表活死染色测量的抑制分数的真值,Y轴代表通过阿霉素处理肿瘤球的明场图像训练的模型预测的药物抑制分数。每个点代表一个球,线性回归的R值为0.82,显示真值与预测的强相关性。
- (b)经过阿霉素和奥沙利铂处理的肿瘤球联合训练和预测。每个点代表一个球,不同颜色代表不同的药物处理。线性回归的R值为0.93,甚至高于单独药物的预测。
体现了模型的迁移能力,相同机制的药物处理有相同的形态特征。
Conclusion
微流控技术在药物研究中受到了缺乏自动化的、快速的和低成本读出方法的限制。作者开发了一个高通量的3D细胞培养平台。通过可编程软件自动化裁剪图片以用于分析,更重要的是,使用卷积神经网络开发了通过明场图像训练的卷积神经网络精准预测癌症球生存率的方法。
Reference
Zhang Z, Chen L, Wang Y, et al. Label-Free Estimation of Therapeutic Efficacy on 3D Cancer Spheres Using Convolutional Neural Network Image Analysis[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(21): 14093–14100.