
一种微流控肿瘤芯片,以评估NK细胞如何响应肿瘤诱导的抑制性环境。
Introduction
在过去数年,多种免疫疗法突破如嵌合抗原受体(CAR)T细胞/NK细胞和免疫检查点抑制剂(ICIs)已经证明在血液癌(如急性髓系白血病和急性淋巴细胞白血病)中取得巨大成功。然而在将其应用到实体瘤中进展缓慢,部分原因可能是实体瘤产生的免疫抑制微环境压力。在这个背景下,最近的研究显示了肿瘤相关环境因子如营养不足、缺氧、废物累积和pH酸化抑制T和NK细胞抗肿瘤活性。因此理解这种微环境压力对免疫细胞的后果对于发展更有效的免疫治疗是非常关键的。然而使用传统的2D模型达到实体瘤微环境的完整性仍具挑战性。
作者的肿瘤芯片模型包括一个微腔,在其中乳腺癌细胞被嵌入一个3D基质。位于微腔一端的内腔排列着内皮细胞,灌注培养基以滋养细胞,模仿肿瘤中的脉管系统。他们的结果证明了NK细胞最初展示了相当的细胞毒性能力,消灭了相当大比例的肿瘤细胞。然而培养在装置中逐渐侵蚀了它们的细胞毒性能力,导致了NK细胞耗竭。此外,作者探索了NK细胞的可塑性和它们扭转免疫耗竭的能力。在这个背景下,结果证明了NK细胞不能从耗竭表型中扭转,显示了尽管移除了肿瘤产生的环境压力,它们发生了多分子和功能改变。
Fig. 1. Tumor-on-a-chip
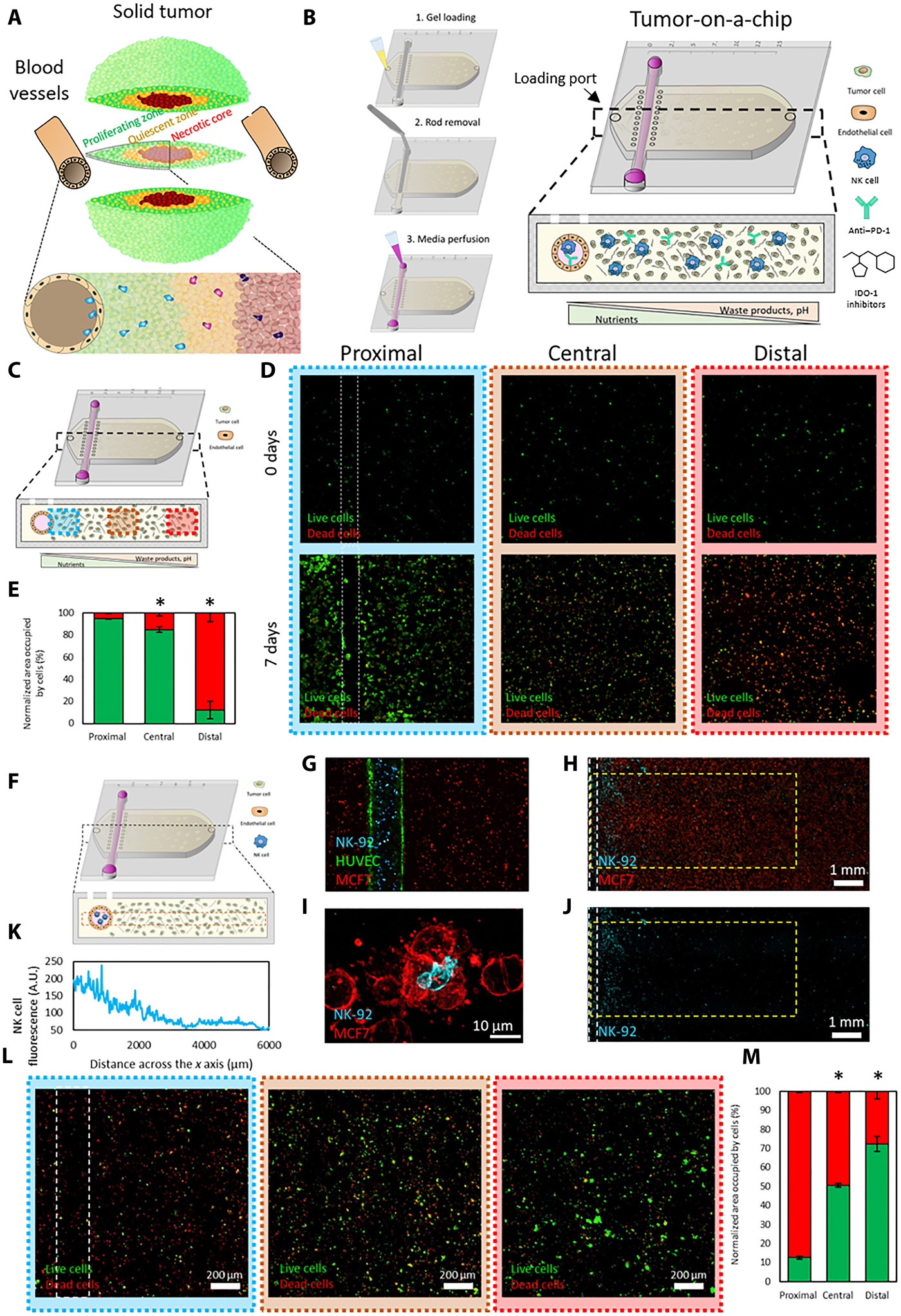
- (A)由于营养不足导致了实体瘤中不同的肿瘤表型的示意图。
- (B)肿瘤芯片的示意图。下方小图展示了微装置的截面。内腔排列着内皮细胞(如HUVECs)以代替血管,允许灌注培养基、NK-92细胞、PD-L1抗体(如阿特朱单抗)或IDO-1抑制剂(如epacadostat)。
- (C)微装置的示意图, 近端、中央和远端区域分别显示为蓝色、橙色和红色。
- (D)共聚焦显微图像显示了0天和7天的存活(绿)与死亡(红)的MCF7细胞。
- (E)近端,中央和远端区域中被活细胞(绿色)和死细胞(红色)占据的区域。
- (F)实验流程示意图。
- (G)共聚焦显微图像显示了肿瘤芯片上的细胞扩散。MCF7细胞(红色)被嵌入胶原凝胶,NK-92细胞(蓝色)和HUVEC细胞(绿色)则嵌在内腔。
- (H)共聚焦显微图像显示了NK-92细胞(蓝色)迁移到腔室和MCF7细胞(红色)。
- (I)共聚焦图像展示了一个NK-92细胞与一个MCF7细胞交战。
- (J)共聚焦图像突出了NK细胞迁移出内腔,进入腔室。
- (K)通过测量NK细胞荧光定量NK-92细胞的x轴迁移。
- (L)由于迁移效果一般,因此将MCF-7和NK-92细胞共培养一周。由于NK细胞接近营养丰富的内腔,近端区域有更高比例的死细胞。
- (M)定量分析显示与内腔的距离和存活癌细胞(绿色)的数目是成比例的。
Fig. 2. Culture in the tumor-on-a-chip microdevice led to NK cell exhaustion
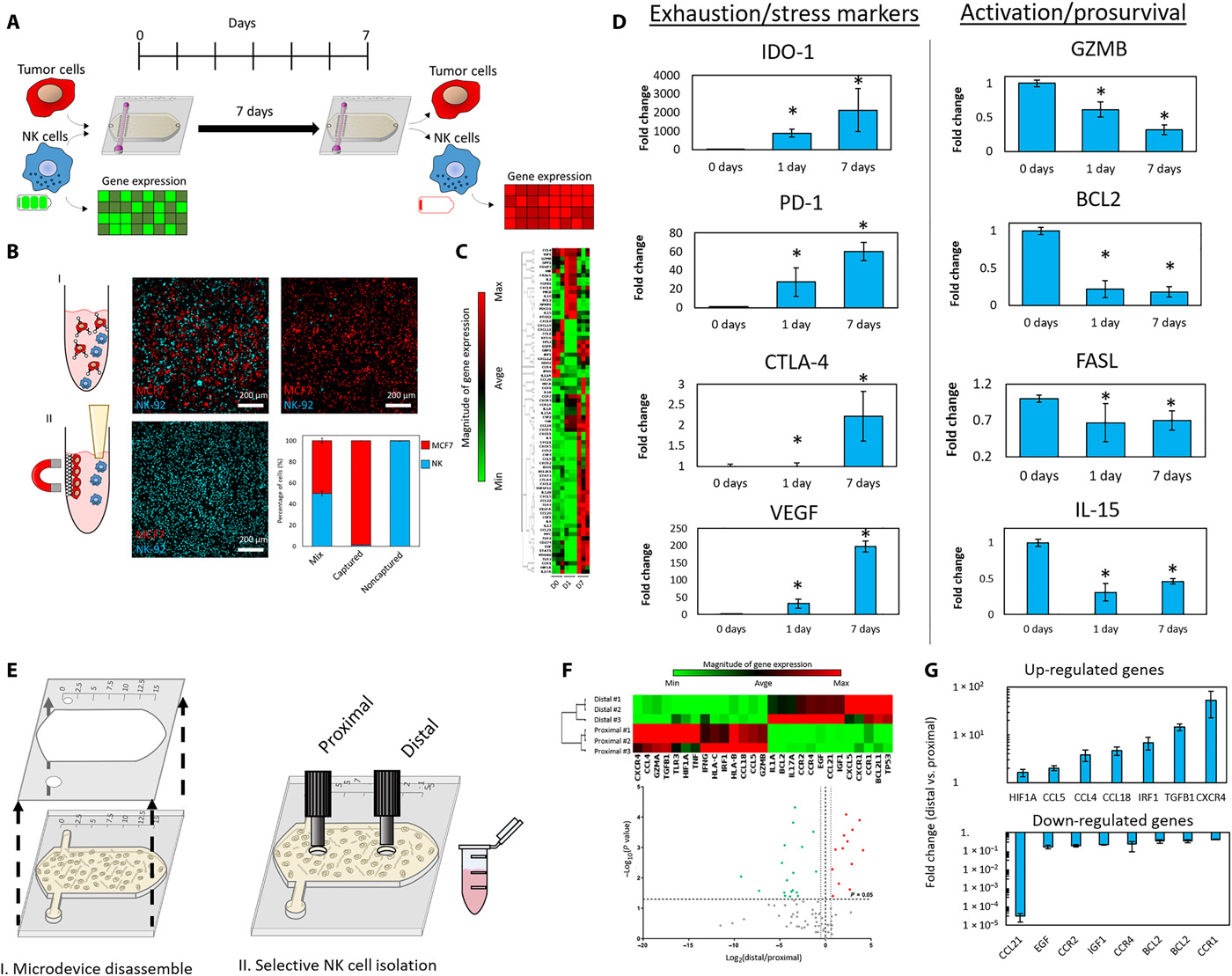
- (A)实验测量免疫耗竭的示意图。NK细胞和MCF7细胞被混合入胶原,以1:3的比例(0.5 million cells / 1 ml:1.5 million cells / 1 ml)共培养7天。这个方法确保NK细胞在水凝胶中保持均匀密度。7天后,分离NK细胞,测量基因表达和其他特征。
- (B)NK细胞分离示意图。MCF7连接到磁珠,由此可以分离NK细胞。共聚焦图像显示了捕获的MCF7细胞(红色)和分离的NK细胞(蓝色)。柱形图突出显示了NK细胞分离的效率。
- (C)聚类图描绘了0天、1天和7天的基因表达。
- (D)柱状图显示了耗竭标记物和激活/促生存基因的上/下调。
- (E)空间控制NK细胞从近端和远端分离的示意图。
- (F)聚类图和火山图定量近端和远端区域的基因表达。
- (G)柱状图描绘了远端区域相比于近端区域增加的上调基因和减少的下调基因。
Fig. 3. Comparison of NK cell exhaustion in the tumor-on-a-chip microdevice with traditional 3D culture

- (A)测量免疫耗竭实验的示意图。NK细胞和MCF7细胞以1:3的比例在孔板中共培养7天。7天后分离NK细胞,测量基因表达和其他特征。这个实验显示了在孔板而不是肿瘤芯片上的相似的耗竭参数。确定了NK细胞耗竭是由芯片里的环境压力引起的,而不是仅由肿瘤细胞存在7天的慢性激活引起的。
- (B)聚类图显示了肿瘤芯片与孔板实验的基因表达变化。
- (C-D)柱状图描绘了肿瘤芯片与孔板相比,耗竭标记物和激活/促生存基因的变化。
- (E)蜘蛛图显示了肿瘤芯片相比于传统的孔板实验差异更大的10个基因通路。NRMOP:negative regulation of multicellular organismal process,多细胞生物过程的负调控;PRISP:positive regulation of immune system process,免疫系统过程的正调控;PRCA:positive regulation of cell activation,细胞激活的正调控;PRCP:positive regulation
of cytokine production,细胞因子产生的正调控。这些通路被GSEA确定为为受影响最大的途径。
Fig. 4. Effect of ICIs and IDO-1 inhibitors in traditional assays and the tumor-on-a-chip
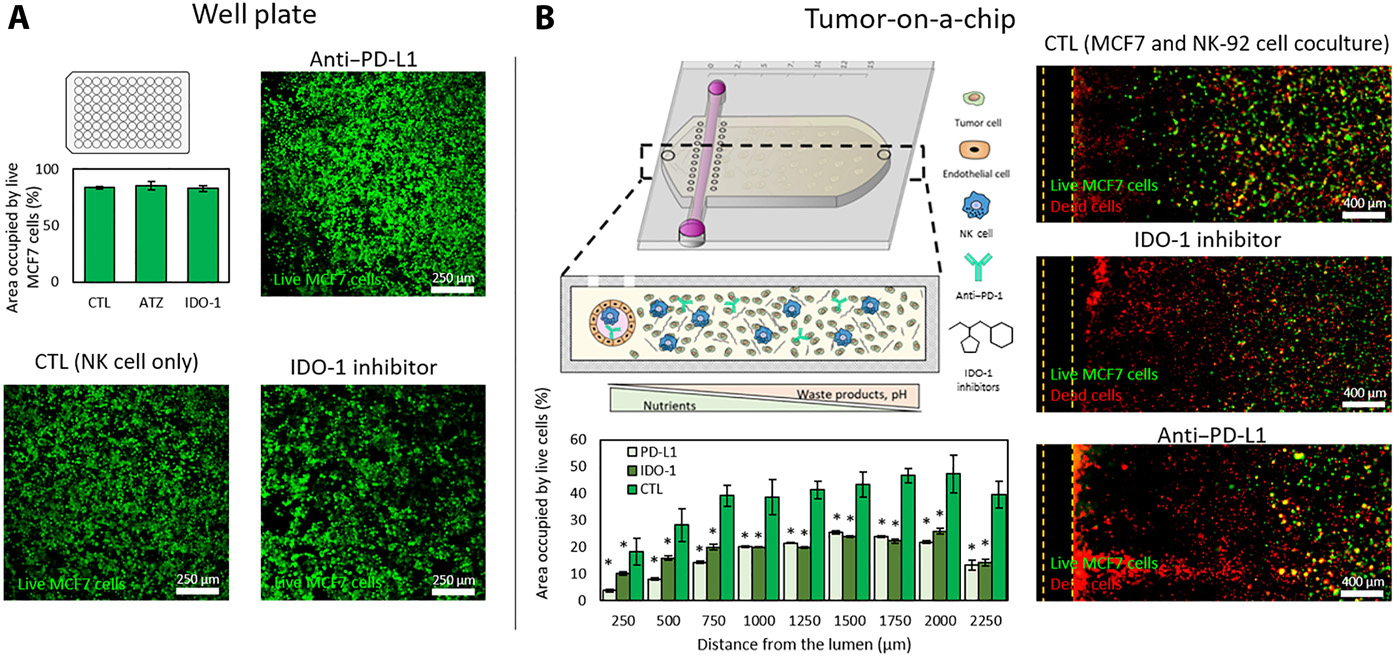
- (A)在传统孔板上评估atezolizumab(PD-L1抗体)和epacadostat(IDO-1抑制剂)的潜在作用。汇合的单层MCF7被接种到96孔板,24小时后添加有/无IDO-1抑制剂或PD-L1抗体的NK-92细胞(9 MCF7:1 NK)。共聚焦图像显示NK-92细胞毒性潜能没有显著性改善。其中,NK细胞没有环境压力,并且没有显示相关通路的上调。
- (B)相似的试验在肿瘤芯片上评估atezolizumab和epacadostat。共聚焦图像证明了IDO-1抑制剂或PD-L1抗体都增加了MCF7细胞坏死。死细胞(红色)集中在内腔近端,活的MCF7细胞(绿色)保持着远端区域。
Fig. 5. NK cell recovery from the tumor-on-a-chip platform
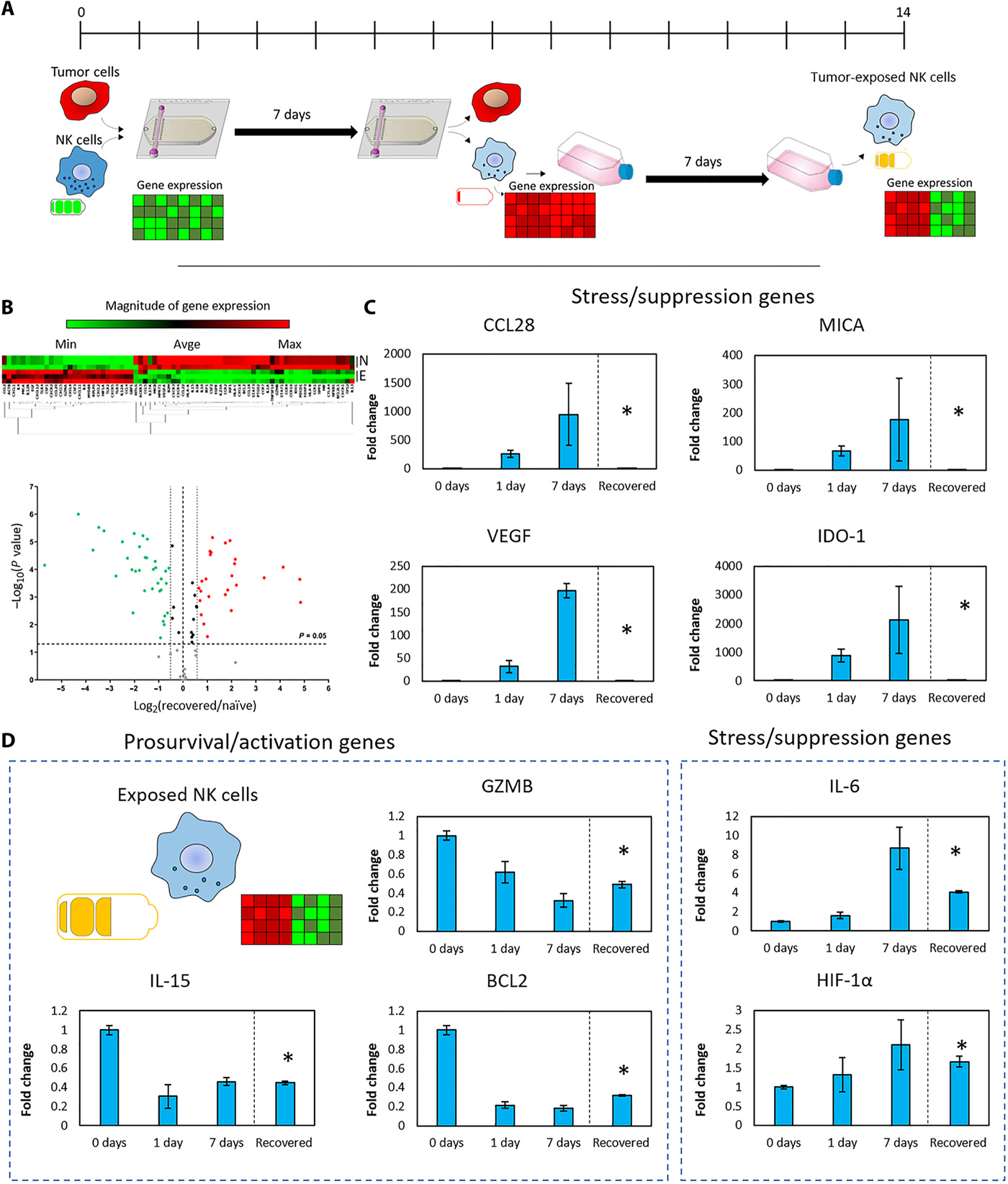
- (A)评估NK-92细胞的恢复能力的实验示意图。NK-92细胞和MCF7细胞共培养(0.5 million NK:1.5 million MCF7 cells/ml)7天。随后,分离NK-92细胞,在传统培养瓶中额外培养一周并分析它们的基因表达。
- (B)暴露NK细胞与天然NK细胞的基因表达聚类和火山图。
- (C)柱状图显示多个在肿瘤芯片中上/下调的基因在1周后恢复到基准表达。
- (D)柱状图显示与天然NK细胞相比,基因部分或没有恢复到基准表达。
Fig. 6. Functional changes in exposed NK cells

- (A)从肿瘤芯片上分离的暴露NK细胞在1周的传统培养瓶培养后展示了多个基因表达的变化。
- (B)光学代谢成像用于可视化细胞内NAD(P)H和FAD荧光强度[氧化还原比=NAD(P)H强度除以FAD强度]和平均荧光持续期(τm)。
- (C)小提琴图显示了基于NAD(P)H和FAD强度的NK细胞氧化还原比。暴露的NK细胞与天然NK细胞相比有更少的氧化还原比,指示代谢重组。此外,暴露的NK细胞显示减少的NAD(P)H τm与增多的FAD τm。
- (D)小提琴图显示氧化还原比、NAD(P)H τm和FAD τm是由不同代谢抑制剂与趋化因子导致:2DG,糖酵解抑制剂;依托莫昔(ETO),脂肪酸氧化抑制剂;寡霉素(Oligo),电子传递链复合体V抑制剂;DMSO,二甲基亚砜。
- (E-F)延时显微镜分析暴露NK细胞在3D胶原水凝胶中迁移。独立的NK细胞轨迹描述为不同颜色。小提琴图显示暴露的NK细胞迁移速度更慢。
- (G-H)暴露和天然NK细胞的细胞毒性分析。单层的MCF7接种到传统孔板,天然或暴露NK细胞添加到顶部。共聚焦图像显示二者的杀伤能力。
- (I)柱状图分析显示不同比例的肿瘤细胞(TC)与NK细胞(NK)在(H)中的MCF7细胞的破坏。暴露的NK细胞显示更少的细胞毒性能力。
Fig. 7. NK cell dysfunction marker comparison

- (A)体内功能失调(如耗竭和失活)的NK细胞的分子改变示意图。
- (B)示意图描绘了模型中与MCF7细胞(接种密度:1.5 million cells/ml)共培养了7天的NK-92细胞(接种密度:0.5 million cells/ml)的变化。
Reference
Ayuso J M, Rehman S, Virumbrales-Munoz M, et al. Microfluidic tumor-on-a-chip model to evaluate the role of tumor environmental stress on NK cell exhaustion[J]. Science Advances, 2021, 7(8): eabc2331.



