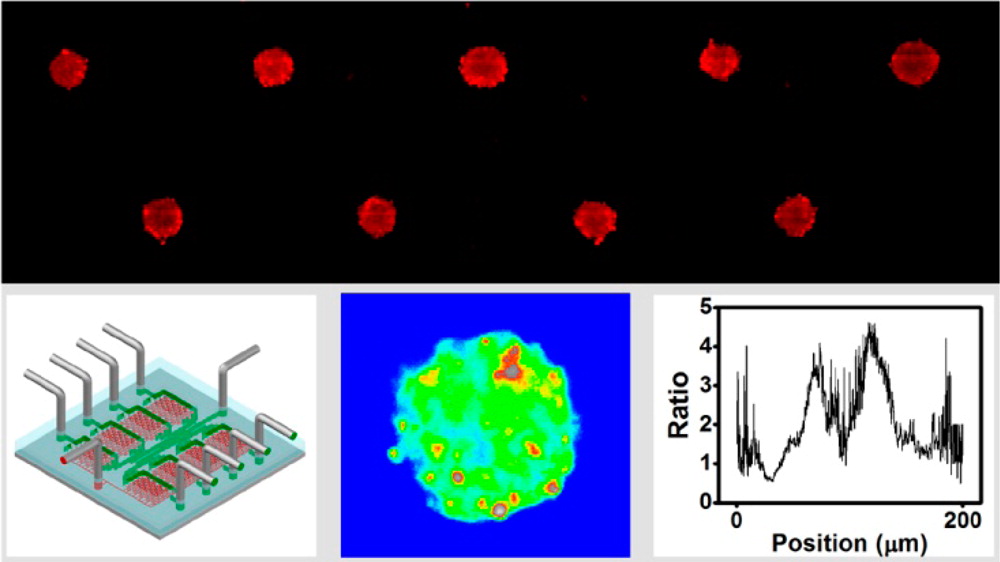
一种基于气动微结构的微流控芯片,以用于对肿瘤反应的时间的、高通量的监测。
Introduction
三维(3D)细胞培养是人为建立的环境,在该环境中,生物细胞(尤其是哺乳动物细胞)可以在三个维度上生长或与其周围环境相互作用。三维培养通常会提高组织结构和细胞分化的水平,这是二维(2D)培养所无法实现的。在癌症研究中,3D肿瘤培养被认为是一种改进的体外模型,可模拟体内肿瘤的生物学特性。当前的3D培养技术费时、费力并且需要大量试剂。因此需要进行改进以实现对3D肿瘤及其流体环绕环境的可扩展控制,以及对肿瘤细胞活性的时间监控。
作者研究了气动微流控在肿瘤样本的多重操作(即细胞捕获和3D培养)和在不同流体微环境和各种抗癌药物治疗中对细胞反应的高通量监测方面的潜力。在建立的微流控装置中,系统地评估了不同流速和加载时间下的细胞定位。证明了气动微流是可重复使用以执行数量稳定的细胞捕获和大小相似的3D肿瘤生产。此外,在培养和化疗过程中,对不同的反应动力学,包括细胞增殖、肿瘤生长/崩溃、细胞活力等进行了肉眼观察和定量分析。此外,在不同的时间点通过荧光监测两种凋亡信(线粒体去极化和caspase-3激活)。
Figure 1. Microfluidic platform for repeatable 3D culture
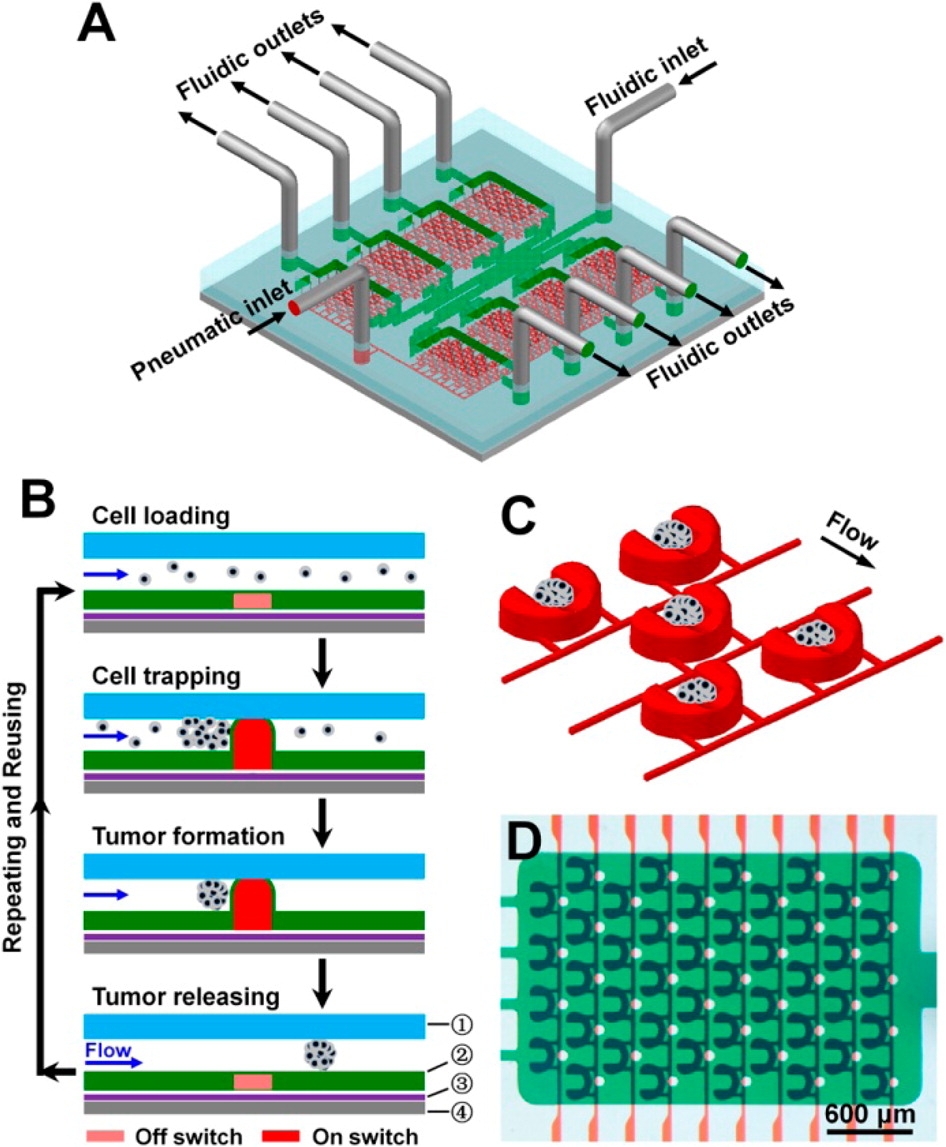
- (A)具有八个腔室的微流控设备(每个腔室中有45个PμSs)。
- (B)在由四层(①流体层、②控制层、③支撑层和④载玻片)组成的单个设备中可重复进行的3D培养操作的示意图。
- (C)用于形成3D肿瘤的空间控制的激活PμSs的示意图。
- (D)对应于腔室的实际PμS阵列的光学图像。食用染料用于可视化设备的不同组件,其中绿色表示流体通道和腔室,红色表示控制通道和PμSs。
Figure 2. Microfluidic cell trapping and device-repeatable evaluation

- (A)在以10μL/ min的流速加载10分钟后,通过PμSs捕获的U251细胞的光学图像。
- (B)对应于(A)的捕获的U251细胞的荧光图像。细胞用DiO(绿色)预染色以进行可视化。
- (C)不同流速(5、10、25、50和100 μL/min)的基于PμSs的细胞捕获。
- (D)不同加载时间(3、5、10、15和20分钟)的基于PμSs的细胞捕获。
- (E)在不同类型的设备中对PμS性能的稳定性评估。具有不同控制层的微流控装置是在PDMS中以各种混合比(即20:1、25:1或30:1)制造的。测试了PμS的持续时间和重复次数。在评估中,以20 psi驱动的PμS最多45天或300次重复。持续时间集中在持续的气动激活上,重复次数集中在重复的激活上。
- (F)研究在微流控设备中使用PμSs进行的可重复细胞捕获。
Figure 3. Investigation of microfluidic 3D tumor culture and device recyclability evaluation
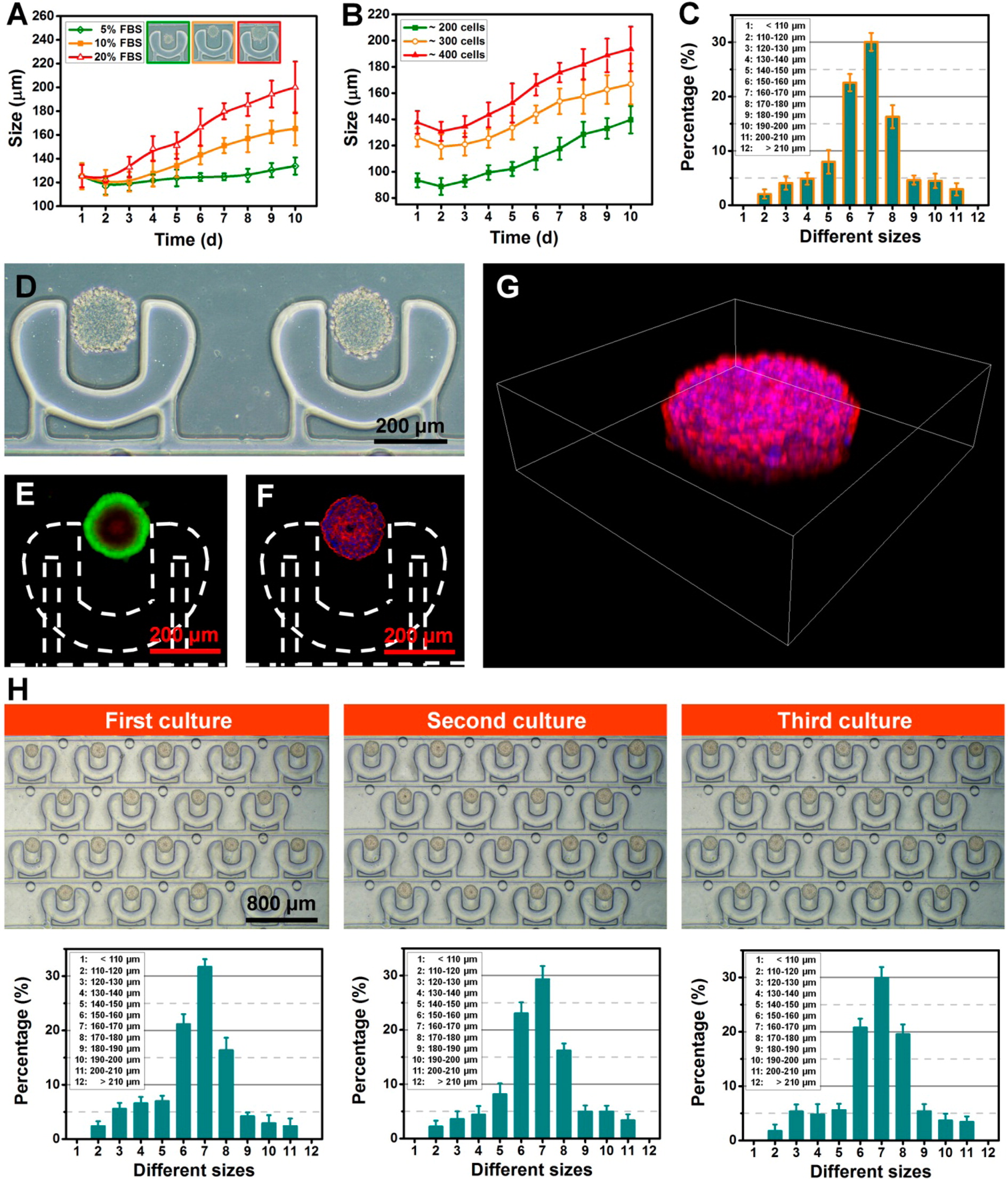
- (A)含有不同浓度FBS(5%,10%和20%)的培养基中的肿瘤直径。
- (B)源自不同数量的捕获细胞的肿瘤的大小动力学。
- (C)在使用10%FBS补充的DMEM的装置中培养10天后肿瘤的大小分布。
- (D)培养10天后U251肿瘤的光学图像。
- (E)通过FDA/PI染色的活/死(绿色/红色)细胞染色的肿瘤的荧光图像。
- (F)肌动蛋白丝(红色)和核(蓝色)染色的荧光图像,用于表现细胞骨架。
- (G)具有与(F)相同染色的U251肿瘤的三维图像。
- (H)在单个设备中可重复培养3D肿瘤。这些设备至少重复使用了3次。光学图像(顶部)显示可以在单个设备中复制阵列状肿瘤。使用单个设备对来自不同培养物的肿瘤大小分布(底部)进行定量分析表明,基于PμSs的微流控技术可用于可重复的肿瘤生成。
Figure 4. Monitoring of response dynamics of 3D tumors to treatments with two anticancer drugs at various concentrations (0.05, 0.25, 1, 5, 25, and 100 μg/mL)

- (A)用1 μg/mL长春新碱(VCR)处理4天的PI染色肿瘤的荧光图像。肿瘤阵列可对反应信号进行高通量分析。
- (B)在用不同浓度的VCR处理4天的肿瘤中的细胞死亡。死细胞(红色)用PI标记。
- (C)用100 μg/mL博来霉素(BLM)治疗的肿瘤的光学和荧光图像。在处理4天后,进行FDA/PI染色以鉴定肿瘤中的活细胞(绿色)和死细胞(红色)。荧光图像对应于BLM治疗4天后肿瘤的光学图像。
- (D)用不同浓度的VCR治疗的肿瘤的大小动力学。
- (E)VCR对U251肿瘤治疗的治疗功效。
- (F)用不同浓度的BLM治疗的肿瘤的大小动力学。
- (G)BLM在U251肿瘤中的治疗功效。其公式详见辅助材料。
Figure 5. Quantitative investigation of mitochondrial depolarization during chemotherapy

- (A)具有5 μg/mL VCR的JC-1染色肿瘤的荧光图像。线粒体中JC-1聚集体(上图:红色)和细胞质中JC-1单体(下图:绿色)具有不同的荧光强度,用于定量分析线粒体膜电位。
- (B)在5 μg/mL VCR处理期间,JC-1聚集体与单体的比率。结果对应于在不同时间处理的肿瘤的虚线标记区域(A)。
- (C)在25 μg/mL BLM处理过程中,JC-1聚集体与其单体的比率。更多的成像信息可以在图S14和S16中找到。
JC-1原理见此。
Figure 6. Caspase-3 activation of U251 cells in 3D tumors treated with different drugs
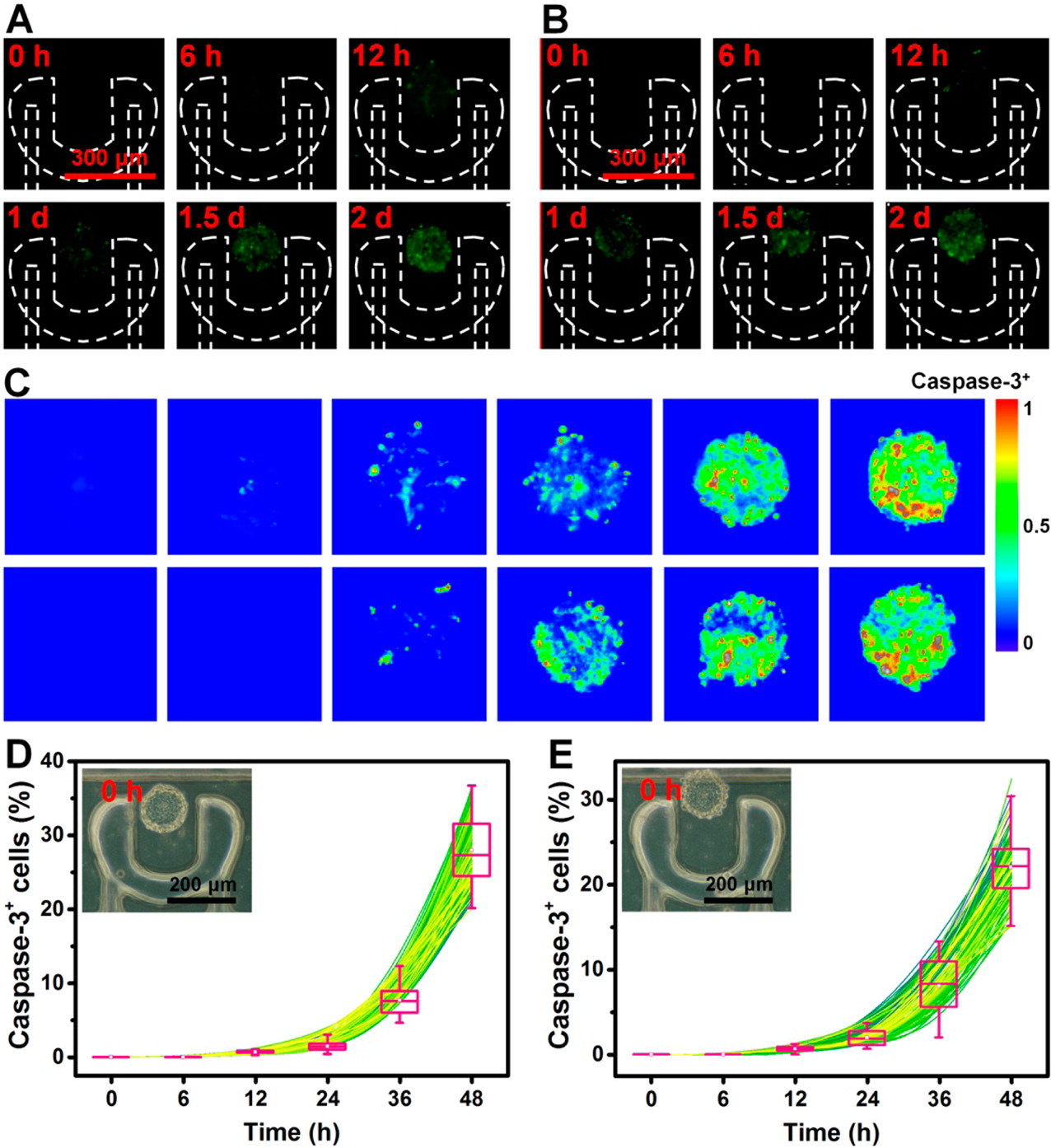
- (A)用5 μg/mL VCR处理的肿瘤中caspase-3+细胞的荧光图像。
- (B)用25 μg/mL BLM处理的肿瘤中caspase-3+细胞的荧光图像。
- (C)在不同治疗时间(从左到右:0、6、12、24、36和48小时),(顶部)VCR和(底部)BLM诱导的caspase-3+细胞在肿瘤中的荧光强度分布,分别对应于(A)和(B)。
- (D)用VCR治疗的肿瘤(n = 156)中caspase-3+细胞的百分比。
- (E)经BLM治疗的肿瘤(n = 131)中caspase-3+细胞的百分比。插图是VCR(D)和BLM(E)治疗之前的U251肿瘤,分别对应于(A)和(B)中的第一个荧光图像。
caspase-3检测原理见此。
Conclusion
- 通过执行可靠的3D肿瘤培养,验证了气动微流控技术在两种化疗药剂的时间和高通量研究中的适用性。
- 证明了在基于PμSs的微流控中稳定的3D肿瘤操作部分是基于分别在各种流体和培养条件下对肿瘤细胞定位和3D肿瘤培养的系统评价。
- 实验证明,高效的细胞捕获和质量均一的肿瘤发生可在单个设备中复现。
- 对定量抗癌评估的响应动力学进行光学监测也显示出非常强大的功能。
与以前的微流控技术进展和传统的3D肿瘤培养方法相比,经过制造优化的气动微流控为生物学/医学研究人员提供了具有可重用和长期操纵特性的微型高通量平台以更好地执行评估肿瘤发生,肿瘤进展和抗癌药物耐药性的测定,也将极大地推动具有仿生、微型和高通量功能的用于细胞分析的小型化工具的发展。
Reference
Liu W, Xu J, Li T, et al. Monitoring Tumor Response to Anticancer Drugs Using Stable Three-Dimensional Culture in a Recyclable Microfluidic Platform[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 87(19): 9752–9760.