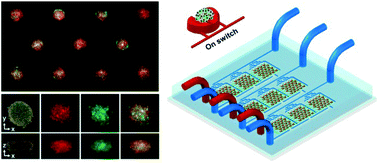
一种基于气动的微流控平台,可以在设备中生产各种异型和同型3D肿瘤阵列。
Introduction
过去数十年,悬滴、转瓶、表面修饰和细胞外支架法被用于3D培养。然而这些技术通常是复杂低效、耗时费力且耗费试剂。更重要的是,亟需人工组织(如3D肿瘤)的规模性控制以及操纵流体环境的方法。
迄今为止,研究者已经开发了大量使用液滴微流控、纸微流控和集成微流控用来进行可控地3D细胞培养的技术平台,它们具有简单、精确和高效的优点。随着对装置功能性/效率和当前对环保的意识的需求增加,注重发展稳健的非一次性微流控系统以用于细胞操纵和分析是十分有必要的。
先前的基于微流控装置的3D肿瘤培养主要聚焦于产生来源于单种类型肿瘤细胞的同型肿瘤(homogeneous tumors)。批量生产、动态操作以及时序分析形状均匀的,基于时空控制和组织模仿原理,将不同类型细胞(如肿瘤细胞和基质细胞)共培养的异型3D肿瘤的微流控装置尚有待发展。
本研究中,作者提出了一种基于气动控制的微流控方法,在拥有平行的PμS阵列的整合装置中产生异型3D肿瘤。
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of a reusable 3D tumor platform using pneumatic microfluidics

基于气动微结构(PμSs)的时空控制,装置中一次3D肿瘤培养循环的典型操作步骤包括细胞装载、细胞捕获、肿瘤培养和形成、芯片上分析(可选)、肿瘤回收和装置清洗以再利用。微流控装置包含3个流体单元,每个单元包括3个小室(C1、C2和C3)。 实际的装置(左上)和相应于小室的PμS(右上)展示在上图。使用食用染料以可视化装置上不同的微流控组件:绿色为流体层的小室,红色为PμS层的通道和PμSs。白色圆点是微流控室的支柱。
Fig. 2 Manipulative optimization of PμSs based on device fabrication and pneumatic control for a stable, repeated and long-term microfluidic manipulation in a single device

- (A)使用不同气压(0到27 psi)驱动由四层(左上:F层即流体层;P层为PμSs层;S层为支持层;glass层为载玻片)组成的装置上的不同PDMS混合比(30:1、35:1、40:1和45:1)制造的PμSs。随着压力的增加(右),关闭PμSs(左下)的状态从静止状态(1)变为半动作状态(2)甚至全动作状态(3)。绿色标记的区域是被激活的PμS接触小室天花板的地方。
- (B)一对装置之间PμSs的接触面积比。
- (C)不同PDMS混合比的PμSs操纵潜能评估。作者执行了最大200次和150天的测试,分别验证PμS激活的重复性和持久性。
- (D)不同PDMS混合比的PμSs在重复(左)和持久(右)激活的气动稳定性
Fig. 3 Microfluidic 3D tumor culture, analysis, and recovery

- (A)PμS辅助细胞捕获。U251细胞和NIH 3T3细胞用DiI(红色)和DiO(绿色)用于特定细胞追踪。
- (B)异型U251肿瘤在基于PμS的装置中培养。
- (C)共培养肿瘤中的细胞活性。活/死(绿/红)细胞分别用FDA/PI染色可视化。荧光图像与(B)中光学图像相对应。
- (D)装置中的3D肿瘤回收。
- (E)共培养的U251肿瘤的细胞骨架展示。分别用红/蓝色表示肌动蛋白丝/核。表现出高度的细胞组织,细胞之间没有细胞间隙。
Fig. 4 Device reusability for 3D tumor culture

- (A)单个装置中的异型U251肿瘤的重复性微流控培养。本研究中完成最大20次培养循环。
- (B)不同装置和不同培养循环中的,基于尺寸比较的肿瘤培养稳定性评估。
- (C)不同装置和不同培养循环中的,基于圆度比较的肿瘤培养稳定性评估。
Fig. 5 Heterotypic and homotypic 3D tumor cultures in high throughput in the PμS-based microfluidic device

- (A)经过装置上5天的共培养/单独培养,产生的阵列样的HepG2/NIH 3T3、MKN-45/NIH 3T3、HepG2和MKN-45肿瘤。
- (B)U251/NIH 3T3(顶部)和U251(底部)肿瘤的尺寸分布。
- (C)HepG2/NIH 3T3(顶部)和HepG2(底部)肿瘤的尺寸分布。
- (D)MKN-45/NIH 3T3(顶部)和MKN-45(底部)肿瘤的尺寸分布。以上,图(B-D)以10 μm的直径范围来确定。
Fig. 6 Spatial distribution of tumor cells and fibroblasts in different types of heterotypic 3D tumors
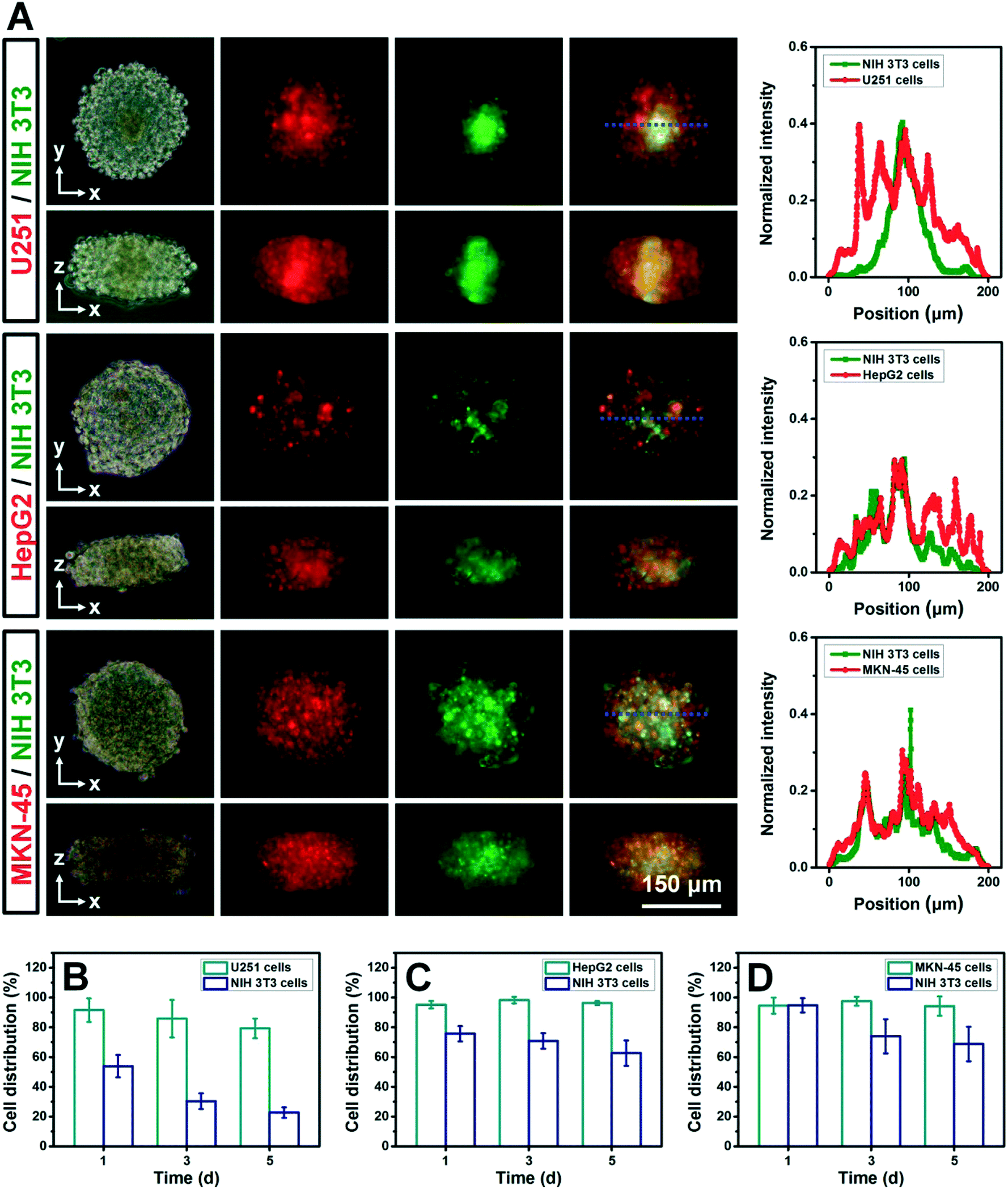
- (A)荧光染色可视化不同肿瘤中U251、HepG2或MKN-45细胞(红色)与NIH 3T3细胞(绿色)共培养在水平和垂直部分的排列。荧光图像(左)中的蓝色虚线与定量读数(右)相对应。
- (B)5天共培养中,肿瘤中U251和NIH 3T3细胞分布比例。
- (C)5天共培养中,肿瘤中HepG2和NIH 3T3细胞分布比例。
- (D)5天共培养中,肿瘤中MKN-45和NIH 3T3细胞分布比例。
Fig. 7 Dynamic monitoring and analysis of phenotypical variances of different heterotypic and homotypic tumors during PμS-based microfluidic 3D culture
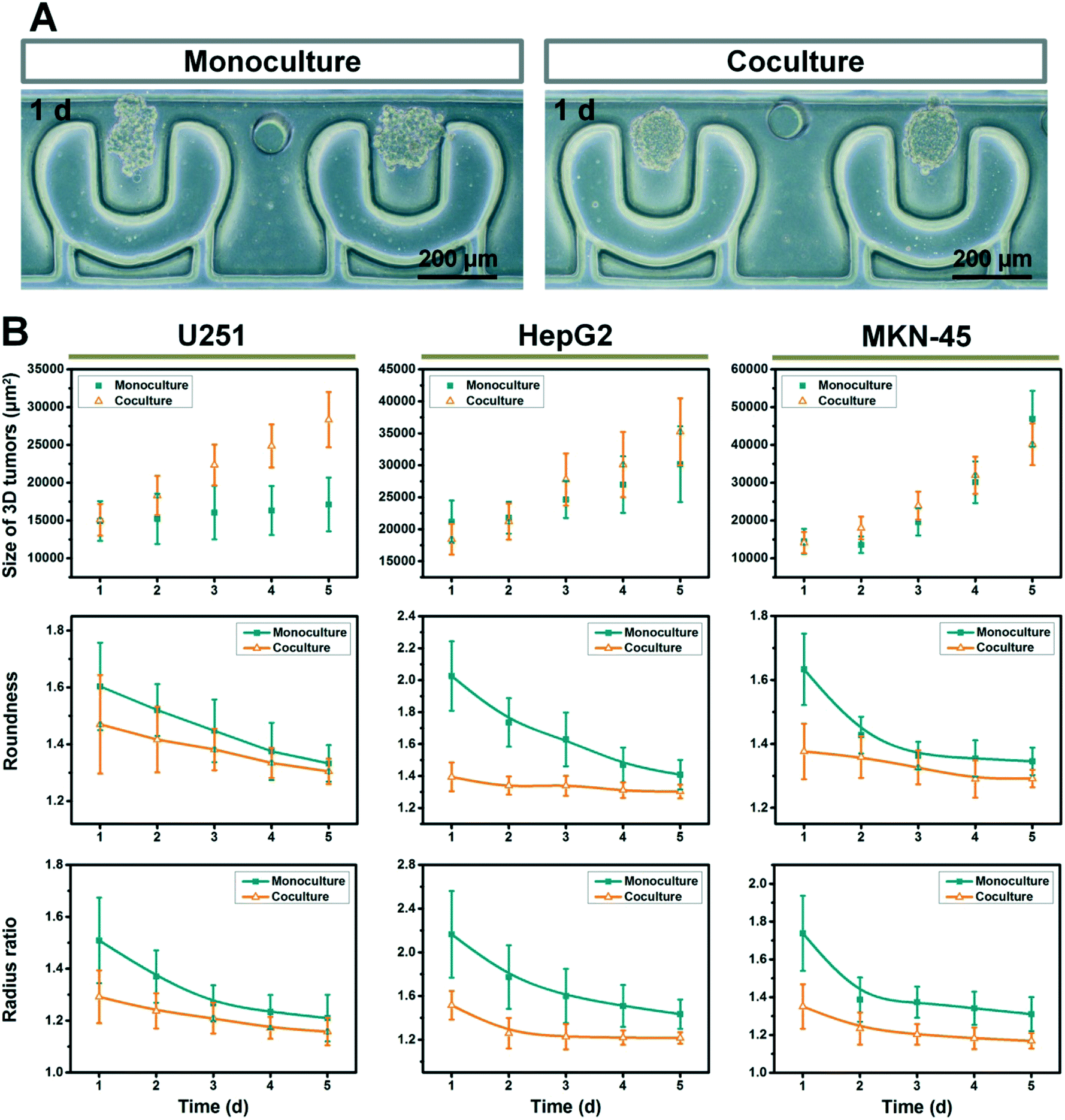
- (A)单独培养(左)和共培养(右)的HepG2肿瘤聚集的光学图像。
- (B)定量比较共培养和单独培养的肿瘤的生长和形状动力学。U251、HepG2和MKN-45细胞来源的肿瘤被纳入评估。
Fig. 8 Real-time analysis of caspase-3 activation in different types of heterotypic and homotypic tumors treated with different drugs (VNR and GEM) at different concentrations (10 and 100 μg mL^−1^ )
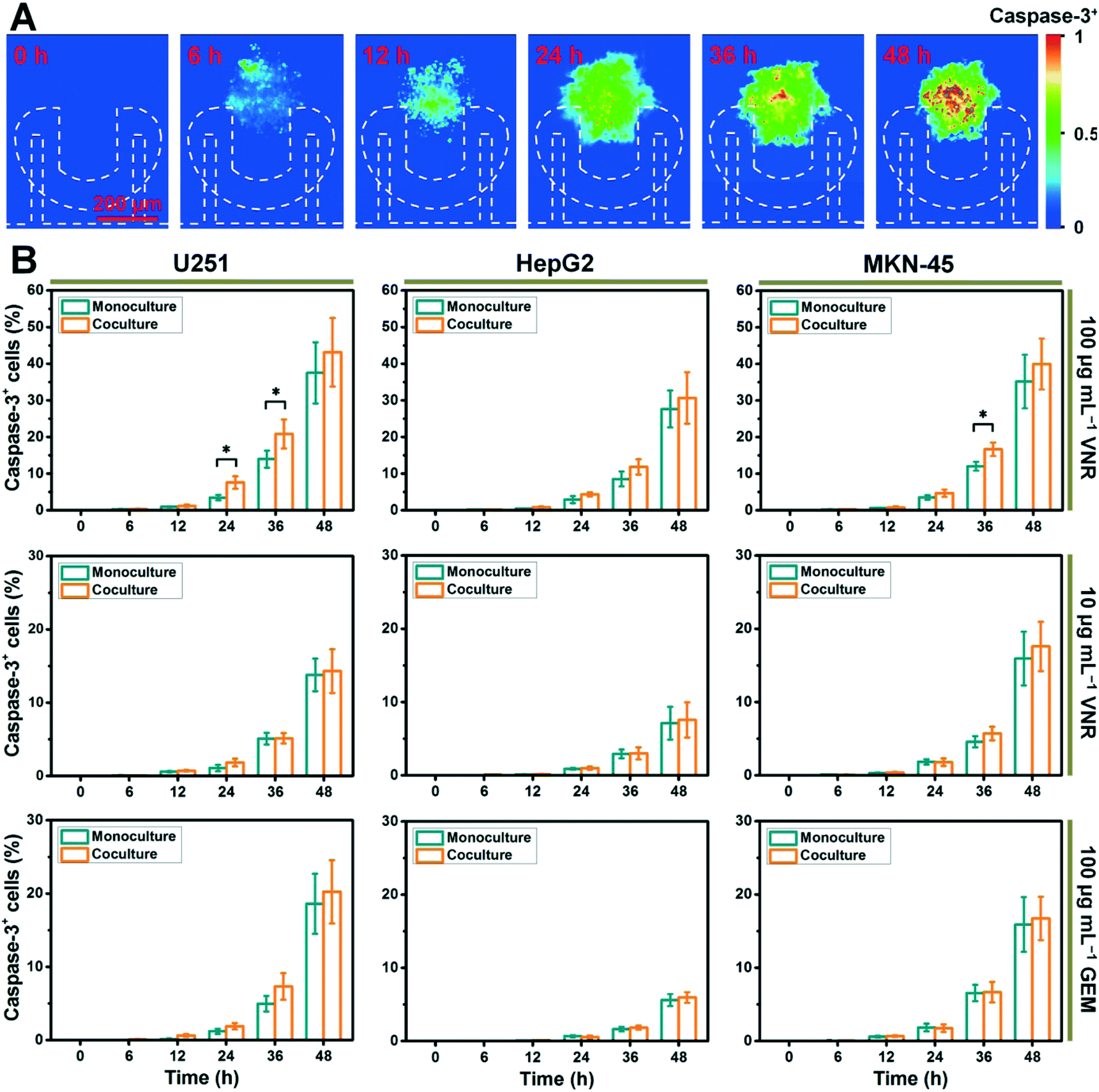
- (A)在不同的处理时间(0、6、12、24、36和48 h),用100 μg mL-1 VNR处理共培养的MKN-45肿瘤中的Caspase-3+细胞分布。Caspase-3+细胞用NucView 488 caspase-3底物荧光染色。伪彩色图像对应于图S13中的荧光图像。
- (B)以10和100 μg mL-1 VNR或GEM处理的共培养和单独培养肿瘤(U251、HepG2或MKN-45)的Caspase-3+细胞比例。
Conclusion
本文提出了一种基于PμS的、稳健的、高通量的异型3D肿瘤微流控培养平台。此外,还证实了成纤维细胞与肿瘤细胞的交流可以促进异型肿瘤在形成过程中出现非典型的外观。
Reference
Liu W, Tian C, Yan M, et al. Heterotypic 3D tumor culture in a reusable platform using pneumatic microfluidics[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2016, 16(21): 4106–4120.