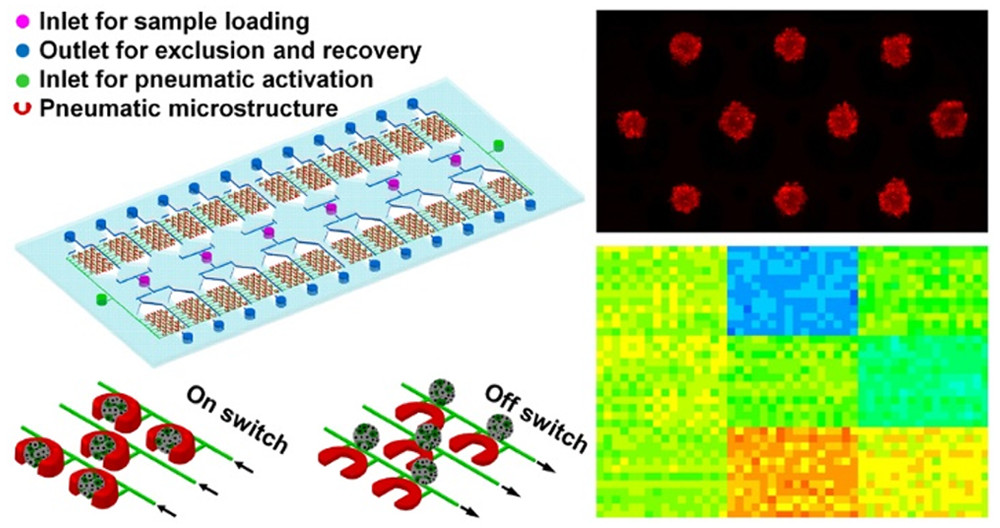
一种基于气动的微流控芯片,用于产生异型肿瘤以用于大规模化疗药物筛选。
Introduction
基于二维(2D)细胞培养的化疗试验极大地加速了抗肿瘤药物的发现和开发的过程,以便快速识别先导候选药物和研究药物疗效机制。以2D单层培养的肿瘤细胞,不能确切地模拟肿瘤模型且缺乏一些体内三维(3D)微环境下的原始表型特征(如细胞通讯和细胞排列),因此在传统的2D培养下的抗肿瘤药物的细胞毒性不能在体内表现。
目前,3D培养的用于药物检测的肿瘤大多不具有体内可见的组织异质性。因此,基于具有异型组织成分的仿生3D肿瘤,以大规模评估和筛选化合物及其化疗仍不在微流控设备的范围之内。同时,微流控浓度生成器被证明对化合物的浓度扩张和体内组织微环境的生化模拟极为有用。然而,通常存在于单个微腔内的基于扩散的梯度不适合对特定浓度药物治疗的肿瘤进行独立操作(如恢复)。与此同时,基于混合器的浓度梯度通常不超过3个数量级,如果使用设计复杂的生成器,可以扩大到6个数量级。并行多浓度操作用于基于3D肿瘤的联合化疗研究在微流控设备上进展较慢。
因此,作者描述了一种易于使用的、具有多个微流控单元集即小室和气动微结构(PμSs)的3D肿瘤平台,用于体外评估使用化学化合物的肿瘤治疗。
Figure 1. Integrated microfluidic platform for heterotypic 3D-tumor-based screening

- (A)拥有6组PμS阵列的微流控平台,每组有4个单元的PμS阵列,每个单元有28个PμSs。
- (B)PμS辅助的微流控操作,包括精确细胞定位;高通量的3D肿瘤形成;基于3D肿瘤的药物处理、芯片上分析和回收的示意图。
Figure 2. Cell localization and 3D tumor production in microfluidic devices with pneumatic control
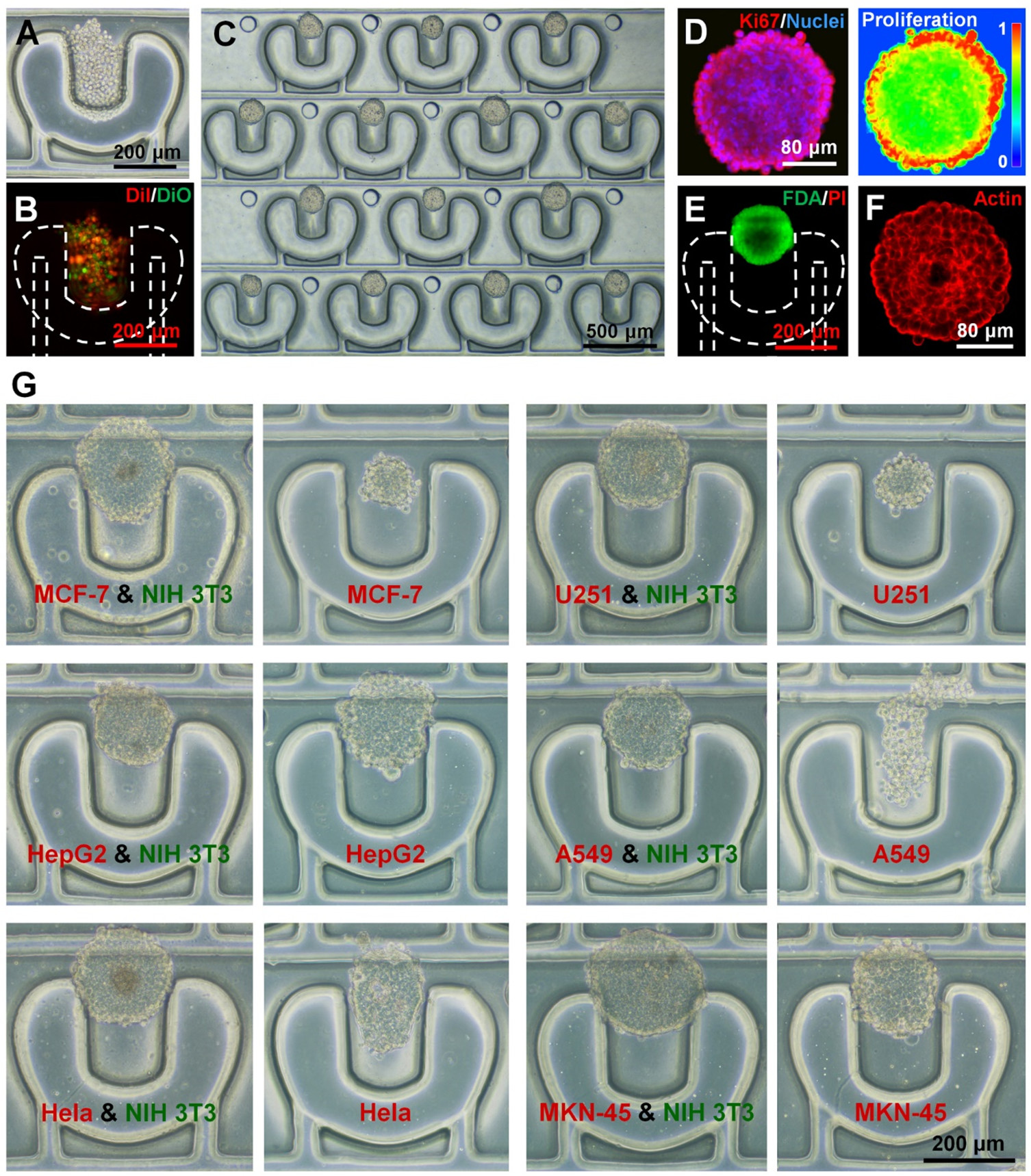
- (A-B)PμS辅助细胞捕获。将A549细胞和NIH 3T3成纤维细胞分别用DiI(红色)和DiO(绿色)染色以进行特定的细胞追踪。
- (C)共培养2天后异型A549与成纤维细胞的肿瘤阵列。
- (D)共培养5天后用Ki67(红色)和核(蓝色)染色评价肿瘤细胞增殖。伪彩色图像显示与细胞增殖相关的Ki67蛋白的荧光强度分布。
- (E)异型肿瘤的细胞活性。活/死(绿/红)细胞由FDA/PI染色确定。
- (F)通过肌动蛋白丝(红色)染色以可视化细胞骨架。
- (G)共培养5天后,芯片上的异型MCF-7、U251、HepG2、A549、HeLa和MKN-45肿瘤(A549培养3天)。
Figure 3. Initial antitumor sorting
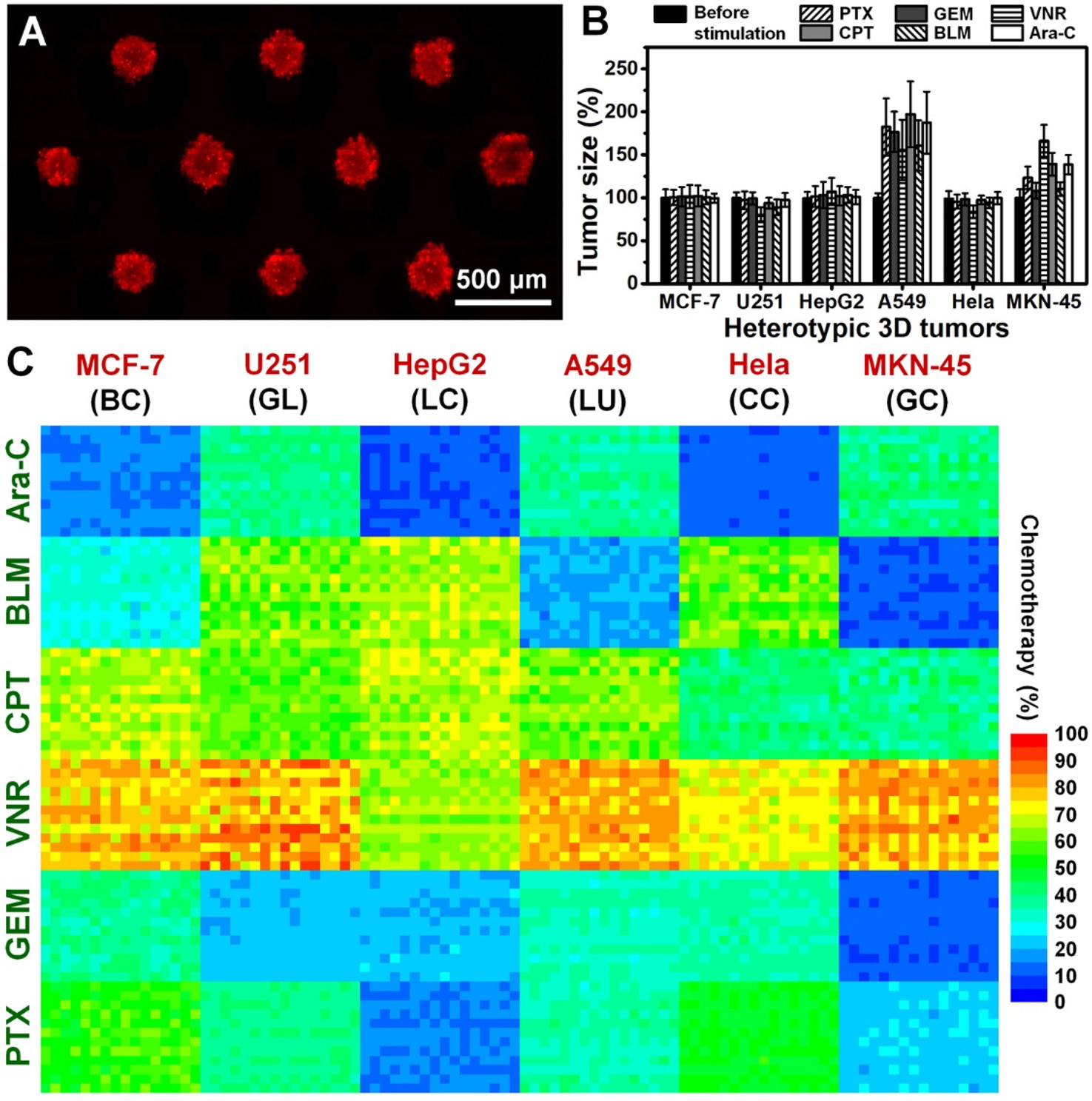
- (A)100 μM长春新碱(VCR)治疗2天后PI染色的A549肿瘤的荧光图像。肿瘤阵列允许对反应信号进行通量分析。
- (B)不同药物(100 μM PTX、GEM、VNR、CPT、BLM和Ara-C)刺激前后异质性MCF-7、U251、HepG2、A549、HeLa和MKN-45肿瘤的大小分布。
- (C)6种药物(100 μM)和6种异型3D肿瘤化疗的正交评价。
Figure 4. Response dynamics of heterotypic tumors to the selected drugs (i.e., MCF-7 and MKN-45 responses to VNR and U251 and HepG2 responses to CPT) at different concentrations (0.01–1000 μM)
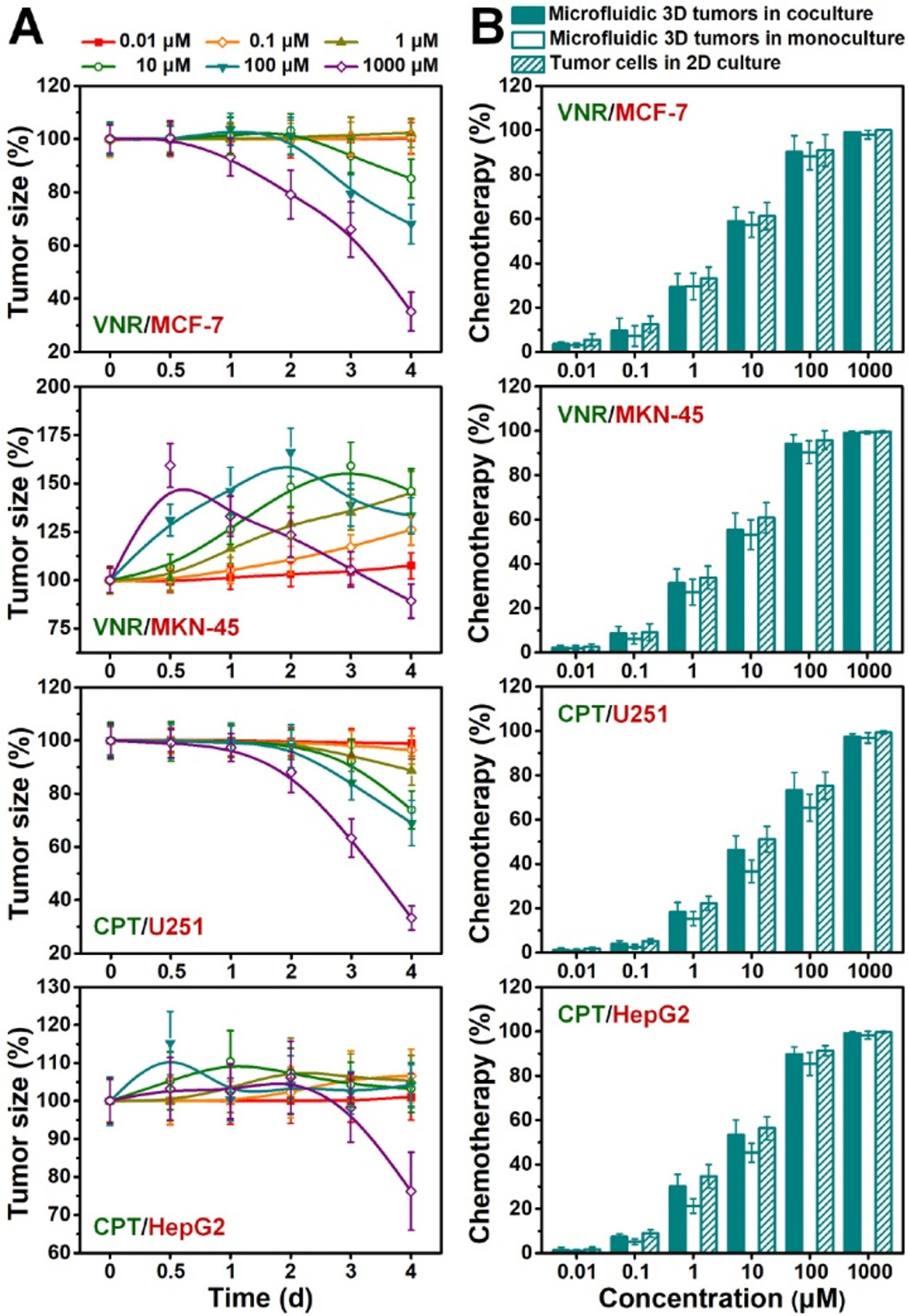
- (A)在不同浓度的药物处理4天后的尺寸动力学。可以看到MCF-7和U251为时间依赖,而MKN-45则在低浓度时尺寸增加,可能原因是化疗期间细胞聚集和去聚集的对抗作用。
- (B)不同异型肿瘤使用VNR和CPT治疗4天后的治疗效果。异型肿瘤比同型有更高的细胞死亡,尽管促进肿瘤形成和生长,共培养3D肿瘤中的异型细胞交流似乎促进了药物反应,从而减少了药物抵抗。
Figure 5. Temporal analysis of caspase-3 activation in different types of heterotypic and homotypic tumors treated with VNR and CPT (10 μM)

- (A)VNR诱导的共培养MKN-45肿瘤在不同时间(从左到右:0、6、12、24、36和48 h)caspase-3+细胞的荧光强度分布。
- (B)用VNR或CPT处理的共培养和单独培养肿瘤(MCF-7、MKN-45或U251、HepG2)中caspase-3+细胞比例。
Figure 6. Flow cytometry analysis of apoptosis in the recovered heterotypic tumors after 4 days of drug treatments

- (A)不同浓度(0.1到10 μM)VNR处理的异型MCF-7共培养(上)和10 μM CPT处理的3D U251共培养、单培养和2D培养(下)中不同状态的细胞定量。流式细胞术前用双膜联蛋白V/FITC和PI染色对细胞进行观察。细胞状态包括左上象限坏死细胞Q1,右上象限晚期凋亡细胞和坏死细胞Q2,右下象限早期凋亡细胞Q3,左下象限健康细胞Q4。
- (B)不同浓度(0.1到100 μM)VNR和CPT处理的不同异型MCF-7(左)和U21肿瘤(右)不同阶段细胞比例。
Conclusion
作者提出了一种使用便利的气动微操作的集成微流控平台以用于大规模基于异型3D肿瘤的抗癌研究。首次展示了集成的异型3D肿瘤系统在筛选化疗评估中的通用性。使用不同的化合物或浓度进行治疗性刺激肿瘤的多平行分割在单个装置中完成,对药物进行初步的抗肿瘤筛选,并对筛选的药物进行进一步的药效学评价。总之,在研究化疗和癌症病理时,异型培养和复杂肿瘤微环境构建的重要性是毋庸置疑的。
Reference
Liu W, Sun M, Han K, et al. Large-Scale Antitumor Screening Based on Heterotypic 3D Tumors Using an Integrated Microfluidic Platform[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(21): 13601–13610.