
一种包括人类CRC样核心和周围的血管化微组织的芯片平台。
Introduction
思路:
- 结直肠癌(Colorectal cancer, CRC)的危害主要是由于癌症转移发生率高和化疗效果不佳所致。
- 二维培养和用于研究化疗疗效的动物模型不能再现人体的肿瘤生理学。
- 微流控技术可以作为一个良好的平台用于揭示癌症转移的关键细胞行为方面、实现精确和具有代表性的药物筛选以及生成脉管系统样结构。
- 微流控技术的另一个特点是能够在溶液中产生良好控制的分子梯度。其重要性在于许多细胞过程是通过识别梯度中的方向性信息来工作的。产生梯度有两种方法,一种是基于流量,一种基于扩散。
- 在CRC的情况下,已知微血管内衬的内皮细胞发挥着关键的“守门员”作用,因此作者使用人类结肠微血管内皮细胞(human colonic microvascular endothelial cells, HCoMECs)开发了他们的微血管模型。
- 吉西他滨(gemcitabine, GEM)正在测试作为晚期结直肠癌患者的治疗方法,但由于其低分子量和高水溶性,GEM的临床益处受到其血浆半衰期短和肿瘤部位周围相对低浓度的阻碍。因此,寻找新的治疗策略势在必行。
- 作者目标开发一个复杂的基于3D微流控芯片的体外模型,模拟人类结直肠肿瘤微环境。该模型能够重建微血管组织的生理功能,有助于评估动态可控梯度递送载有抗癌药物的纳米颗粒的效率。这种梯度是由仿生微血管的侧通道产生和维持的。总之,这些结果表明,该3D平台适用于在比以前更生理的环境中进行药效/毒性筛选。
Microfluidic chip fabrication and characterization
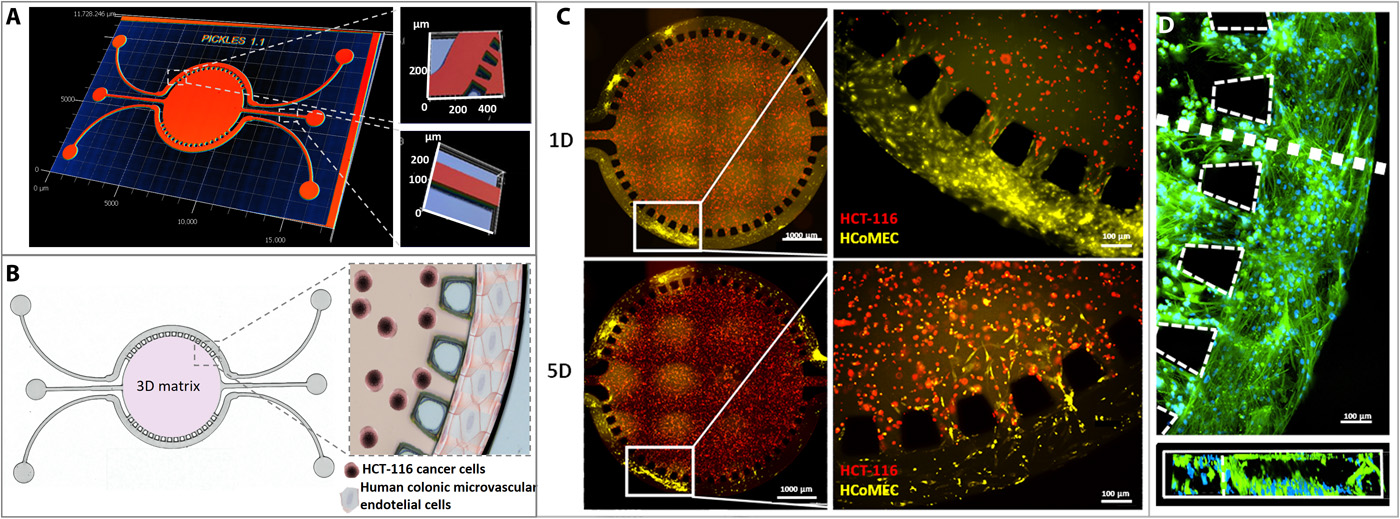
- (A)微流控芯片的3D图像。分为三个隔室,其中中央腔室直径为5 mm,深度为126 μm,具有单独的入口和出口用于水凝胶注射。两个横向通道,每个宽度为100 μm,深度为126 μm,没有相互连接,从而可以灌注两种不同溶液。
- (B)芯片设计示意图和放大图像:圆形微流控中心室,其中HCT-116人结肠癌细胞嵌入基质胶中; HCoMECs细胞被接种在侧通道中以形成3D血管样集合。
- (C)建立结直肠肿瘤芯片的微血管三维微环境。用CellTrace Red(红色)标记CRC细胞,用CellTrace Yellow(黄色)标记HCoMEC,如图所示,内皮细胞以3D血管样方式培养,附着在微流控芯片的横向通道壁上。正如预期的那样,这些细胞对加载在基质胶中的血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)的信号作出反应,通过将柱子之间的间隙从侧向通道迁移到水凝胶中。
- (D)培养5天后微流控侧通道的荧光显微镜图像,模拟HCoMECs前血管化,其中DAPI染细胞核,鬼笔环肽染F-肌动蛋白。微通道截面的荧光图像显示内皮细胞对齐并在微通道内形成内皮化的管腔。
Endothelial invasion
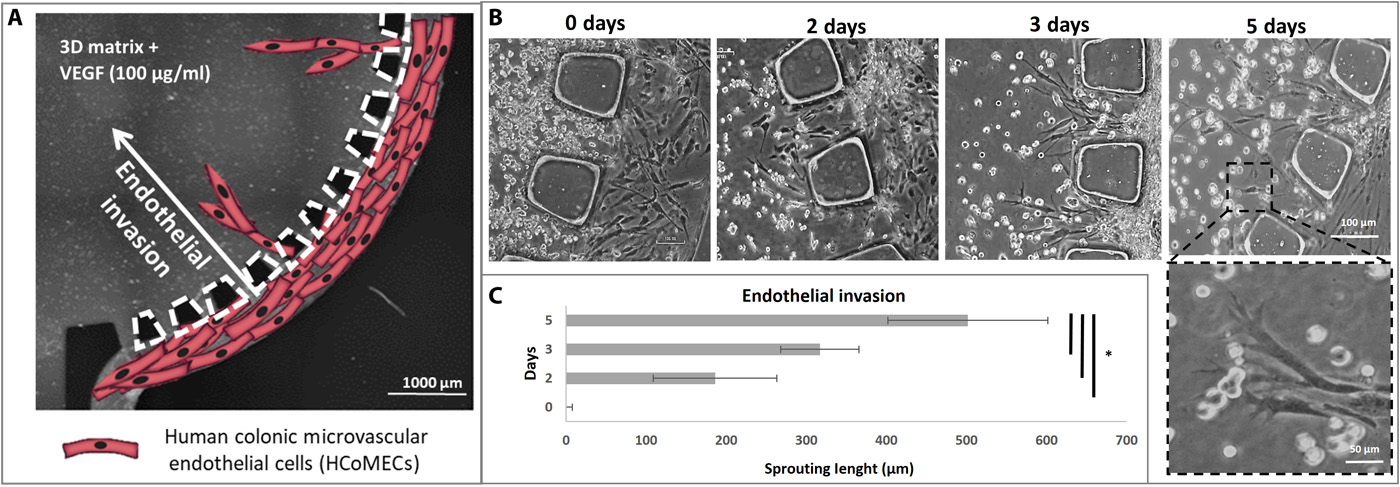
- 虽然我们本身并没有模仿血管生成现象,但在这个模型中,我们观察到内皮细胞侵入水凝胶核心但不形成吻合。
- (A)横向通道中的HCoMEC侵入含有VEGF/Matrigel的中央腔室的示意图。
- (B)微流控装置中内皮芽的形成,领先的细胞尖端充满了丝状伪足样的突起,在形态上概括了体内内皮细胞出芽。随着出芽继续侵入并延伸到整个三维基质,它们变得更长,包含逐渐增多的细胞,并开始形成相互连接的分支,正如它在肿瘤发展的早期阶段发生的那样。
- (C)内皮侵袭的量化,HCoMECs可以在5天后延展到500 μm。
Validation of the integrated microfluidic gradient chip device
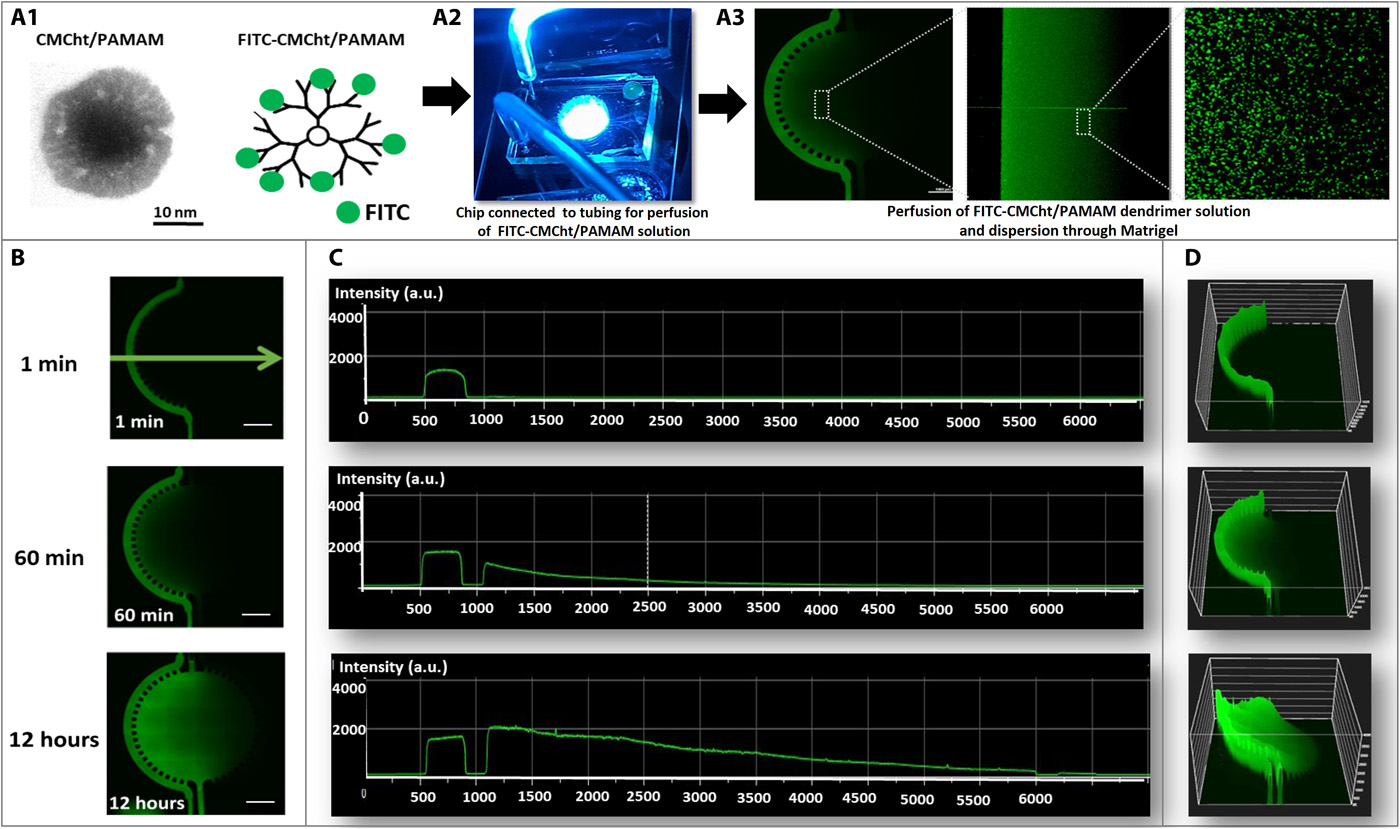
- (A)
- A1:单个羧甲基壳聚糖/树枝状聚酰胺-胺(CMCht/PAMAM)聚合物纳米颗粒的透射电子显微镜图像,平均尺寸为 50 nm;
- A2:连接到灌注纳米颗粒溶液的管子的芯片的代表性图像;
- A3:FITC 标记的CMCht/PAMAM树枝状聚合物纳米颗粒在Matrigel中扩散的共聚焦显微镜图像及放大。
- (B)12小时的荧光图像显示FITC标记的纳米颗粒的扩散梯度。
- (C)对应(B)的荧光定量分析,横坐标为芯片距离(μm),纵坐标为荧光强度(au)。
- (D)FITC标记的纳米粒子梯度根据荧光强度的3D投影。
Drug screening validation
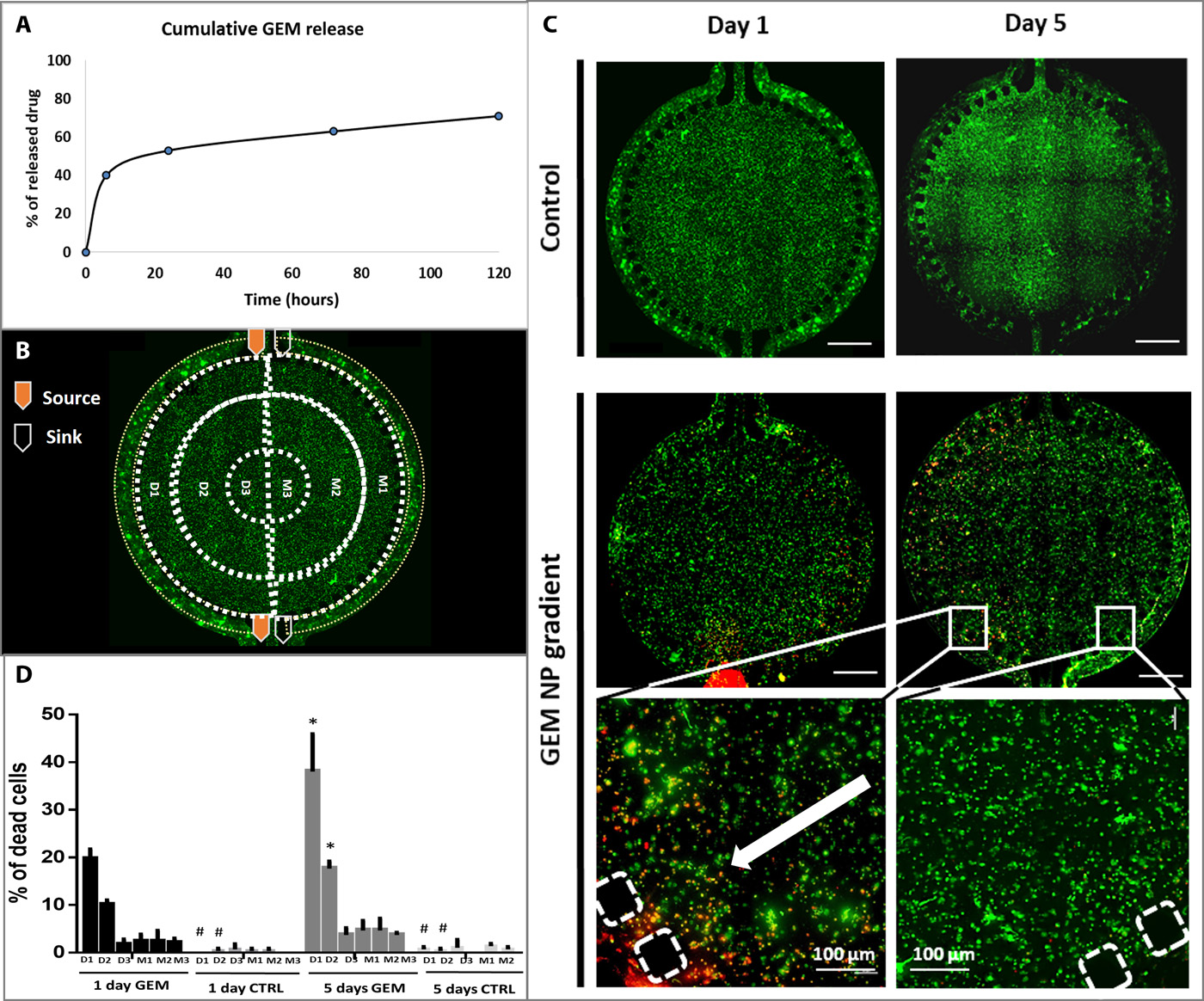
通过创建GEM浓度梯度来研究微流控装置内细胞的浓度依赖性响应。GEM-CMCht/PAMAM的包封率为52.99±3.5%,载药率为9.42±3.5%。纳米颗粒在与细胞接触后立即内化,降低了药物降解的机会,这种细胞内释放机制代表了载有GEM的纳米颗粒作为抗肿瘤剂的重要性的关键因素。
(A)GEM的释放曲线:GEM在pH 7.4的PBS中的累积释放,在37°C下以60 rpm搅拌,通过设置为275 nm的紫外分光光度计测定。
- (B)一个入口和一个出口灌注培养基,另一个入口和出口灌注载有GEM的纳米颗粒的培养基。M1、M2和M3分配给经过培养基处理的芯片区域,D1、D2和D3分配给经过药物处理的芯片区域。
- (C)在第1天和第5天在微流控芯片上进行的活/死检测的荧光显微镜图像的代表性图像。通过控制组的细胞活力观察,氧气可以通过PDMS或Matrigel自由渗透到细胞中,营养物质也可以通过侧通道灌注动态供给。证明该微流控模型能支持HCoMECs和 HCT-116细胞的稳定共培养。
- (D)细胞死亡的量化。细胞死亡以梯度方式发生,毒性逐步衰减,表明GEM可以有效地从纳米颗粒中释放出来并被癌细胞吸收。
Gene expression analysis and immunocytochemistry on a chip
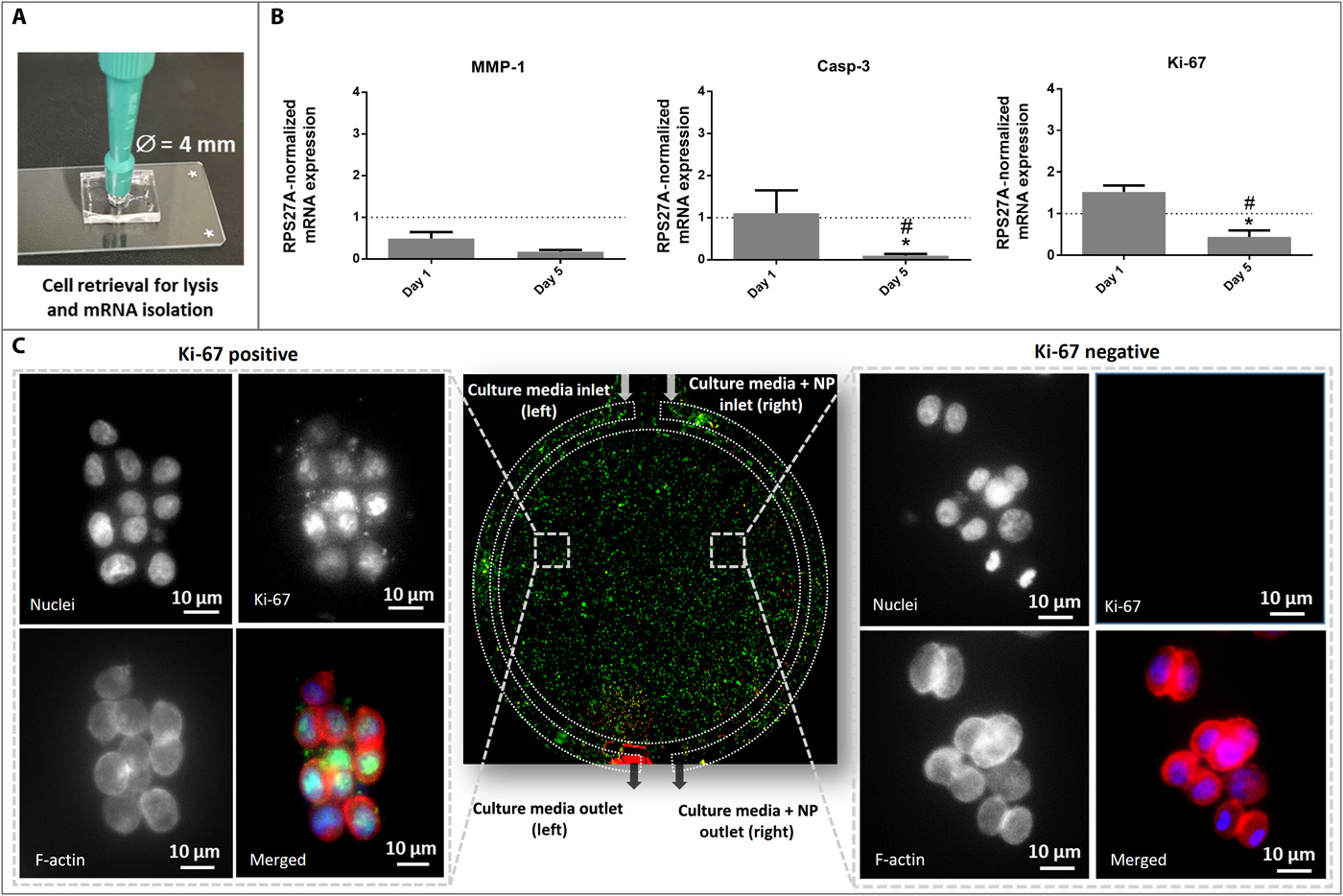
- (A)从芯片中提取含有HCT-116细胞的水凝胶,用于基因表达分析。
- (B)第1天和第 5天时,GEM组与对照组的Ki-67、Casp-3和MMP-1 (与转移表型相关)的基因表达。对照值用虚线表示,可以看到MMP-1 存在下调,Ki-67与Casp-3存在显著影响。
- (C)免疫组织化学:中间图为整个芯片的代表性图像。横向图像代表细胞水平的放大图,显示培养5天后免疫细胞化学Ki-67染色,其中DAPI细胞核染色为蓝色、Ki-67染色为绿色、F-肌动蛋白染色为红色。
Discussion
该芯片模型中,由水凝胶定义的“肿瘤”核心由由外部注射泵供给的相邻“微血管”网络提供支持每种细胞类型的特定生理事件。通过每一侧灌注不同溶液能够产生和维持稳定的梯度。结果显示:
- 红色的CRC细胞和黄色的内皮细胞增殖,沿流动方向伸长,并覆盖横向通道,因此在第5天形成血管状结构。
- 内皮细胞响应VEGF侵入中央室,定义了出芽的早期阶段。
通过梯度试验,显然较远区域释放的较少量的纳米颗粒不足以诱导细胞死亡。且低细胞死亡水平证实了3D培养对抗癌药物的敏感性更低。这可能是由于多种因素造成的,包括基质硬度、抗癌药物渗透性降低、促存活信号传导增加和/或赋予耐药性的基因上调。
此外,进行的基因表达分析作为概念证明来证明该平台既可用作药物筛选平台又可用于遗传分析。结果显示所有测试基因的下调。
- MMP-1结果:MMP-1是一种降解ECM的胶原酶,专门针对I、II和III型胶原蛋白,被认为与预后不良的晚期结肠癌有关。因此HCT-116细胞暴露于抗癌药物会导致MMP-1表达下调是有道理的。
- Casp-3结果:在两个时间点获得的下调证实了之前的活/死测定结果。此外,GEM诱导的细胞凋亡可能与活性氧、ERK(细胞外信号调节激酶)、Akt、Bcl-2和p38 MAPK(丝裂原活化蛋白激酶)途径有关,与Casp-3无关。
- Ki-67结果:从第1天到第5天暴露于药物的细胞的显著差异表明药物降低了细胞增殖。
本肿瘤芯片平台包括人类CRC样核心和周围的血管化微组织,实现了径向药物渗透进入实体瘤的仿生模型,是一种很有前途的工具用于评估基于抗癌纳米颗粒的治疗效果。
Reference
Carvalho M R, Barata D, Teixeira L M, et al. Colorectal tumor-on-a-chip system: A 3D tool for precision onco-nanomedicine[J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5(5): eaaw1317.



