
一种用来准确评估抗血管生成的纳米药物的肿瘤血管模型。
Introduction
思路:
- 癌症血管生成是肿瘤进展的一个主要标志,也是肿瘤微环境(TME)最突出的特征。因此,调控癌症血管生成一直是最有希望的癌症治疗策略之一,血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)及其受体(VEGFR)的结合被认为是调控癌症血管生成的主要目标。目前抗VEGF单克隆抗体贝伐珠单抗(Avastin)已经获得临床批准并被广泛使用,但仍需要开发更易生产和副作用更低的治疗方案。
- RNA干扰(RNAi)因其高选择性和易于合成而在治疗方面具有巨大的潜力。目前研究已经证明了RNAi靶向肿瘤中血管内皮生长因子通路的抗血管生成潜力。然而,上述RNAi研究中使用的二维(2D)体外模型并不适合分析抗血管生成作用,因为它们不能反映内皮细胞(ECs)的病理性三维萌芽。
- 微流控器官芯片技术完全可以在体外再现功能性三维血管生成的萌芽,但目前缺乏可靠的体外癌症血管生成模型和精确的基于三维成像的肿瘤血管分析。
- 在这项研究中,作者提出了一个肿瘤血管模型,来准确评估抗血管生成的纳米药物。
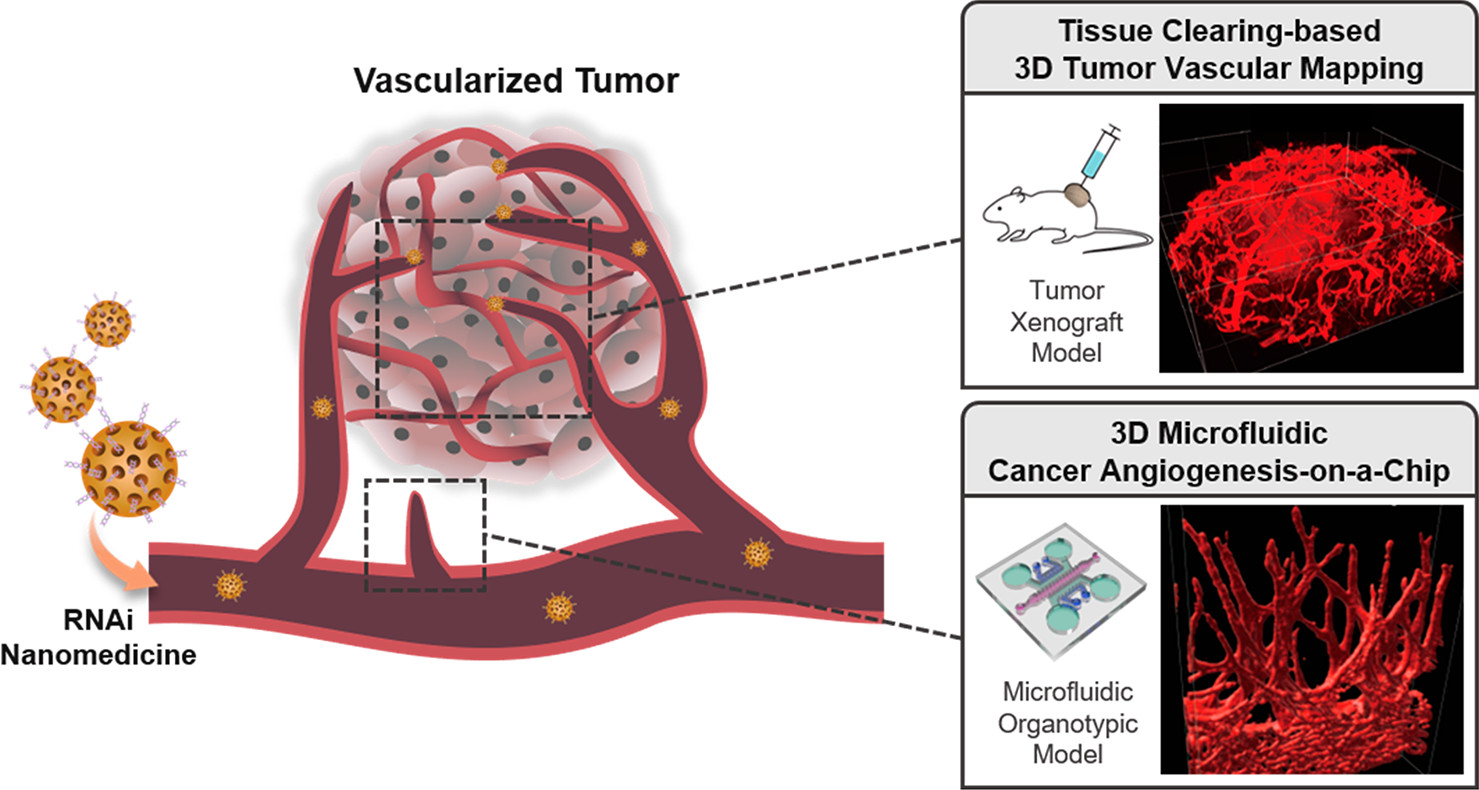
利用三维微流控癌症血管生成芯片和基于组织清除的三维肿瘤血管映射技术进行基于RNAi的纳米医学评估研究的示意图。
基于介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒(MSN)作为载体传递siRNA(siVEGF或siVEGFR),作者首先在二维培养系统中对ECs进行了快速分子分析,以验证目标基因干扰的结果。随后,引入了微流控癌症血管生成芯片,再现了TME中的三维血管芽生成,以有效筛选siVEGF/MSN或siVEGFR/MSN,缩小了抗血管生成作用的潜在目标和范围。最后,利用清晰无阻的脑成像鸡尾酒和基于计算分析(CUBIC)的组织清除技术,对人类肿瘤异种移植体进行了三维血管绘图,对整个肿瘤组织血管进行了准确无误的成像。
Antiangiogenesis on 2D Culture System
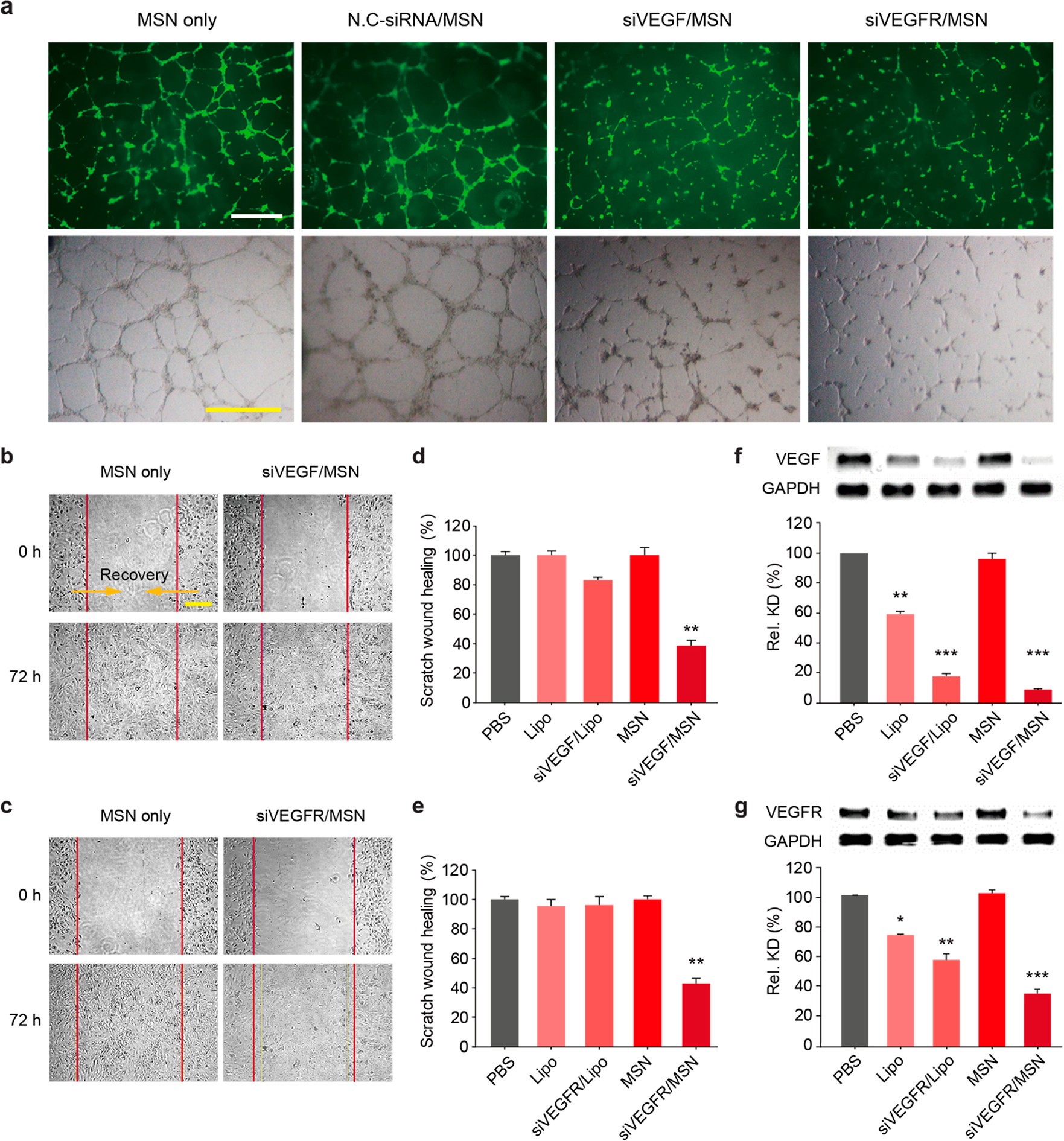
- (a)处理48 h后,HUVEC接种在Matrigel上形成的血管网络的荧光和白光图像。与对照组(空白/阴性)相比,用siVEGF/MSN和siVEGFR/MSN处理的HUVECs显示出被抑制的血管网络,即呈现出更短的血管与更少的分支。
- (b-c)处理72 h后,HUVEC划痕实验的代表性白光图像。结果显示,用siVEGF/MSN或siVEGFR/MSN处理后,细胞迁移受到抑制。
- (d-e)迁移距离的定量分析显示,与脂质体(Lipo)作为对照相比,迁移距离显著减少。
- (f-g) 定量评估由siVEGF/MSN和siVEGFR/MSN诱导的HUVEC中VEGF/VEGFR表达的下调情况。表明siVEGF/MSN和siVEGFR/MSN在ECs中的抗血管生成活性是通过调节VEGF信号通路发生的。因此,VEGF和VEGFR都是抑制血管生成的重要目标,也就是说siVEGF/MSN和siVEGFR/MSN都是作为纳米医学的有效候选药物。
Regulation of 3D Angiogenesis in Vitro by siVEGFR/MSN in Microfluidic Chip
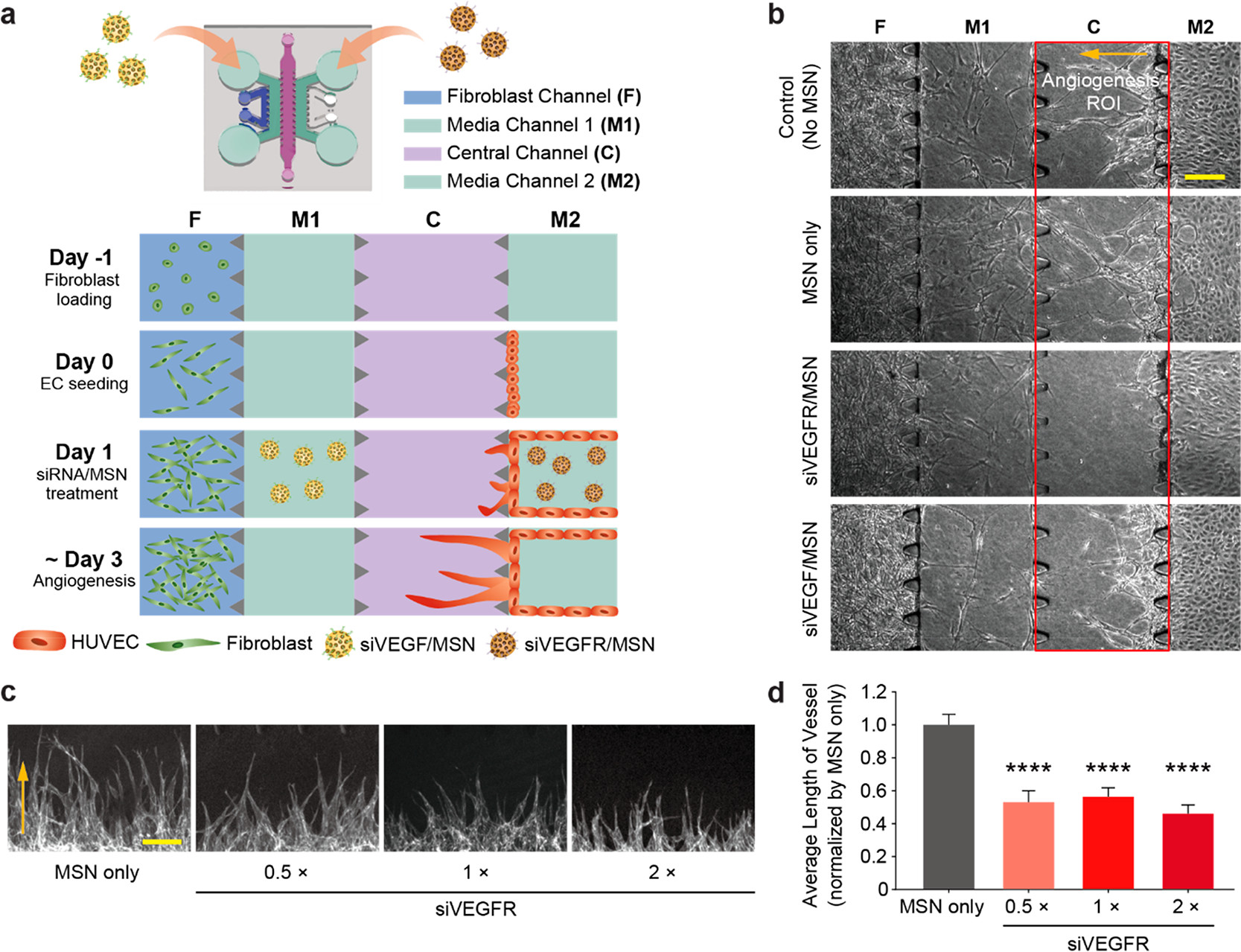
- (a) 血管生成试验的芯片设计示意图。细胞被装入三维纤维蛋白水凝胶,然后孵化过夜;次日通过培养基通道引入siVEGF/MSN或siVEGFR/MSN 6 h。
- (b)不同处理条件的代表性白光图像。红框表示通道C的边界,其中EC三维萌芽发生,血管生成萌芽的方向以橙色箭头表示。
- (c)不同siVEGFR剂量条件下,血管生成芽的代表性z-堆叠共聚焦图像。
- (d)不同siVEGFR剂量条件下,血管平均长度的定量分析。结果成功验证了siVEGFR/MSN的抗血管生成作用。由于VEGFR主要在ECs上表达,与TME中发现的不同细胞来源如成纤维细胞、肿瘤、ECs等分泌的可溶性VEGF家族成员相比,可作为一个更具体的目标。因此,该研究随后以siVEGFR/MSN为重点。
Regulation of 3D Cancer Angiogenesis in Vitro by siVEGFR/MSN in Microfluidic Chip
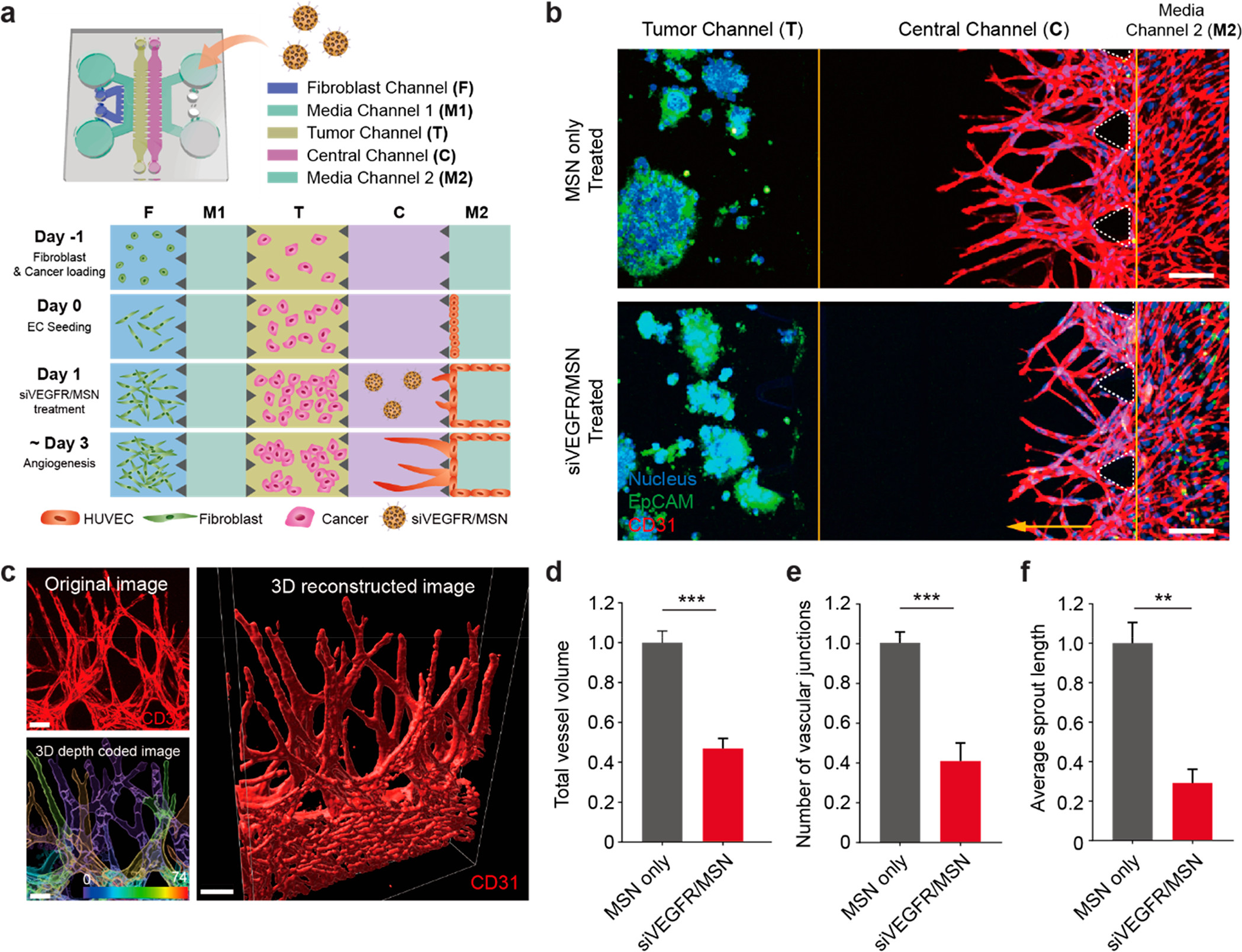
- (a)癌症血管生成试验的芯片设计示意图。不同癌细胞(HepG2、SW620和A549细胞)在肿瘤通道(T)上进行3D培养,旁边是中央通道(C),ECs向癌细胞发芽。在这个平台上,单独的癌细胞系没有产生3D血管生成萌芽的潜力,所有样品的侧通道F上都应用了成纤维细胞,从而提供了促血管生成因子的基础水平。
- (b)HepG2血管生成试验的正交视图中的代表性共聚焦显微图像,无论是否经过siVEGFR/MSN处理。通道C中的黄色箭头表示EC向癌细胞萌发的方向。第4天培养后的EpCAM(绿色)、细胞核(蓝色)和CD31(红色)免疫染色。结果表明,siVEGFR/MSN具有抗血管生成作用。
- (c)血管生成萌芽的三维重建共聚焦图像。三维深度涂层图像(右上角)表示不同深度点的每个三维芽。
- (d-f)对与HepG2共培养的血管生成萌芽的总血管体积、平均萌芽长度和血管连接点数量进行定量分析。结果显示,siVEGFR/MSN处理组与仅MSN处理组相比,总血管体积、平均萌芽长度和血管连接点的数量都明显减少。
3D Imaging-Based Analysis of Tumor Growth and Vasculature Suppression by siVEGFR/MSN

- (a)siVEGFR/MSN输送到肿瘤的示意图。准备HepG2的异种移植小鼠,每3天通过瘤内注射siVEGFR/MSN。
- (b)肿瘤组织中均匀分散的siVEGFR/MSN(青色)的代表性三维图像。
- (c)肿瘤体积的相对大小。只有siVEGFR/MSN治疗组表现出对肿瘤生长的明显抑制。
- (d)经PBS或siVEGFR/MSN处理的肿瘤血管系统的代表性三维图像。siVEGFR/MSN注射组显示血管数量明显减少,血管形态发生变化。
- (e-g)血管特性的量化。siVEGFR/MSN治疗组的血管体积(血管所占体积的百分比)、分支点数量都明显降低。但PBS和siVEGFR/MSN治疗组之间的总血管长度密度没有差异,只有siVEGFR/MSN治疗组的血管长度密度在核心区明显减少,可能是外围和核心区域不同的TME造成的。
Morphological Normalization of Tumor Blood Vasculature Induced by siVEGFR/MSN
瘤组织中活跃的血管生成不仅促进了血管的生长,也产生了不规则的血管,造成了肿瘤组织中药物输送的不均匀。(因此,药物介导的血管正常化(如通过DC101)已被用来加强纳米药物的传递。
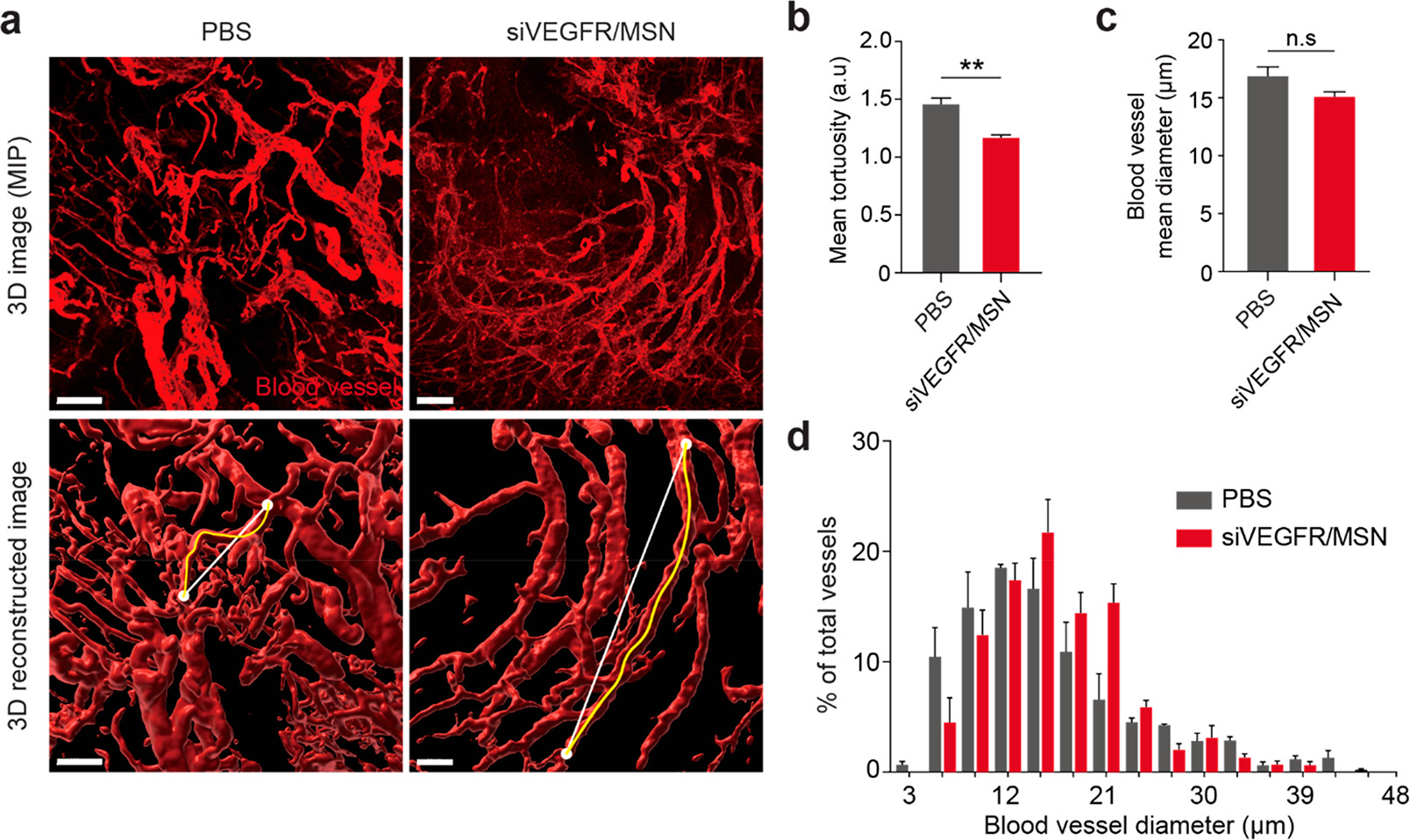
- (a)肿瘤组织的整体清除的三维图像显示,siVEGFR/MSN治疗使肿瘤异种移植的血管正常化。MIP,即Maximum Intensity Projection,最大密度投影成像。
- (b)siVEGFR/MSN治疗导致了肿瘤血管的形态正常化,由血管迂回度(血管段的长度与连接该段的相邻分支点的直线的比率)衡量,结果显示siVEGFR/MSN治疗组的血管迂曲度明显低于PBS治疗组。
- (c)siVEGFR/MSN处理组和PBS处理组的平均血管直径相比略有下降,认为没有差异。
- (d)MSN-siVEGFR2改变了血管直径的分布,减少了分布的方差。在siVEGFR/MSN处理的肿瘤中没有小血管(<10μm)和非常大的血管(>30μm),表明siVEGFR/MSN诱导了血管的形态正常化。
Conclusions
- 针对血管生成途径的基于RNAi的纳米医学的临床前研究已被证明是有效的癌症治疗方法。然而以前的研究中使用的体外模型或体内分析方法并没有为评估三维血管生成的形态表型而进行优化。因此作者实施了一个策略,涉及一个三维微流控癌症血管生成模型和基于三维成像的分析。
- 与经典的二维体外试验相比,在测试纳米颗粒给药的纳米药物时,能够提供更可靠的结果。
Reference
Lee S, Kim S, Koo D-J, et al. 3D Microfluidic Platform and Tumor Vascular Mapping for Evaluating Anti-Angiogenic RNAi-Based Nanomedicine[J]. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(1): 338–350.



