
一种高通量的微流控平台,用于筛选针对受限迁移的药物。
Introduction
思路:
- 癌症转移由几个连续的步骤组成,包括:局部侵袭、内渗、循环生存、外渗和定植。细胞迁移是癌症转移级联中的一个关键过程,由于实体肿瘤组织的硬度和机械特性,癌细胞面临更严峻的迁移条件。在肝癌、非小细胞肺癌、胰腺导管腺癌和其他类型的肿瘤中,结缔组织形成(即形成致密的胶原基质)很常见,表明肿瘤的侵略性和不良的临床结果。纤维化的基质和坚硬的细胞外基质形成封闭的孔隙(直径从1到20 μm不等)或通道状的轨道,宽度不到3到30 μm,高度100到600 μm不等。因此,受限迁移对癌症转移至关重要。
- 很多化合物可以抑制非受限的细胞迁移,如Rho相关激酶(p160ROCK)抑制剂Y-27632,肌球蛋白轻链激酶的特异性抑制剂ML-7,肌球蛋白II的抑制剂blebbistatin,RhoA、B、C的抑制剂CT04。然而,可用于受限迁移的药物却很少。针对受限迁移的药物和非受限迁移的药物之间存在着明显的区别。据报道,肌球蛋白、Rho/ROCK或β1-整合素的抑制剂可以抑制非受限迁移,但不能抑制受限迁移。
- 微流控技术提供了一种理想的方法来做高含量和高通量的药物筛选,而且试剂消耗少。微流控设备还可以模拟真实的人类血管,其直径≈100至200 μm,将更容易创造一个更真实的细胞生长环境,在组织区间有适当的剪切应力和流体阻力。然而,大多数微流控设备被用来筛选细胞毒性药物,忽略了癌细胞的其他特征。
- 在这项工作中,作者设计了一个具有5 μm高的迁移通道的微流控芯片,可以在一个装置中实现多功能的受限迁移相关的抑制剂筛选。此外,该芯片还可以作为一个共培养系统,研究封闭条件下的细胞与细胞之间的相互作用,为下游抑制剂的筛选提供一个更真实的环境。随后,作者应用该装置在肝癌(HCC)、非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)、乳腺癌和胰腺导管腺癌(PDAC)细胞的新型机械感受器化合物库中筛选出对封闭迁移有效的药物:线粒体酸5(MA-5)、SB-705498和二苯基碘氯化铵(DPI),它们分别靶向线粒体、肌动蛋白聚合和细胞活力。
Fabrication of Multifunctional Confined Migration Microfluidic Device
癌细胞穿透邻近组织是转移的基本特征,可分为单细胞侵袭、多细胞流和集体侵袭。癌细胞集体侵袭已被认为是实体瘤进展的关键机制。在此设计的微流控装置专门模拟了集体侵袭过程,以均匀的顶盖高度为细胞提供限制。
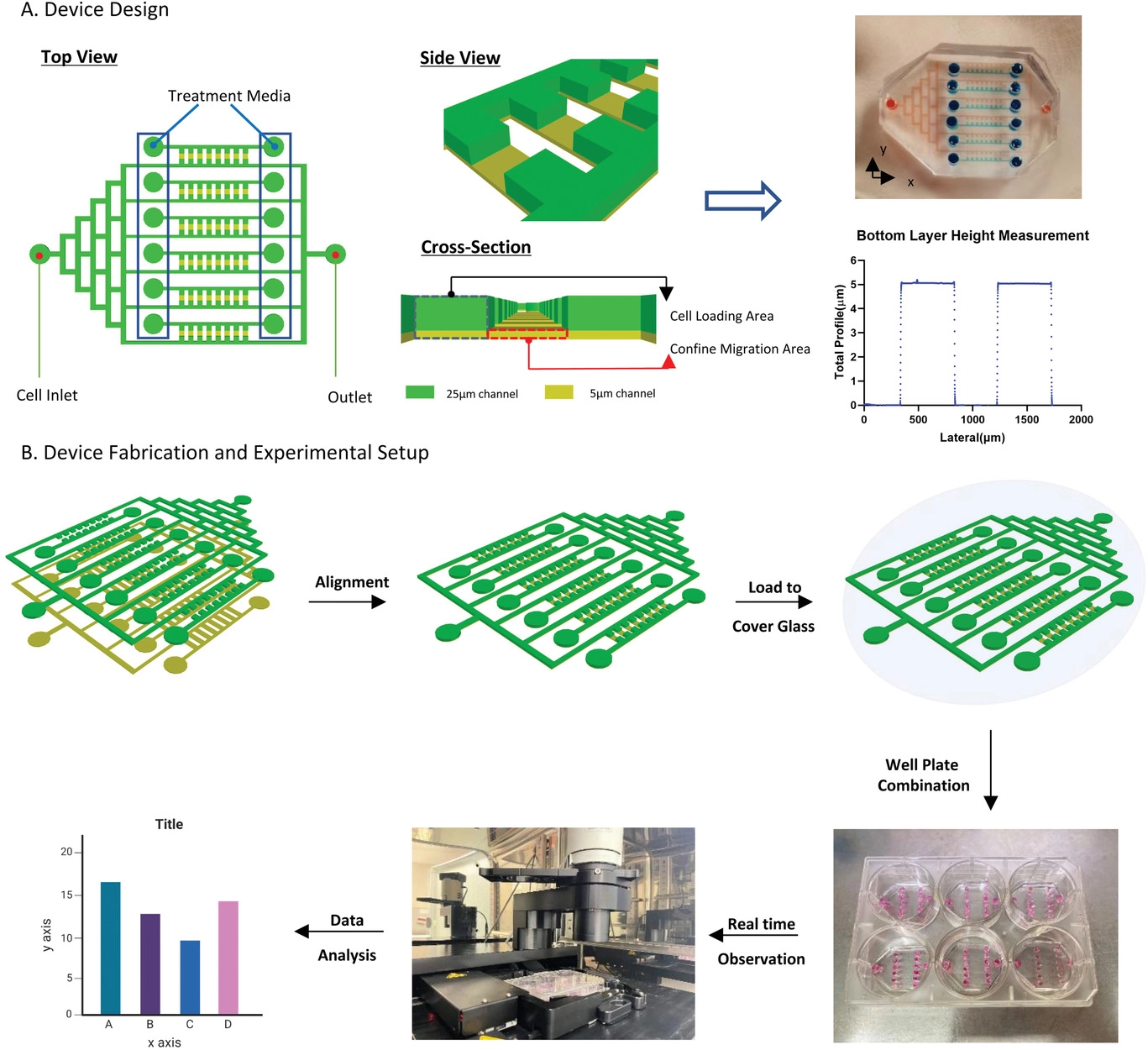
- (A)装置设计:芯片包含两层,底层高度为5 µm,上层高度为25 µm,通过对齐可以在中间产生限制区域。
- (B)装置制造和实验的示意图。
Simulation of the Cell Loading and Fluid Flow

- (A-B)细胞流动轨迹分析和细胞加载到腔室模拟。
- (C)细胞从金字塔入口加载并平均分配到每个通道的白光图像。为了消除每个室从入口到出口因流动而导致的细胞数量减少,还在相反的入口处再次加入细胞溶液,以确保每个室的细胞数量相等。
- (D)通道内药物扩散的水平视图。10s 内溶液浓度已在每个腔室中保持稳定。
- (E)24 h内,平行通道之间的干扰视图,反映出平行通道之间的干扰很小,适合于多药筛选。
Cell Morphology Changes and on-Chip Mechanoreceptors Compound Library Screening Targeting Confined Migration
作者随后选择了一个机械受体库化合物库,其中包含188个化合物,通过微流控装置进行筛选。这些化合物的目标是瞬时受体电位(TRP)通道、Piezo、线粒体、钠或钾通道,因为它们广泛参与了细胞迁移或机械感应。还增加了两个针对线粒体的化合物(MA-5和延胡索酸水合酶-IN-1(Fumarate hydratase-IN-1)),因为它们是细胞迁移的能量来源,以供筛选。此外还增加了另外三个化合物(AKT激酶抑制剂、PQR620、CP21R7)分别针对AKT、mTOR和GSK-3,因为它们也是参与癌细胞迁移和机械感应的经典目标。
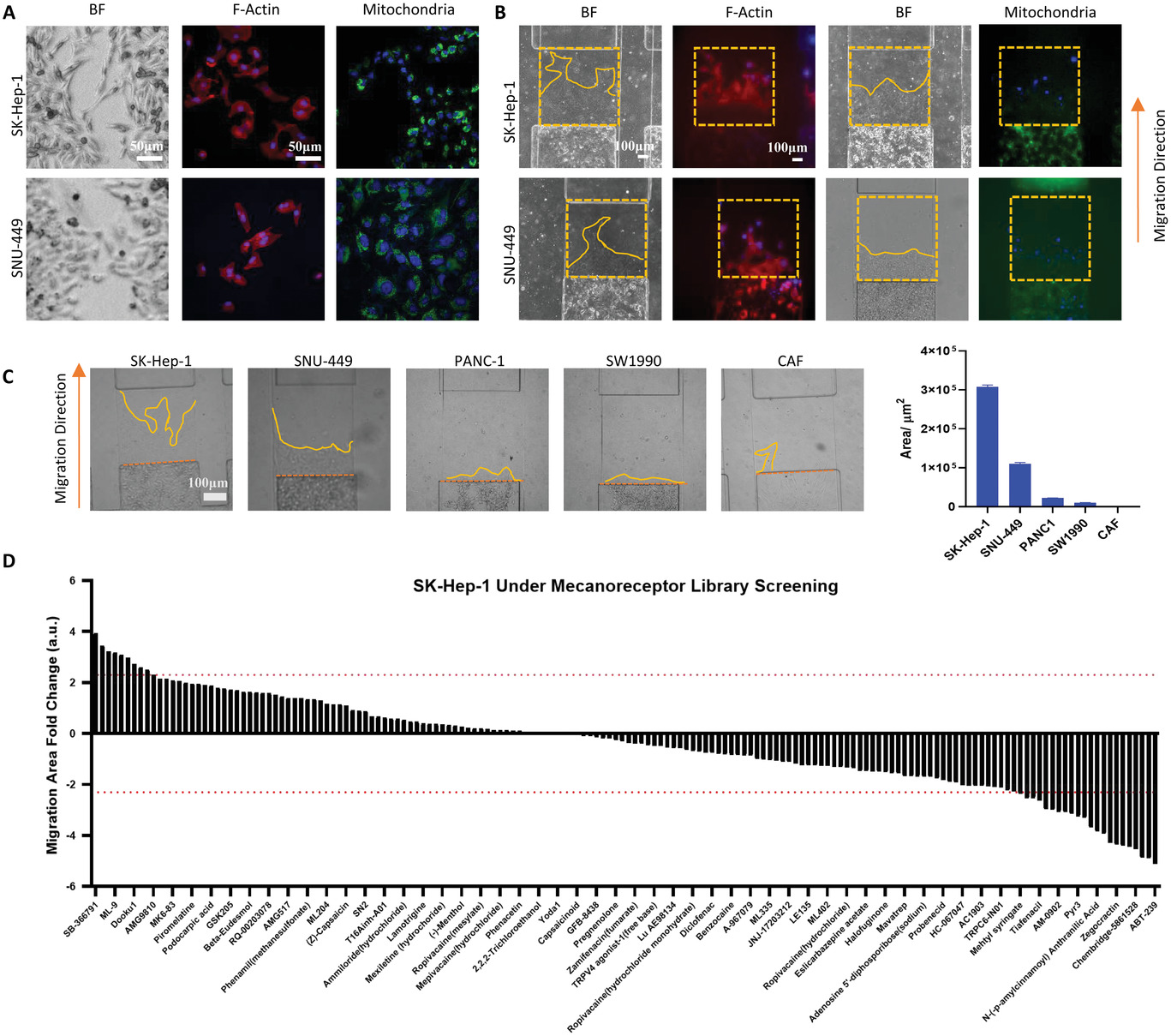
- (A)人肝癌细胞系SK-Hep-1和SNU-449在培养皿上的形态、F-肌动蛋白和线粒体染色。可以发现细胞呈纺锤形,在非限制的二维条件下,细胞丝组织良好,线粒体染色清晰,阳性点意味着大的线粒体。
- (B)SK-Hep-1和SNU-449在微流控装置上的形态、F-actin和线粒体染色。相比之下,受限情况下细胞丝的组织程度较低,线粒体的染色很弱。
- (C)SK-Hep-1、SNU-449、胰腺癌细胞系PANC-1、SW1990和原发性癌症相关的成纤维细胞受限迁移能力比较。在所有测试的细胞中,SK-Hep-1细胞在封闭通道中迁移得最快。后续药物筛选应用于SK-Hep-1 HCC细胞系。
- (D)通过微流控设备使用HCC细胞系SK-Hep-1进行机械受体化合物库筛选(迁移倍数变化=log2(迁移面积倍数变化)),在166个化合物中,有22个化合物显著抑制了细胞受限迁移。
Validation of Significant Confined Migration Inhibitor Among Multiple Cell Lines

- (A)单通道受限迁移装置的示意图。可以避免化合物之间的相互干扰,实现精确的筛选。
- (B)22种重要的受限迁移抑制剂对SK-Hep-1、SW1990、A549和MDA-MD-231的作用热图。
- (C)受限迁移抑制剂对SK-Hep-1、SW1990、A549和MDA-MD-231的作用维恩图。发现有三个化合物: MA-5、SB-705498和DPI,可以最显著地抑制HCC、PDAC、NSCLC和MDA-MD-231细胞的受限迁移。
- (D)24 h后,用化合物处理的SK-Hep-1的受限迁移。专注于抑制受限迁移的药物并不多见,唯一报道的有效抑制剂是硼替佐米(Bortezomib)和达尼瑞辛(Danirixin)的组合。这两种药物通过单细胞横向受限迁移装置进行筛选,可以同时抑制细胞生长和迁移。结果表明,该装置适合于高通量筛选受限迁移相关药物。
MA-5 Inhibits Mitochondria Re-Localization During Confined Migration
线粒体是ATP的生物合成工厂,是包括细胞迁移在内的所有细胞活动的能量来源,它们的功能是线粒体网络的融合和裂变之间的动态转换。线粒体裂变可以促进线粒体重新分布和细胞迁移,而线粒体融合可以促进ATP的产生。MA-5通过调节细胞ATP水平来改善线粒体缺失的非恶性疾病,也被发现可以抑制活性氧的产生。
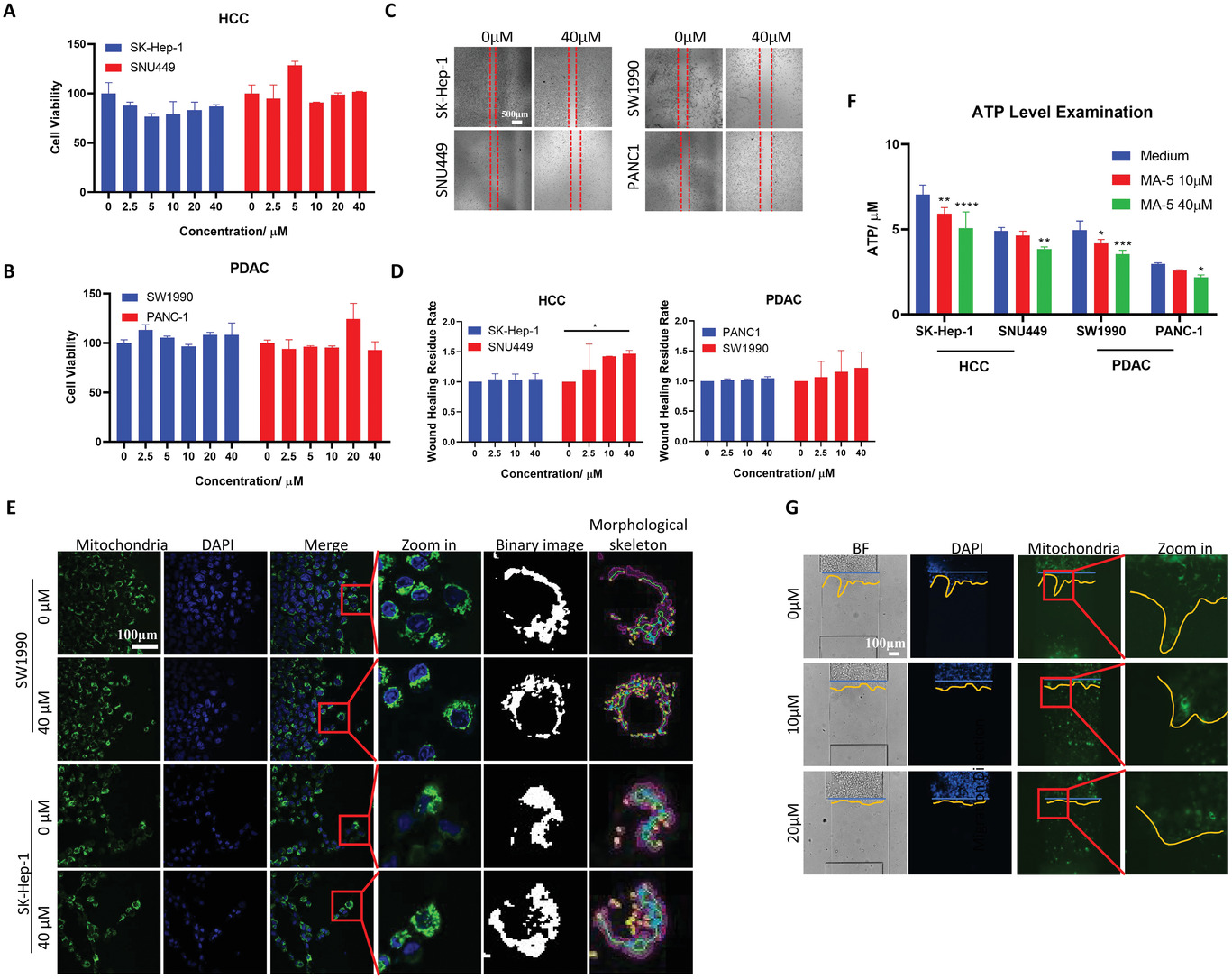
- (A)通过MTT测试HCC细胞系的生存能力。
- (B)PDAC细胞系的MTT活力测试。发现MA-5对HCC和PDAC细胞系的细胞活力没有明显影响。
- (C)不同MA-5浓度下的细胞伤口愈合试验。
- (D)不同MA-5浓度下HCC、NSCLC和PDAC细胞系的伤口愈合残留率。40 μM对HCC和PDAC细胞的迁移有最好的抑制率。
- (E)共聚焦显微镜下,SW1990和SK-Hep-1线粒体在有和没有MA-5的情况下的分布。可以观察到线粒体沿着细胞迁移的方向被极化,尤其是在领导细胞中。但加入MA-5后,线粒体极化现象减少。随着MA-5浓度的增加,更多的细胞从线粒体极化堆积转为均匀分布在细胞膜上。
- (F)有和没有MA-5处理的细胞系的ATP水平。结果显示,MA-5可以明显降低ATP水平。
- (G)线粒体分布的芯片上染色。这些结果表明,MA-5可以抑制癌细胞迁移过程中的线粒体再定位和ATP的合成。此外,MA-5可以成为一种有前途的治疗癌症的药物,因为它可以特异性地抑制癌细胞迁移并促进非恶性细胞的生存。
TRPV1 Receptor Antagonist SB-705498 Suppressed Actin Polymerization in Cancer Cells
TRP通道已被认为是不同组织和细胞类型中钙、钠和镁离子的重要调节器。TRP家族被分为七个亚家族: TRPA(ankyrin)、TRPC(canonical)、TRPM(melastatin)、TRPML(mucolipin)、TRPN(NOMPC)、TRPP(polycystin)和TRPV(vanilloid)。它们在结构上表现出共同的特点。TRP亚家族与许多细胞功能有关,包括细胞分化、凋亡、增殖和通过感知环境实现离子平衡。TRP通道也被广泛认为是缓解癌痛的分子目标。近年来,也有报道称TRP通道家族成员的失调与肿瘤进展的不同阶段有关,并与临床参数密切相关。
SB-705498,一种TRPV1拮抗剂,通过减少肌动蛋白丝来抑制癌细胞的受限和非受限迁移。

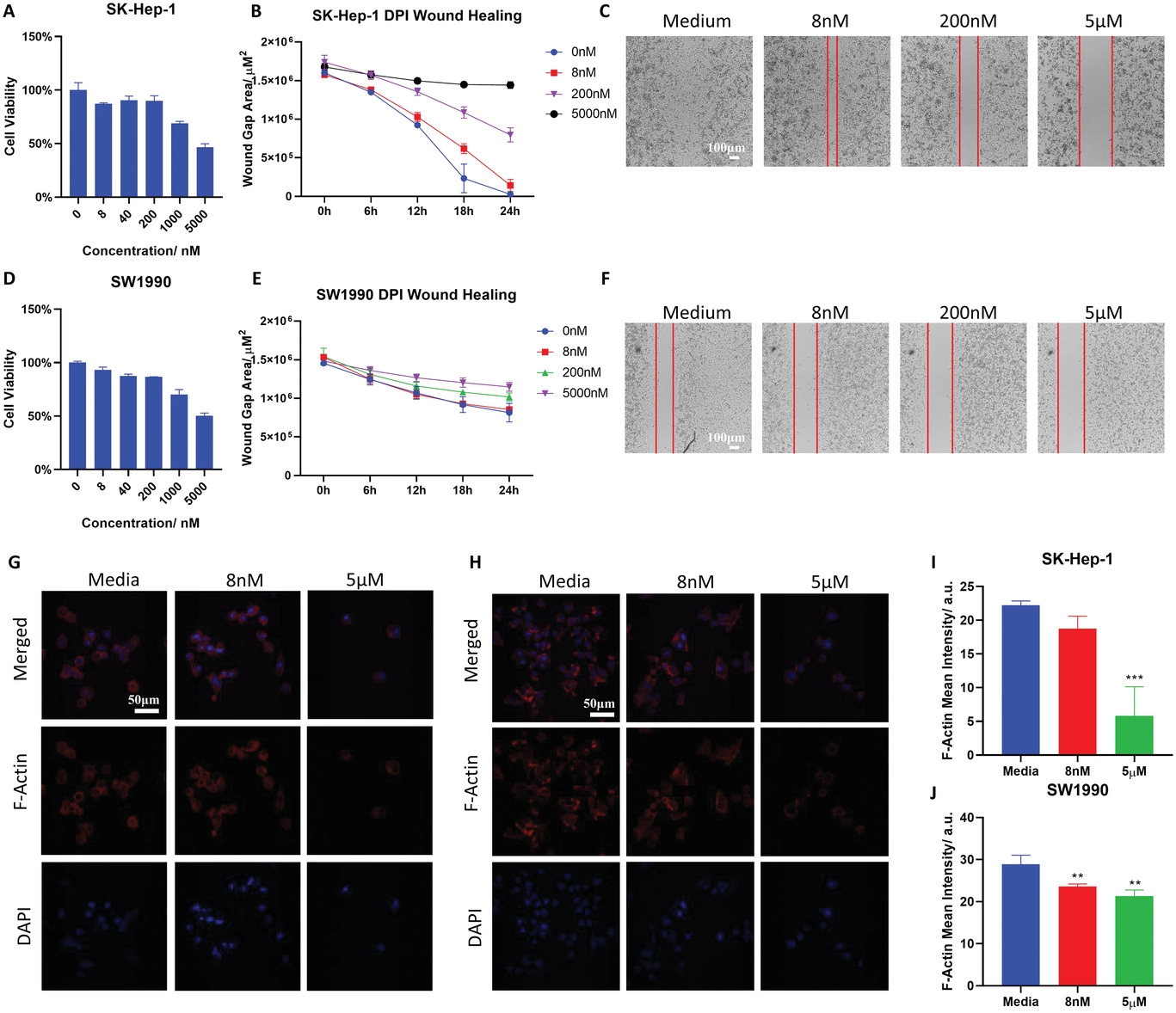
- (A)通过MTT对SK-Hep-1细胞系进行活力测试。发现SB-705498对SK-Hep1细胞的增殖略有促进作用。
- (B-C) 在不同浓度的SB-705498下,SK-Hep-1细胞的伤口愈合间隙面积测量和图像。发现SB-705498对SK-Hep1细胞非受限迁移有极大的抑制作用。
- (D)用MTT测试SW1990细胞系的活力。发现SB-705498不影响SW1990细胞增殖。
- (E-F)在不同浓度的SB-705498下,SW1990细胞的伤口愈合间隙面积测量和图像。发现SB-705498抑制了PDAC SW1990细胞的非受限迁移。
- (G-H)在8 nM和5 µM SB-705498下,SK-Hep-1和SW1990的F-actin染色。
- (I-J)在8 nM和5 µM SB-705498下SK-Hep-1和SW1990的F-actin平均强度测量。细胞骨架动态是细胞迁移的关键,结果表明在SK-Hep-1和SW1990细胞中,F-actin都减少。
DPI Depresses Cell Proliferation and Actin Polymerization in Cancer Cells
作为专门的活性氧生产者,NADPH氧化酶(NOX)参与了多种病理过程,包括宿主防御、翻译后修饰、细胞信号传导、基因表达调节和细胞分化。DPI是一种NOX抑制剂,可以诱导乳腺癌和结肠癌细胞的衰老和抑制HCC细胞的增殖。
- (A)通过MTT进行SK-Hep-1细胞系活力测试。发现DPI对SK-Hep1细胞有细胞毒性作用。
- (B-C) 在不同浓度的DPI下,SK-Hep-1细胞的伤口愈合间隙面积测量和图像。发现DPI抑制了SK-Hep-1细胞的非受限迁移。
- (D)用MTT测试SW1990细胞系的活力。发现DPI对SW1990细胞有细胞毒性作用。
- (E-F)在不同浓度的DPI下,SW1990细胞的伤口愈合间隙面积的测量和图像。发现DPI抑制了SW1990细胞的非受限迁移。
- (G-H)在8 nM和5 µM DPI下SK-Hep-1和SW1990的F-actin染色。
- (I-J)在8 nM和5 µM DPI下SK-Hep-1和SW1990的F-actin平均强度测量。发现DPI抑制了肌动蛋白聚合。总的来说,DPI可以抑制细胞活力、受限与非受限迁移和癌细胞的肌动蛋白聚合。
Conclusion
作为癌症转移的关键步骤,受限迁移是一个潜在的癌症治疗目标。这里设计的微流控装置为针对这一过程的药物的高通量和高含量筛选提供了一种有效的方法。利用这个装置,作者发现了三种可以显著抑制癌细胞受限的新化合物: MA-5, SB-705498, 和DPI。这些化合物分别针对线粒体、肌动蛋白聚合和细胞活力。
Reference
Yang Z, Zhou Z, Si T, et al. High Throughput Confined Migration Microfluidic Device for Drug Screening[J]. Small, 2023.



